YOLOv8 Oriented Bounding Boxes Object Detection with OpenVINO™#
This Jupyter notebook can be launched on-line, opening an interactive environment in a browser window. You can also make a local installation. Choose one of the following options:
YOLOv8-OBB is introduced by Ultralytics.
Oriented object detection goes a step further than object detection and introduce an extra angle to locate objects more accurate in an image.
The output of an oriented object detector is a set of rotated bounding boxes that exactly enclose the objects in the image, along with class labels and confidence scores for each box. Object detection is a good choice when you need to identify objects of interest in a scene, but don’t need to know exactly where the object is or its exact shape.
Table of contents:
This is a self-contained example that relies solely on its own code.
We recommend running the notebook in a virtual environment. You only need a Jupyter server to start. For details, please refer to Installation Guide.
Prerequisites#
%pip install -q "ultralytics==8.2.24" "openvino>=2024.0.0" "nncf>=2.9.0" tqdm
Import required utility functions. The lower cell will download the notebook_utils Python module from GitHub.
from pathlib import Path
# Fetch `notebook_utils` module
import requests
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/notebook_utils.py",
)
open("notebook_utils.py", "w").write(r.text)
from notebook_utils import download_file, device_widget
Get PyTorch model#
Generally, PyTorch models represent an instance of the
torch.nn.Module
class, initialized by a state dictionary with model weights. We will use
the YOLOv8 pretrained OBB large model (also known as yolov8l-obbn)
pre-trained on a DOTAv1 dataset, which is available in this
repo. Similar steps are
also applicable to other YOLOv8 models.
from ultralytics import YOLO
model = YOLO("yolov8l-obb.pt")
Prepare dataset and dataloader#
YOLOv8-obb is pre-trained on the DOTA dataset. Also, Ultralytics provides DOTA8 dataset. It is a small, but versatile oriented object detection dataset composed of the first 8 images of 8 images of the split DOTAv1 set, 4 for training and 4 for validation. This dataset is ideal for testing and debugging object detection models, or for experimenting with new detection approaches. With 8 images, it is small enough to be easily manageable, yet diverse enough to test training pipelines for errors and act as a sanity check before training larger datasets.
The original model repository uses a Validator wrapper, which represents the accuracy validation pipeline. It creates dataloader and evaluation metrics and updates metrics on each data batch produced by the dataloader. Besides that, it is responsible for data preprocessing and results postprocessing. For class initialization, the configuration should be provided. We will use the default setup, but it can be replaced with some parameters overriding to test on custom data. The model has connected the task_map, which allows to get a validator class instance.
from ultralytics.cfg import get_cfg
from ultralytics.data.utils import check_det_dataset
from ultralytics.utils import DEFAULT_CFG, DATASETS_DIR
CFG_URL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/dota8.yaml"
OUT_DIR = Path("./datasets")
CFG_PATH = OUT_DIR / "dota8.yaml"
download_file(CFG_URL, CFG_PATH.name, CFG_PATH.parent)
args = get_cfg(cfg=DEFAULT_CFG)
args.data = CFG_PATH
args.task = model.task
validator = model.task_map[model.task]["validator"](args=args)
validator.stride = 32
validator.data = check_det_dataset(str(args.data))
data_loader = validator.get_dataloader(DATASETS_DIR / "dota8", 1)
example_image_path = list(data_loader)[1]["im_file"][0]
datasets/dota8.yaml: 0%| | 0.00/608 [00:00<?, ?B/s]
Dataset 'datasets/dota8.yaml' images not found ⚠️, missing path '/home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets/dota8/images/val' Downloading ultralytics/yolov5 to '/home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets/dota8.zip'...
