Text-to-speech (TTS) with Parler-TTS and OpenVINO#
This Jupyter notebook can be launched after a local installation only.
Parler-TTS is a lightweight text-to-speech (TTS) model that can generate high-quality, natural sounding speech in the style of a given speaker (gender, pitch, speaking style, etc). It is a reproduction of work from the paper Natural language guidance of high-fidelity text-to-speech with synthetic annotations by Dan Lyth and Simon King, from Stability AI and Edinburgh University respectively.
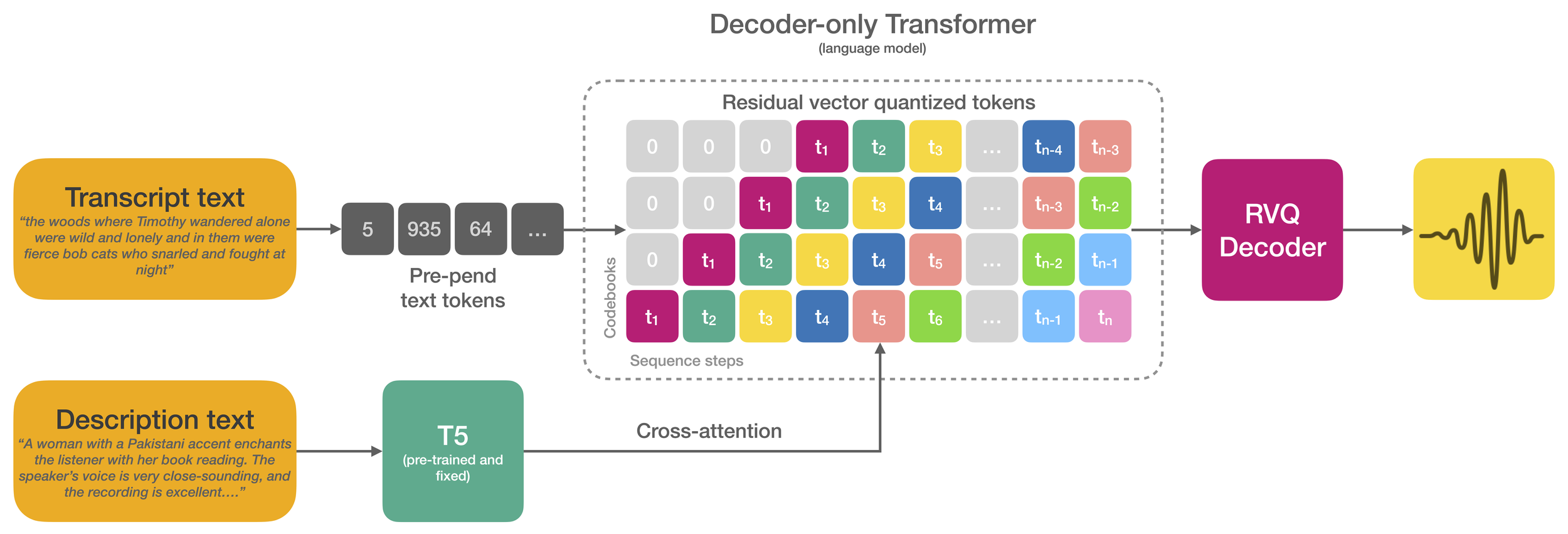
Text-to-speech models trained on large-scale datasets have demonstrated impressive in-context learning capabilities and naturalness. However, control of speaker identity and style in these models typically requires conditioning on reference speech recordings, limiting creative applications. Alternatively, natural language prompting of speaker identity and style has demonstrated promising results and provides an intuitive method of control. However, reliance on human-labeled descriptions prevents scaling to large datasets.
This work bridges the gap between these two approaches. The authors propose a scalable method for labeling various aspects of speaker identity, style, and recording conditions. This method then is applied to a 45k hour dataset, which is used to train a speech language model. Furthermore, the authors propose simple methods for increasing audio fidelity, significantly outperforming recent work despite relying entirely on found data.
Table of contents:
This is a self-contained example that relies solely on its own code.
We recommend running the notebook in a virtual environment. You only need a Jupyter server to start. For details, please refer to Installation Guide.
