InstantID: Zero-shot Identity-Preserving Generation using OpenVINO#
This Jupyter notebook can be launched after a local installation only.
Nowadays has been significant progress in personalized image synthesis with methods such as Textual Inversion, DreamBooth, and LoRA. However, their real-world applicability is hindered by high storage demands, lengthy fine-tuning processes, and the need for multiple reference images. Conversely, existing ID embedding-based methods, while requiring only a single forward inference, face challenges: they either necessitate extensive fine-tuning across numerous model parameters, lack compatibility with community pre-trained models, or fail to maintain high face fidelity.
InstantID is a tuning-free method to
achieve ID-Preserving generation with only single image, supporting
various downstream tasks. 
Given only one reference ID image, InstantID aims to generate customized images with various poses or styles from a single reference ID image while ensuring high fidelity. Following figure provides an overview of the method. It incorporates three crucial components:
An ID embedding that captures robust semantic face information;
A lightweight adapted module with decoupled cross-attention, facilitating the use of an image as a visual prompt;
An IdentityNet that encodes the detailed features from the reference facial image with additional spatial control.
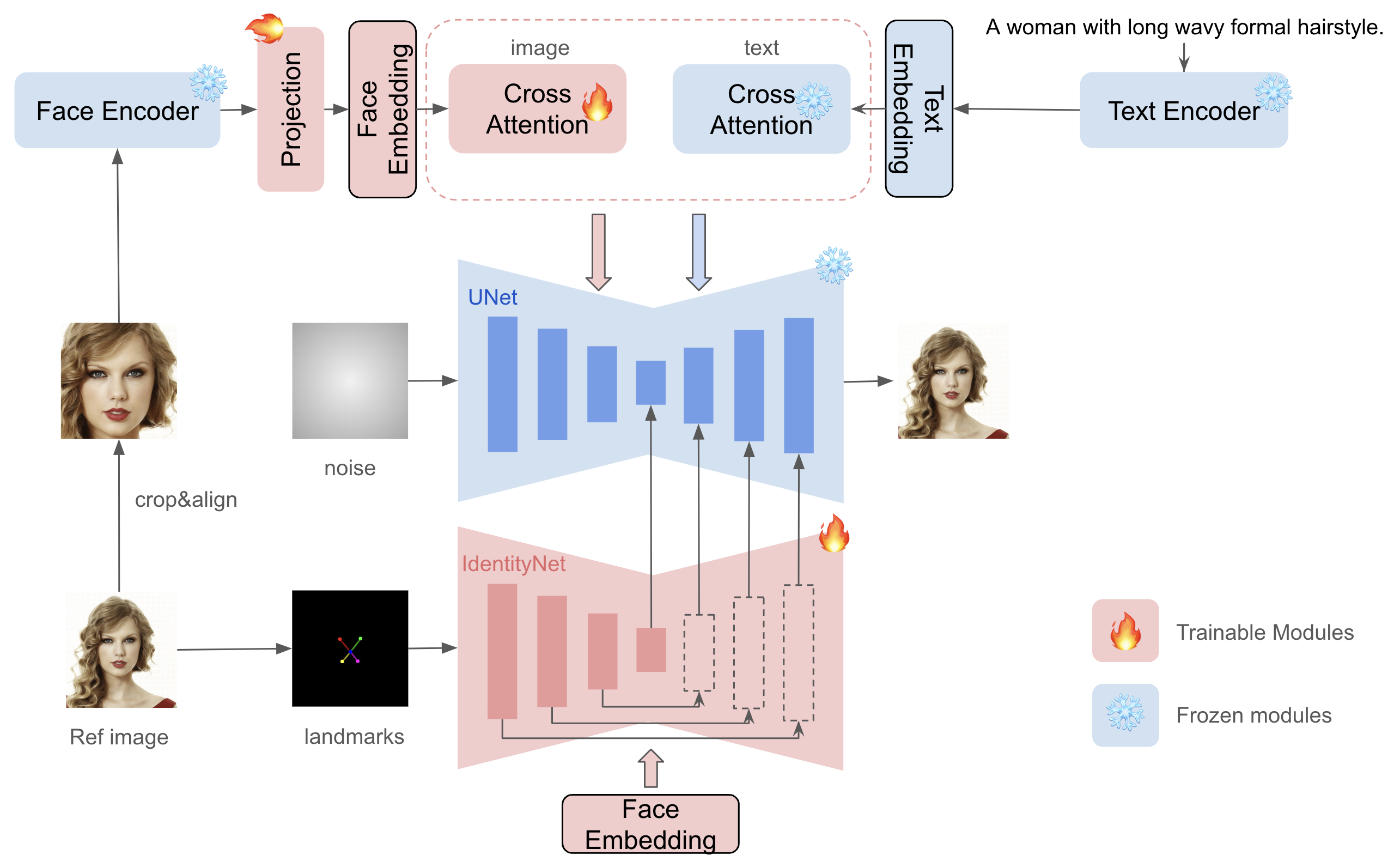
instantid-components.png#
The difference InstantID from previous works in the following aspects: 1. do not involve UNet training, so it can preserve the generation ability of the original text-to-image model and be compatible with existing pre-trained models and ControlNets in the community; 2. doesn’t require test-time tuning, so for a specific character, there is no need to collect multiple images for fine-tuning, only a single image needs to be inferred once; 3. achieve better face fidelity, and retain the editability of text.
You can find more details about the approach with project web page, paper and original repository
In this tutorial, we consider how to use InstantID with OpenVINO. An additional part demonstrates how to run optimization with NNCF to speed up pipeline.
Table of contents:
Installation Instructions#
This is a self-contained example that relies solely on its own code.