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1.24M/1.24M [00:00<00:00, 1.63MB/s]
Unzipping /home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets/dota8.zip to /home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets/dota8...: 100%|██████████| 27/27 [00:00<00:00, 644.45file/s]
Dataset download success ✅ (4.1s), saved to /home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets
val: Scanning /home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets/dota8/labels/train... 8 images, 0 backgrounds, 0 corrupt: 100%|██████████| 8/8 [00:00<00:00, 266.41it/s]
val: New cache created: /home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets/dota8/labels/train.cache
Run inference#
from PIL import Image
res = model(example_image_path, device="cpu")
Image.fromarray(res[0].plot()[:, :, ::-1])
image 1/1 /home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets/dota8/images/train/P1053__1024__0___90.jpg: 1024x1024 4915.2ms
Speed: 18.6ms preprocess, 4915.2ms inference, 50.9ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 1024, 1024)
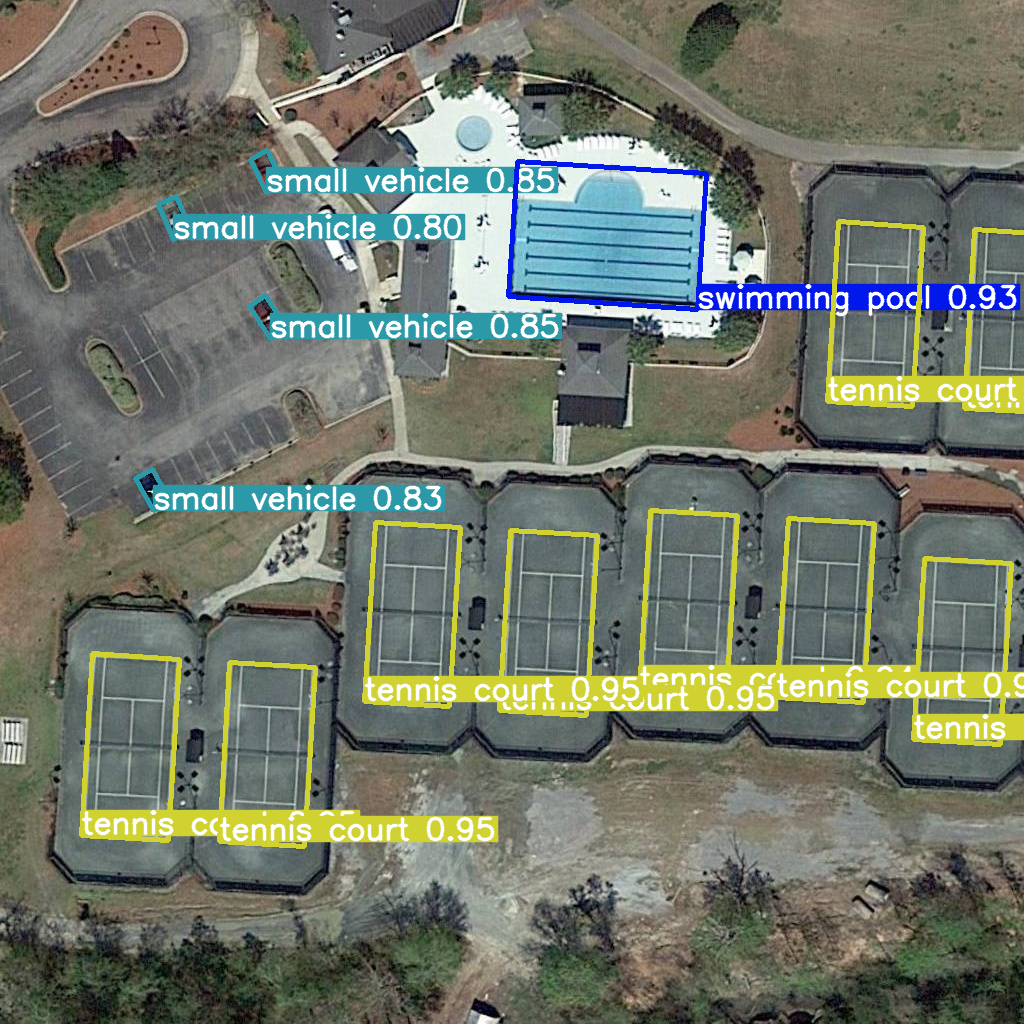
Convert PyTorch model to OpenVINO IR#
YOLOv8 provides API for convenient model exporting to different formats
including OpenVINO IR. model.export is responsible for model
conversion. We need to specify the format, and additionally, we can
preserve dynamic shapes in the model.