Prerequisites#
import os
os.environ["GIT_CLONE_PROTECTION_ACTIVE"] = "false"
%pip uninstall -q -y torch torchvision torchaudio
%pip install -q "openvino>=2024.2.0"
%pip install -q git+https://github.com/huggingface/parler-tts.git "gradio>=4.19" transformers "torch>=2.2" "torchaudio" --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
ERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.
easyocr 1.7.2 requires torchvision>=0.5, which is not installed.
mobileclip 0.1.0 requires clip-benchmark>=1.4.0, which is not installed.
mobileclip 0.1.0 requires torchvision==0.14.1, which is not installed.
open-clip-torch 2.22.0 requires torchvision, which is not installed.
timm 1.0.12 requires torchvision, which is not installed.
ultralytics 8.1.24 requires torchvision>=0.9.0, which is not installed.
open-clip-torch 2.22.0 requires protobuf<4, but you have protobuf 4.25.5 which is incompatible.
tensorflow 2.12.0 requires keras<2.13,>=2.12.0, but you have keras 2.13.1 which is incompatible.
tensorflow 2.12.0 requires numpy<1.24,>=1.22, but you have numpy 1.24.4 which is incompatible.
tensorflow 2.12.0 requires tensorboard<2.13,>=2.12, but you have tensorboard 2.13.0 which is incompatible.
tensorflow 2.12.0 requires tensorflow-estimator<2.13,>=2.12.0, but you have tensorflow-estimator 2.13.0 which is incompatible.
tensorflow-cpu 2.13.1 requires numpy<=1.24.3,>=1.22, but you have numpy 1.24.4 which is incompatible.
tensorflow-cpu 2.13.1 requires typing-extensions<4.6.0,>=3.6.6, but you have typing-extensions 4.12.2 which is incompatible.
tensorflow-metadata 1.14.0 requires protobuf<4.21,>=3.20.3, but you have protobuf 4.25.5 which is incompatible.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Load the original model and inference#
import torch
from parler_tts import ParlerTTSForConditionalGeneration
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
import soundfile as sf
device = "cpu"
repo_id = "parler-tts/parler_tts_mini_v0.1"
model = ParlerTTSForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(repo_id).to(device)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(repo_id)
prompt = "Hey, how are you doing today?"
description = "A female speaker with a slightly low-pitched voice delivers her words quite expressively, in a very confined sounding environment with clear audio quality. She speaks very fast."
input_ids = tokenizer(description, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(device)
prompt_input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(device)
generation = model.generate(input_ids=input_ids, prompt_input_ids=prompt_input_ids)
audio_arr = generation.cpu().numpy().squeeze()
sf.write("parler_tts_out.wav", audio_arr, model.config.sampling_rate)
2024-12-10 02:43:30.030324: I tensorflow/core/util/port.cc:110] oneDNN custom operations are on. You may see slightly different numerical results due to floating-point round-off errors from different computation orders. To turn them off, set the environment variable TF_ENABLE_ONEDNN_OPTS=0.
2024-12-10 02:43:30.055592: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:182] This TensorFlow binary is optimized to use available CPU instructions in performance-critical operations.
To enable the following instructions: AVX2 AVX512F AVX512_VNNI FMA, in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
Flash attention 2 is not installed
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/835/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/utils/weight_norm.py:134: FutureWarning: torch.nn.utils.weight_norm is deprecated in favor of torch.nn.utils.parametrizations.weight_norm.