We recommend running the notebook in a virtual environment. You only need a Jupyter server to start. For details, please refer to Installation Guide.
Prerequisites#
import requests
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/notebook_utils.py",
)
open("notebook_utils.py", "w").write(r.text)
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/cmd_helper.py",
)
open("cmd_helper.py", "w").write(r.text)
from cmd_helper import clone_repo
clone_repo("https://github.com/InstantID/InstantID.git")
%pip install -q "openvino>=2023.3.0" opencv-python transformers "diffusers>=0.24.0" "matplotlib>=3.4" accelerate gdown "scikit-image>=0.19.2" "gradio>=4.19" "nncf>=2.9.0" "datasets>=2.14.6" "peft>=0.6.2"
Convert and prepare Face IdentityNet#
For getting face embeddings and pose key points, InstantID uses InsightFace face analytic library. Its models are distributed in ONNX format and can be run with OpenVINO. For preparing the face image, we need to detect the bounding boxes and keypoints for the face using the RetinaFace model, crop the detected face, align the face location using landmarks, and provide each face into the Arcface face embedding model for getting the person’s identity embeddings.
The code below downloads the InsightFace Antelopev2 model kit and provides a simple interface compatible with InsightFace for getting face recognition results.
from pathlib import Path
MODELS_DIR = Path("models")
face_detector_path = MODELS_DIR / "antelopev2" / "scrfd_10g_bnkps.onnx"
face_embeddings_path = MODELS_DIR / "antelopev2" / "glintr100.onnx"
from zipfile import ZipFile
import gdown
archive_file = Path("antelopev2.zip")
if not face_detector_path.exists() or face_embeddings_path.exists():
if not archive_file.exists():
gdown.download(
"https://drive.google.com/uc?id=18wEUfMNohBJ4K3Ly5wpTejPfDzp-8fI8",
str(archive_file),
)
with ZipFile(archive_file, "r") as zip_face_models:
zip_face_models.extractall(MODELS_DIR)
import cv2
import numpy as np
from skimage import transform as trans
def softmax(z):
assert len(z.shape) == 2
s = np.max(z, axis=1)
s = s[:, np.newaxis] # necessary step to do broadcasting
e_x = np.exp(z - s)
div = np.sum(e_x, axis=1)
div = div[:, np.newaxis] # dito
return e_x / div
def distance2bbox(points, distance, max_shape=None):
"""Decode distance prediction to bounding box.