from pathlib import Path
models_dir = Path("./models")
models_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
OV_MODEL_NAME = "yolov8l-obb"
OV_MODEL_PATH = Path(f"{OV_MODEL_NAME}_openvino_model/{OV_MODEL_NAME}.xml")
if not OV_MODEL_PATH.exists():
model.export(format="openvino", dynamic=True, half=True)
Ultralytics YOLOv8.1.24 🚀 Python-3.8.10 torch-2.1.2+cpu CPU (Intel Core(TM) i9-10980XE 3.00GHz)
PyTorch: starting from 'yolov8l-obb.pt' with input shape (1, 3, 1024, 1024) BCHW and output shape(s) (1, 20, 21504) (85.4 MB)
OpenVINO: starting export with openvino 2024.0.0-14509-34caeefd078-releases/2024/0...
OpenVINO: export success ✅ 5.6s, saved as 'yolov8l-obb_openvino_model/' (85.4 MB)
Export complete (18.7s)
Results saved to /home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks_new_clone/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/yolov8-optimization
Predict: yolo predict task=obb model=yolov8l-obb_openvino_model imgsz=1024 half
Validate: yolo val task=obb model=yolov8l-obb_openvino_model imgsz=1024 data=runs/DOTAv1.0-ms.yaml half
Visualize: https://netron.app
Select inference device#
Select device from dropdown list for running inference using OpenVINO
device = device_widget()
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
Compile model#
import openvino as ov
core = ov.Core()
ov_model = core.read_model(OV_MODEL_PATH)
ov_config = {}
if device.value != "CPU":
ov_model.reshape({0: [1, 3, 1024, 1024]})
if "GPU" in device.value or ("AUTO" in device.value and "GPU" in core.available_devices):
ov_config = {"GPU_DISABLE_WINOGRAD_CONVOLUTION": "YES"}
compiled_ov_model = core.compile_model(ov_model, device.value, ov_config)
Prepare the model for inference#
We can reuse the base model pipeline for pre- and postprocessing just replacing the inference method where we will use the IR model for inference.
import torch
def infer(*args):
result = compiled_ov_model(args)[0]
return torch.from_numpy(result)
model.predictor.inference = infer
Run inference#
res = model(example_image_path, device="cpu")