WeightNorm.apply(module, name, dim)
Config of the text_encoder: <class 'transformers.models.t5.modeling_t5.T5EncoderModel'> is overwritten by shared text_encoder config: T5Config {
"_name_or_path": "google/flan-t5-base",
"architectures": [
"T5ForConditionalGeneration"
],
"classifier_dropout": 0.0,
"d_ff": 2048,
"d_kv": 64,
"d_model": 768,
"decoder_start_token_id": 0,
"dense_act_fn": "gelu_new",
"dropout_rate": 0.1,
"eos_token_id": 1,
"feed_forward_proj": "gated-gelu",
"initializer_factor": 1.0,
"is_encoder_decoder": true,
"is_gated_act": true,
"layer_norm_epsilon": 1e-06,
"model_type": "t5",
"n_positions": 512,
"num_decoder_layers": 12,
"num_heads": 12,
"num_layers": 12,
"output_past": true,
"pad_token_id": 0,
"relative_attention_max_distance": 128,
"relative_attention_num_buckets": 32,
"task_specific_params": {
"summarization": {
"early_stopping": true,
"length_penalty": 2.0,
"max_length": 200,
"min_length": 30,
"no_repeat_ngram_size": 3,
"num_beams": 4,
"prefix": "summarize: "
},
"translation_en_to_de": {
"early_stopping": true,
"max_length": 300,
"num_beams": 4,
"prefix": "translate English to German: "
},
"translation_en_to_fr": {
"early_stopping": true,
"max_length": 300,
"num_beams": 4,
"prefix": "translate English to French: "
},
"translation_en_to_ro": {
"early_stopping": true,
"max_length": 300,
"num_beams": 4,
"prefix": "translate English to Romanian: "
}
},
"tie_word_embeddings": false,
"transformers_version": "4.46.1",
"use_cache": true,
"vocab_size": 32128
}
Config of the audio_encoder: <class 'parler_tts.dac_wrapper.modeling_dac.DACModel'> is overwritten by shared audio_encoder config: DACConfig {
"_name_or_path": "ylacombe/dac_44khZ_8kbps",
"architectures": [
"DACModel"
],
"codebook_size": 1024,
"frame_rate": 86,
"latent_dim": 1024,
"model_bitrate": 8,
"model_type": "dac_on_the_hub",
"num_codebooks": 9,
"sampling_rate": 44100,
"torch_dtype": "float32",
"transformers_version": "4.46.1"
}
Config of the decoder: <class 'parler_tts.modeling_parler_tts.ParlerTTSForCausalLM'> is overwritten by shared decoder config: ParlerTTSDecoderConfig {
"_name_or_path": "/fsx/yoach/tmp/artefacts/decoder_400M/",
"activation_dropout": 0.0,
"activation_function": "gelu",
"add_cross_attention": true,
"architectures": [
"ParlerTTSForCausalLM"
],
"attention_dropout": 0.0,
"bos_token_id": 1025,
"codebook_weights": null,
"cross_attention_implementation_strategy": null,
"dropout": 0.1,
"eos_token_id": 1024,
"ffn_dim": 4096,
"hidden_size": 1024,
"initializer_factor": 0.02,
"is_decoder": true,
"layerdrop": 0.0,
"max_position_embeddings": 4096,
"model_type": "parler_tts_decoder",
"num_attention_heads": 16,
"num_codebooks": 9,
"num_cross_attention_key_value_heads": 16,
"num_hidden_layers": 24,
"num_key_value_heads": 16,
"pad_token_id": 1024,
"rope_embeddings": false,
"rope_theta": 10000.0,
"scale_embedding": false,
"tie_word_embeddings": false,
"torch_dtype": "float32",
"transformers_version": "4.46.1",
"use_cache": true,
"use_fused_lm_heads": false,
"vocab_size": 1088
}
You set add_prefix_space. The tokenizer needs to be converted from the slow tokenizers
The attention mask is not set and cannot be inferred from input because pad token is same as eos token. As a consequence, you may observe unexpected behavior. Please pass your input's attention_mask to obtain reliable results.
import IPython.display as ipd
ipd.Audio("parler_tts_out.wav")
Convert the model to OpenVINO IR#
Let’s define the conversion function for PyTorch modules. We use
ov.convert_model function to obtain OpenVINO Intermediate
Representation object and ov.save_model function to save it as XML
file.
import openvino as ov
from pathlib import Path
def convert(model: torch.nn.Module, xml_path: str, example_input):
xml_path = Path(xml_path)
if not xml_path.exists():
xml_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
with torch.no_grad():
converted_model = ov.convert_model(model, example_input=example_input)
ov.save_model(converted_model, xml_path)
# cleanup memory
torch._C._jit_clear_class_registry()
torch.jit._recursive.concrete_type_store = torch.jit._recursive.ConcreteTypeStore()
torch.jit._state._clear_class_state()
In the pipeline two models are used: Text Encoder (T5EncoderModel)
and Decoder (ParlerTTSDecoder). Lets convert them one by one.
TEXT_ENCODER_OV_PATH = Path("models/text_encoder_ir.xml")
example_input = {
"input_ids": torch.ones((1, 39), dtype=torch.int64),
}
text_encoder_ov_model = convert(model.text_encoder, TEXT_ENCODER_OV_PATH, example_input)
WARNING:tensorflow:Please fix your imports. Module tensorflow.python.training.tracking.base has been moved to tensorflow.python.trackable.base. The old module will be deleted in version 2.11.