Args:
points (Tensor): Shape (n, 2), [x, y].
distance (Tensor): Distance from the given point to 4
boundaries (left, top, right, bottom).
max_shape (tuple): Shape of the image.
Returns:
Tensor: Decoded bboxes.
"""
x1 = points[:, 0] - distance[:, 0]
y1 = points[:, 1] - distance[:, 1]
x2 = points[:, 0] + distance[:, 2]
y2 = points[:, 1] + distance[:, 3]
if max_shape is not None:
x1 = x1.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[1])
y1 = y1.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[0])
x2 = x2.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[1])
y2 = y2.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[0])
return np.stack([x1, y1, x2, y2], axis=-1)
def distance2kps(points, distance, max_shape=None):
"""Decode distance prediction to bounding box.
Args:
points (Tensor): Shape (n, 2), [x, y].
distance (Tensor): Distance from the given point to 4
boundaries (left, top, right, bottom).
max_shape (tuple): Shape of the image.
Returns:
Tensor: Decoded bboxes.
"""
preds = []
for i in range(0, distance.shape[1], 2):
px = points[:, i % 2] + distance[:, i]
py = points[:, i % 2 + 1] + distance[:, i + 1]
if max_shape is not None:
px = px.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[1])
py = py.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[0])
preds.append(px)
preds.append(py)
return np.stack(preds, axis=-1)
def prepare_input(image, std, mean, reverse_channels=True):
normalized_image = (image.astype(np.float32) - mean) / std
if reverse_channels:
normalized_image = normalized_image[:, :, ::-1]
input_tensor = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(normalized_image, (2, 0, 1)), 0)
return input_tensor
class RetinaFace:
def __init__(self, ov_model):
self.taskname = "detection"
self.ov_model = ov_model
self.center_cache = {}
self.nms_thresh = 0.4
self.det_thresh = 0.5
self._init_vars()
def _init_vars(self):
self.input_size = (640, 640)
outputs = self.ov_model.outputs
self.input_mean = 127.5
self.input_std = 128.0
self.use_kps = False
self._anchor_ratio = 1.0
self._num_anchors = 1
if len(outputs) == 6:
self.fmc = 3
self._feat_stride_fpn = [8, 16, 32]
self._num_anchors = 2
elif len(outputs) == 9:
self.fmc = 3
self._feat_stride_fpn = [8, 16, 32]
self._num_anchors = 2
self.use_kps = True
elif len(outputs) == 10:
self.fmc = 5
self._feat_stride_fpn = [8, 16, 32, 64, 128]
self._num_anchors = 1
elif len(outputs) == 15:
self.fmc = 5
self._feat_stride_fpn = [8, 16, 32, 64, 128]
self._num_anchors = 1
self.use_kps = True
def prepare(self, **kwargs):
nms_thresh = kwargs.get("nms_thresh", None)
if nms_thresh is not None:
self.nms_thresh = nms_thresh
det_thresh = kwargs.get("det_thresh", None)
if det_thresh is not None:
self.det_thresh = det_thresh
input_size = kwargs.get("input_size", None)
if input_size is not None:
if self.input_size is not None:
print("warning: det_size is already set in detection model, ignore")
else:
self.input_size = input_size
def forward(self, img, threshold):
scores_list = []
bboxes_list = []
kpss_list = []
blob = prepare_input(img, self.input_mean, self.input_std, True)
net_outs = self.ov_model(blob)
input_height = blob.shape[2]
input_width = blob.shape[3]
fmc = self.fmc
for idx, stride in enumerate(self._feat_stride_fpn):
scores = net_outs[idx]
bbox_preds = net_outs[idx + fmc]
bbox_preds = bbox_preds * stride
if self.use_kps:
kps_preds = net_outs[idx + fmc * 2] * stride
height = input_height // stride
width = input_width // stride