Image.fromarray(res[0].plot()[:, :, ::-1])
image 1/1 /home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets/dota8/images/train/P1053__1024__0___90.jpg: 1024x1024 338.0ms
Speed: 4.7ms preprocess, 338.0ms inference, 3.7ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 1024, 1024)
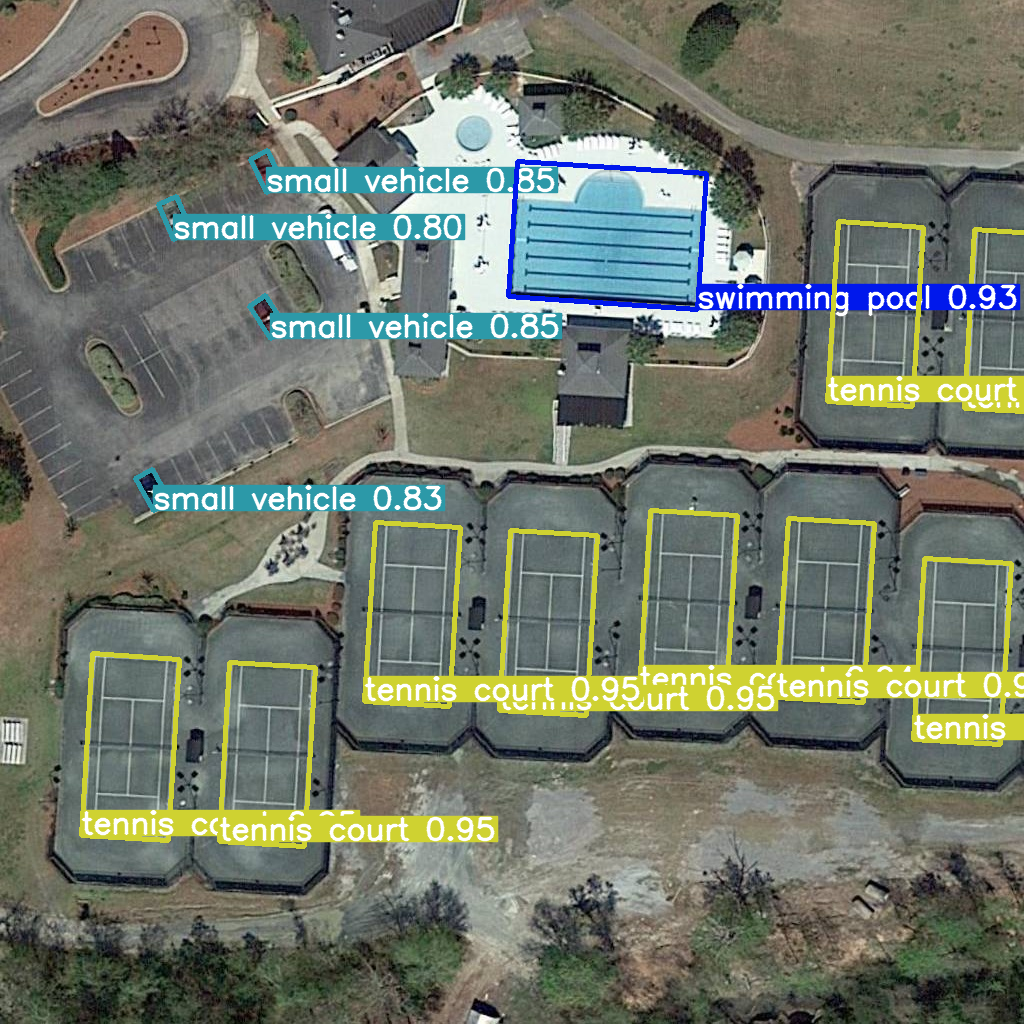
Quantization#
NNCF enables
post-training quantization by adding quantization layers into model
graph and then using a subset of the training dataset to initialize the
parameters of these additional quantization layers. Quantized operations
are executed in INT8 instead of FP32/FP16 making model
inference faster.
The optimization process contains the following steps:
Create a calibration dataset for quantization.
Run
nncf.quantize()to obtain quantized model.Save the
INT8model usingopenvino.save_model()function.
Please select below whether you would like to run quantization to improve model inference speed.
import ipywidgets as widgets
INT8_OV_PATH = Path("model/int8_model.xml")
to_quantize = widgets.Checkbox(
value=True,
description="Quantization",
disabled=False,
)
to_quantize
Checkbox(value=True, description='Quantization')
Let’s load skip magic extension to skip quantization if
to_quantize is not selected
# Fetch skip_kernel_extension module
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/skip_kernel_extension.py",
)
open("skip_kernel_extension.py", "w").write(r.text)
%load_ext skip_kernel_extension
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
from typing import Dict
import nncf
def transform_fn(data_item: Dict):
input_tensor = validator.preprocess(data_item)["img"].numpy()
return input_tensor
quantization_dataset = nncf.Dataset(data_loader, transform_fn)
INFO:nncf:NNCF initialized successfully. Supported frameworks detected: torch, tensorflow, onnx, openvino
Create a quantized model from the pre-trained converted OpenVINO model.
NOTE: Quantization is time and memory consuming operation. Running quantization code below may take some time.