[ WARNING ] Please fix your imports. Module %s has been moved to %s. The old module will be deleted in version %s. /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/835/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/modeling_utils.py:5006: FutureWarning: _is_quantized_training_enabled is going to be deprecated in transformers 4.39.0. Please use model.hf_quantizer.is_trainable instead warnings.warn( loss_type=None was set in the config but it is unrecognised.Using the default loss: ForCausalLMLoss.
The Decoder Model performs in generation pipeline and we can separate it
into two stage. In the first stage the model generates
past_key_values into output for the second stage. In the second
stage the model produces tokens during several runs.
DECODER_STAGE_1_OV_PATH = Path("models/decoder_stage_1_ir.xml")
class DecoderStage1Wrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, decoder):
super().__init__()
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, input_ids=None, encoder_hidden_states=None, encoder_attention_mask=None, prompt_hidden_states=None):
return self.decoder(
input_ids=input_ids,
return_dict=False,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
prompt_hidden_states=prompt_hidden_states,
)
example_input = {
"input_ids": torch.ones((9, 1), dtype=torch.int64),
"encoder_hidden_states": torch.ones((1, 39, 1024), dtype=torch.float32),
"encoder_attention_mask": torch.ones((1, 39), dtype=torch.int64),
"prompt_hidden_states": torch.ones((1, 9, 1024), dtype=torch.float32),
}
decoder_1_ov_model = convert(DecoderStage1Wrapper(model.decoder.model.decoder), DECODER_STAGE_1_OV_PATH, example_input)
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/835/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/parler_tts/modeling_parler_tts.py:367: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
if seq_len > self.weights.size(0):
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/835/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/parler_tts/modeling_parler_tts.py:1713: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
if sequence_length != 1:
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/835/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/parler_tts/modeling_parler_tts.py:916: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
if attn_output.size() != (bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_dim):
DECODER_STAGE_2_OV_PATH = Path("models/decoder_stage_2_ir.xml")
class DecoderStage2Wrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, decoder):
super().__init__()
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, input_ids=None, encoder_hidden_states=None, encoder_attention_mask=None, past_key_values=None):
past_key_values = tuple(tuple(past_key_values[i : i + 4]) for i in range(0, len(past_key_values), 4))
return self.decoder(
input_ids=input_ids,
return_dict=False,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_attention_mask,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
)
example_input = {
"input_ids": torch.ones((9, 1), dtype=torch.int64),
"encoder_hidden_states": torch.ones((1, 39, 1024), dtype=torch.float32),
"encoder_attention_mask": torch.ones((1, 39), dtype=torch.int64),
"past_key_values": (
(
torch.ones(1, 16, 10, 64, dtype=torch.float32),
torch.ones(1, 16, 10, 64, dtype=torch.float32),
torch.ones(1, 16, 39, 64, dtype=torch.float32),
torch.ones(1, 16, 39, 64, dtype=torch.float32),
)
* 24
),
}
decoder_2_ov_model = convert(DecoderStage2Wrapper(model.decoder.model.decoder), DECODER_STAGE_2_OV_PATH, example_input)
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/835/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/cache_utils.py:458: TracerWarning: Using len to get tensor shape might cause the trace to be incorrect. Recommended usage would be tensor.shape[0]. Passing a tensor of different shape might lead to errors or silently give incorrect results.
or len(self.key_cache[layer_idx]) == 0 # the layer has no cache
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/835/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/cache_utils.py:443: TracerWarning: Using len to get tensor shape might cause the trace to be incorrect. Recommended usage would be tensor.shape[0]. Passing a tensor of different shape might lead to errors or silently give incorrect results.
elif len(self.key_cache[layer_idx]) == 0: # fills previously skipped layers; checking for tensor causes errors
Compiling models and inference#
Select device from dropdown list for running inference using OpenVINO.
import requests
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/notebook_utils.py",
)
open("notebook_utils.py", "w").write(r.text)
from notebook_utils import device_widget
device = device_widget()
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
Let’s create callable wrapper classes for compiled models to allow
interaction with original pipeline. Note that all of wrapper classes
return torch.Tensors instead of np.arrays. In the
DecoderWrapper we separates the pipeline into two stages.