key = (height, width, stride)
if key in self.center_cache:
anchor_centers = self.center_cache[key]
else:
anchor_centers = np.stack(np.mgrid[:height, :width][::-1], axis=-1).astype(np.float32)
anchor_centers = (anchor_centers * stride).reshape((-1, 2))
if self._num_anchors > 1:
anchor_centers = np.stack([anchor_centers] * self._num_anchors, axis=1).reshape((-1, 2))
if len(self.center_cache) < 100:
self.center_cache[key] = anchor_centers
pos_inds = np.where(scores >= threshold)[0]
bboxes = distance2bbox(anchor_centers, bbox_preds)
pos_scores = scores[pos_inds]
pos_bboxes = bboxes[pos_inds]
scores_list.append(pos_scores)
bboxes_list.append(pos_bboxes)
if self.use_kps:
kpss = distance2kps(anchor_centers, kps_preds)
# kpss = kps_preds
kpss = kpss.reshape((kpss.shape[0], -1, 2))
pos_kpss = kpss[pos_inds]
kpss_list.append(pos_kpss)
return scores_list, bboxes_list, kpss_list
def detect(self, img, input_size=None, max_num=0, metric="default"):
assert input_size is not None or self.input_size is not None
input_size = self.input_size if input_size is None else input_size
im_ratio = float(img.shape[0]) / img.shape[1]
model_ratio = float(input_size[1]) / input_size[0]
if im_ratio > model_ratio:
new_height = input_size[1]
new_width = int(new_height / im_ratio)
else:
new_width = input_size[0]
new_height = int(new_width * im_ratio)
det_scale = float(new_height) / img.shape[0]
resized_img = cv2.resize(img, (new_width, new_height))
det_img = np.zeros((input_size[1], input_size[0], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
det_img[:new_height, :new_width, :] = resized_img
scores_list, bboxes_list, kpss_list = self.forward(det_img, self.det_thresh)
scores = np.vstack(scores_list)
scores_ravel = scores.ravel()
order = scores_ravel.argsort()[::-1]
bboxes = np.vstack(bboxes_list) / det_scale
if self.use_kps:
kpss = np.vstack(kpss_list) / det_scale
pre_det = np.hstack((bboxes, scores)).astype(np.float32, copy=False)
pre_det = pre_det[order, :]
keep = self.nms(pre_det)
det = pre_det[keep, :]
if self.use_kps:
kpss = kpss[order, :, :]
kpss = kpss[keep, :, :]
else:
kpss = None
if max_num > 0 and det.shape[0] > max_num:
area = (det[:, 2] - det[:, 0]) * (det[:, 3] - det[:, 1])
img_center = img.shape[0] // 2, img.shape[1] // 2
offsets = np.vstack(
[
(det[:, 0] + det[:, 2]) / 2 - img_center[1],
(det[:, 1] + det[:, 3]) / 2 - img_center[0],
]
)
offset_dist_squared = np.sum(np.power(offsets, 2.0), 0)
if metric == "max":
values = area
else:
values = area - offset_dist_squared * 2.0 # some extra weight on the centering
bindex = np.argsort(values)[::-1] # some extra weight on the centering
bindex = bindex[0:max_num]
det = det[bindex, :]
if kpss is not None:
kpss = kpss[bindex, :]
return det, kpss
def nms(self, dets):
thresh = self.nms_thresh
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
return keep
arcface_dst = np.array(
[
[38.2946, 51.6963],
[73.5318, 51.5014],
[56.0252, 71.7366],
[41.5493, 92.3655],
[70.7299, 92.2041],
],
dtype=np.float32,
)
def estimate_norm(lmk, image_size=112, mode="arcface"):
assert lmk.shape == (5, 2)
assert image_size % 112 == 0 or image_size % 128 == 0
if image_size % 112 == 0:
ratio = float(image_size) / 112.0
diff_x = 0
else:
ratio = float(image_size) / 128.0
diff_x = 8.0 * ratio
dst = arcface_dst * ratio
dst[:, 0] += diff_x
tform = trans.SimilarityTransform()
tform.estimate(lmk, dst)
M = tform.params[0:2, :]
return M
def norm_crop(img, landmark, image_size=112, mode="arcface"):