NOTE: We use the tiny DOTA8 dataset as a calibration dataset. It gives a good enough result for tutorial purpose. For batter results, use a bigger dataset. Usually 300 examples are enough.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
print("Loading quantized model")
quantized_model = core.read_model(INT8_OV_PATH)
else:
ov_model.reshape({0: [1, 3, -1, -1]})
quantized_model = nncf.quantize(
ov_model,
quantization_dataset,
preset=nncf.QuantizationPreset.MIXED,
)
ov.save_model(quantized_model, INT8_OV_PATH)
ov_config = {}
if device.value != "CPU":
quantized_model.reshape({0: [1, 3, 1024, 1024]})
if "GPU" in device.value or ("AUTO" in device.value and "GPU" in core.available_devices):
ov_config = {"GPU_DISABLE_WINOGRAD_CONVOLUTION": "YES"}
model_optimized = core.compile_model(quantized_model, device.value, ov_config)
Output()
Output()
We can reuse the base model pipeline in the same way as for IR model.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
def infer(*args):
result = model_optimized(args)[0]
return torch.from_numpy(result)
model.predictor.inference = infer
Run inference
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
res = model(example_image_path, device='cpu')
Image.fromarray(res[0].plot()[:, :, ::-1])
image 1/1 /home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/fast-segment-anything/datasets/dota8/images/train/P1053__1024__0___90.jpg: 1024x1024 240.5ms
Speed: 3.2ms preprocess, 240.5ms inference, 4.2ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 1024, 1024)
You can see that the result is almost the same but it has a small difference. One small vehicle was recognized as two vehicles. But one large car was also identified, unlike the original model.
Compare inference time and model sizes#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
fp16_ir_model_size = OV_MODEL_PATH.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024
quantized_model_size = INT8_OV_PATH.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024
print(f"FP16 model size: {fp16_ir_model_size:.2f} KB")
print(f"INT8 model size: {quantized_model_size:.2f} KB")
print(f"Model compression rate: {fp16_ir_model_size / quantized_model_size:.3f}")
FP16 model size: 86849.05 KB
INT8 model size: 43494.78 KB
Model compression rate: 1.997
# Inference FP32 model (OpenVINO IR)
!benchmark_app -m $OV_MODEL_PATH -d $device.value -api async -shape "[1,3,640,640]"
[Step 1/11] Parsing and validating input arguments [ INFO ] Parsing input parameters [Step 2/11] Loading OpenVINO Runtime [ WARNING ] Default duration 120 seconds is used for unknown device AUTO [ INFO ] OpenVINO: [ INFO ] Build ................................. 2024.0.0-14509-34caeefd078-releases/2024/0 [ INFO ] [ INFO ] Device info: [ INFO ] AUTO [ INFO ] Build ................................. 