from collections import namedtuple
import torch.nn as nn
EncoderOutput = namedtuple("EncoderOutput", "last_hidden_state")
DecoderOutput = namedtuple("DecoderOutput", ("last_hidden_state", "past_key_values", "hidden_states", "attentions", "cross_attentions"))
core = ov.Core()
class TextEncoderModelWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder_ir_path, config):
ov_config = {}
if "GPU" in device.value:
ov_config = {"INFERENCE_PRECISION_HINT": "f32"}
self.encoder = core.compile_model(encoder_ir_path, device.value, ov_config)
self.config = config
self.dtype = self.config.torch_dtype
def __call__(self, input_ids, **_):
last_hidden_state = self.encoder(input_ids)[0]
return EncoderOutput(torch.from_numpy(last_hidden_state))
class DecoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, decoder_stage_1_ir_path, decoder_stage_2_ir_path, config):
super().__init__()
self.decoder_stage_1 = core.compile_model(decoder_stage_1_ir_path, device.value)
self.decoder_stage_2 = core.compile_model(decoder_stage_2_ir_path, device.value)
self.config = config
self.embed_tokens = None
embed_dim = config.vocab_size + 1 # + 1 for pad token id
self.embed_tokens = nn.ModuleList([nn.Embedding(embed_dim, config.hidden_size) for _ in range(config.num_codebooks)])
def __call__(self, input_ids=None, encoder_hidden_states=None, encoder_attention_mask=None, past_key_values=None, prompt_hidden_states=None, **kwargs):
inputs = {}
if input_ids is not None:
inputs["input_ids"] = input_ids
if encoder_hidden_states is not None:
inputs["encoder_hidden_states"] = encoder_hidden_states
if encoder_attention_mask is not None:
inputs["encoder_attention_mask"] = encoder_attention_mask
if prompt_hidden_states is not None:
inputs["prompt_hidden_states"] = prompt_hidden_states
if past_key_values is not None:
past_key_values = tuple(past_key_value for pkv_per_layer in past_key_values for past_key_value in pkv_per_layer)
inputs["past_key_values"] = past_key_values
arguments = (
input_ids,
encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask,
*past_key_values,
)
outs = self.decoder_stage_2(arguments)
else:
outs = self.decoder_stage_1(inputs)
outs = [torch.from_numpy(out) for out in outs.values()]
past_key_values = list(list(outs[i : i + 4]) for i in range(1, len(outs), 4))
return DecoderOutput(outs[0], past_key_values, None, None, None)
Now we can replace the original models by our wrapped OpenVINO models and run inference.
model.text_encoder = TextEncoderModelWrapper(TEXT_ENCODER_OV_PATH, model.text_encoder.config)
model.decoder.model.decoder = DecoderWrapper(DECODER_STAGE_1_OV_PATH, DECODER_STAGE_2_OV_PATH, model.decoder.model.decoder.config)
model._supports_cache_class = False
model._supports_static_cache = False
generation = model.generate(input_ids=input_ids, prompt_input_ids=prompt_input_ids)
audio_arr = generation.cpu().numpy().squeeze()
sf.write("parler_tts_out.wav", audio_arr, model.config.sampling_rate)
import IPython.display as ipd
ipd.Audio("parler_tts_out.wav")
Interactive inference#
from transformers import AutoFeatureExtractor, set_seed
feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(repo_id)
SAMPLE_RATE = feature_extractor.sampling_rate
def infer(prompt, description, seed):
set_seed(seed)
input_ids = tokenizer(description, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to("cpu")
prompt_input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to("cpu")
generation = model.generate(input_ids=input_ids, prompt_input_ids=prompt_input_ids)
audio_arr = generation.cpu().numpy().squeeze()
sr = SAMPLE_RATE
return sr, audio_arr
import requests
if not Path("gradio_helper.py").exists():
r = requests.get(url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/notebooks/parler-tts-text-to-speech/gradio_helper.py")
open("gradio_helper.py", "w").write(r.text)
from gradio_helper import make_demo
demo = make_demo(fn=infer)
try:
demo.queue().launch(debug=False)
except Exception:
demo.queue().launch(share=True, debug=False)
# if you are launching remotely, specify server_name and server_port
# demo.launch(server_name='your server name', server_port='server port in int')
# Read more in the docs: https://gradio.app/docs/
Running on local URL: http://127.0.0.1:7860 To create a public link, set share=True in launch().
# please uncomment and run this cell for stopping gradio interface
# demo.close()