2024.0.0-14509-34caeefd078-releases/2024/0 [ INFO ] [ INFO ] [Step 3/11] Setting device configuration [ WARNING ] Performance hint was not explicitly specified in command line. Device(AUTO) performance hint will be set to PerformanceMode.THROUGHPUT. [Step 4/11] Reading model files [ INFO ] Loading model files [ INFO ] Read model took 25.07 ms [ INFO ] Original model I/O parameters: [ INFO ] Model inputs: [ INFO ] x (node: x) : f32 / [...] / [?,3,?,?] [ INFO ] Model outputs: [ INFO ] *NO_NAME* (node: __module.model.22/aten::cat/Concat_9) : f32 / [...] / [?,20,16..] [Step 5/11] Resizing model to match image sizes and given batch [ INFO ] Model batch size: 1 [ INFO ] Reshaping model: 'x': [1,3,640,640] [ INFO ] Reshape model took 10.42 ms [Step 6/11] Configuring input of the model [ INFO ] Model inputs: [ INFO ] x (node: x) : u8 / [N,C,H,W] / [1,3,640,640] [ INFO ] Model outputs: [ INFO ] *NO_NAME* (node: __module.model.22/aten::cat/Concat_9) : f32 / [...] / [1,20,8400] [Step 7/11] Loading the model to the device [ INFO ] Compile model took 645.51 ms [Step 8/11] Querying optimal runtime parameters [ INFO ] Model: [ INFO ] NETWORK_NAME: Model0 [ INFO ] EXECUTION_DEVICES: ['CPU'] [ INFO ] PERFORMANCE_HINT: PerformanceMode.THROUGHPUT [ INFO ] OPTIMAL_NUMBER_OF_INFER_REQUESTS: 12 [ INFO ] MULTI_DEVICE_PRIORITIES: CPU [ INFO ] CPU: [ INFO ] AFFINITY: Affinity.CORE [ INFO ] CPU_DENORMALS_OPTIMIZATION: False [ INFO ] CPU_SPARSE_WEIGHTS_DECOMPRESSION_RATE: 1.0 [ INFO ] DYNAMIC_QUANTIZATION_GROUP_SIZE: 0 [ INFO ] ENABLE_CPU_PINNING: True [ INFO ] ENABLE_HYPER_THREADING: True [ INFO ] EXECUTION_DEVICES: ['CPU'] [ INFO ] EXECUTION_MODE_HINT: ExecutionMode.PERFORMANCE [ INFO ] INFERENCE_NUM_THREADS: 36 [ INFO ] INFERENCE_PRECISION_HINT: <Type: 'float32'> [ INFO ] KV_CACHE_PRECISION: <Type: 'float16'> [ INFO ] LOG_LEVEL: Level.NO [ INFO ] NETWORK_NAME: Model0 [ INFO ] NUM_STREAMS: 12 [ INFO ] OPTIMAL_NUMBER_OF_INFER_REQUESTS: 12 [ INFO ] PERFORMANCE_HINT: THROUGHPUT [ INFO ] PERFORMANCE_HINT_NUM_REQUESTS: 0 [ INFO ] PERF_COUNT: NO [ INFO ] SCHEDULING_CORE_TYPE: SchedulingCoreType.ANY_CORE [ INFO ] MODEL_PRIORITY: Priority.MEDIUM [ INFO ] LOADED_FROM_CACHE: False [Step 9/11] Creating infer requests and preparing input tensors [ WARNING ] No input files were given for input 'x'!. This input will be filled with random values! [ INFO ] Fill input 'x' with random values [Step 10/11] Measuring performance (Start inference asynchronously, 12 inference requests, limits: 120000 ms duration) [ INFO ] Benchmarking in inference only mode (inputs filling are not included in measurement loop). [ INFO ] First inference took 362.70 ms [Step 11/11] Dumping statistics report [ INFO ] Execution Devices:['CPU'] [ INFO ] Count: 1620 iterations [ INFO ] Duration: 121527.01 ms [ INFO ] Latency: [ INFO ] Median: 884.92 ms [ INFO ] Average: 897.13 ms [ INFO ] Min: 599.38 ms [ INFO ] Max: 1131.46 ms [ INFO ] Throughput: 13.33 FPS
if INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
# Inference INT8 model (Quantized model)
!benchmark_app -m $INT8_OV_PATH -d $device.value -api async -shape "[1,3,640,640]" -t 15
[Step 1/11] Parsing and validating input arguments [ INFO ] Parsing input parameters [Step 2/11] Loading OpenVINO Runtime [ INFO ] OpenVINO: [ INFO ] Build ................................. 2024.0.0-14509-34caeefd078-releases/2024/0 [ INFO ] [ INFO ] Device info: [ INFO ] AUTO [ INFO ] Build ................................. 2024.0.0-14509-34caeefd078-releases/2024/0 [ INFO ] [ INFO ] [Step 3/11] Setting device configuration [ WARNING ] Performance hint was not explicitly specified in command line. Device(AUTO) performance hint will be set to PerformanceMode.THROUGHPUT. [Step 4/11] Reading model files [ INFO ] Loading model files [ INFO ] Read model took 46.47 ms [ INFO ] Original model I/O parameters: [ INFO ] Model inputs: [ INFO ] x (node: x) : f32 / [...] / [?,3,?,?] [ INFO ] Model outputs: [ INFO ] *NO_NAME* (node: __module.model.22/aten::cat/Concat_9) : f32 / [...] / [?,20,16..] [Step 5/11] Resizing model to match image sizes and given batch [ INFO ] Model batch size: 1 [ INFO ] Reshaping model: 'x': [1,3,640,640] [ INFO ] Reshape model took 20.10 ms [Step 6/11] Configuring input of the model [ INFO ] Model inputs: [ INFO ] x (node: x) : u8 / [N,C,H,W] / [1,3,640,640] [ INFO ] Model outputs: [ INFO ] *NO_NAME* (node: __module.model.22/aten::cat/Concat_9) : f32 / [...] / [1,20,8400] [Step 7/11] Loading the model to the device [ INFO ] Compile model took 1201.42 ms [Step 8/11] Querying optimal runtime parameters [ INFO ] Model: [ INFO ] NETWORK_NAME: Model0 [ INFO ] EXECUTION_DEVICES: ['CPU'] [ INFO ] PERFORMANCE_HINT: PerformanceMode.THROUGHPUT [ INFO ] OPTIMAL_NUMBER_OF_INFER_REQUESTS: 12 [ INFO ] MULTI_DEVICE_PRIORITIES: CPU [ INFO ] CPU: [ INFO ] AFFINITY: Affinity.CORE [ INFO ] CPU_DENORMALS_OPTIMIZATION: False [ INFO ] CPU_SPARSE_WEIGHTS_DECOMPRESSION_RATE: 1.0 [ INFO ] DYNAMIC_QUANTIZATION_GROUP_SIZE: 0 [ INFO ] ENABLE_CPU_PINNING: True [ INFO ] ENABLE_HYPER_THREADING: True [ INFO ] EXECUTION_DEVICES: ['CPU'] [ INFO ] EXECUTION_MODE_HINT: ExecutionMode.PERFORMANCE [ INFO ] INFERENCE_NUM_THREADS: 36 [ INFO ] INFERENCE_PRECISION_HINT: <Type: 'float32'> [ INFO ] KV_CACHE_PRECISION: <Type: 'float16'> [ INFO ] LOG_LEVEL: Level.NO [ INFO ] NETWORK_NAME: Model0 [ INFO ] NUM_STREAMS: 12 [ INFO ] OPTIMAL_NUMBER_OF_INFER_REQUESTS: 12 [ INFO ] PERFORMANCE_HINT: THROUGHPUT [ INFO ] PERFORMANCE_HINT_NUM_REQUESTS: 0 [ INFO ] PERF_COUNT: NO [ INFO ] SCHEDULING_CORE_TYPE: SchedulingCoreType.ANY_CORE [ INFO ] MODEL_PRIORITY: Priority.MEDIUM [ INFO ] LOADED_FROM_CACHE: False [Step 9/11] Creating infer requests and preparing input tensors [ WARNING ] No input files were given for input 'x'!. This input will be filled with random values! [ INFO ] Fill input 'x' with random values [Step 10/11] Measuring performance (Start inference asynchronously, 12 inference requests, limits: 15000 ms duration) [ INFO ] Benchmarking in inference only mode (inputs filling are not included in measurement loop). [ INFO ] First inference took 124.20 ms [Step 11/11] Dumping statistics report [ INFO ] Execution Devices:['CPU'] [ INFO ] Count: 708 iterations [ INFO ] Duration: 15216.46 ms [ INFO ] Latency: [ INFO ] Median: 252.23 ms [ INFO ] Average: 255.76 ms [ INFO ] Min: 176.97 ms [ INFO ] Max: 344.41 ms [ INFO ] Throughput: 46.53 FPS