M = estimate_norm(landmark, image_size, mode)
warped = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (image_size, image_size), borderValue=0.0)
return warped
class FaceEmbeddings:
def __init__(self, ov_model):
self.ov_model = ov_model
self.taskname = "recognition"
input_mean = 127.5
input_std = 127.5
self.input_mean = input_mean
self.input_std = input_std
input_shape = self.ov_model.inputs[0].partial_shape
self.input_size = (input_shape[3].get_length(), input_shape[2].get_length())
self.input_shape = input_shape
def get(self, img, kps):
aimg = norm_crop(img, landmark=kps, image_size=self.input_size[0])
embedding = self.get_feat(aimg).flatten()
return embedding
def get_feat(self, imgs):
if not isinstance(imgs, list):
imgs = [imgs]
input_size = self.input_size
blob = np.concatenate([prepare_input(cv2.resize(img, input_size), self.input_mean, self.input_std, True) for img in imgs])
net_out = self.ov_model(blob)[0]
return net_out
def forward(self, batch_data):
blob = (batch_data - self.input_mean) / self.input_std
net_out = self.ov_model(blob)[0]
return net_out
class OVFaceAnalysis:
def __init__(self, detect_model, embedding_model):
self.det_model = RetinaFace(detect_model)
self.embed_model = FaceEmbeddings(embedding_model)
def get(self, img, max_num=0):
bboxes, kpss = self.det_model.detect(img, max_num=max_num, metric="default")
if bboxes.shape[0] == 0:
return []
ret = []
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
bbox = bboxes[i, 0:4]
det_score = bboxes[i, 4]
kps = None
if kpss is not None:
kps = kpss[i]
embedding = self.embed_model.get(img, kps)
ret.append({"bbox": bbox, "score": det_score, "kps": kps, "embedding": embedding})
return ret
Now, let’s see models inference result
Select Inference Device for Face Recognition#
import openvino as ov
from notebook_utils import device_widget
device = device_widget()
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
core = ov.Core()
face_detector = core.compile_model(face_detector_path, device.value)
face_embedding = core.compile_model(face_embeddings_path, device.value)
app = OVFaceAnalysis(face_detector, face_embedding)
Perform Face Identity extraction#
Now, we can apply our OVFaceAnalysis pipeline on an image for
collection face embeddings and key points for reflection on the
generated image
import PIL.Image
from pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl_instantid import draw_kps
def get_face_info(face_image: PIL.Image.Image):
r"""
Retrieve face information from the input face image.
Args:
face_image (PIL.Image.Image):
An image containing a face.
Returns:
face_emb (numpy.ndarray):
Facial embedding extracted from the face image.
face_kps (PIL.Image.Image):
Facial keypoints drawn on the face image.
"""
face_image = face_image.resize((832, 800))
# prepare face emb
face_info = app.get(cv2.cvtColor(np.array(face_image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
if len(face_info) == 0:
raise RuntimeError("Couldn't find the face on the image")
face_info = sorted(
face_info,
key=lambda x: (x["bbox"][2] - x["bbox"][0]) * x["bbox"][3] - x["bbox"][1],
)[
-1
] # only use the maximum face
face_emb = face_info["embedding"]
face_kps = draw_kps(face_image, face_info["kps"])
return face_emb, face_kps
from diffusers.utils import load_image
face_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/YiYiXu/testing-images/resolve/main/vermeer.jpg")
face_emb, face_kps = get_face_info(face_image)
face_image
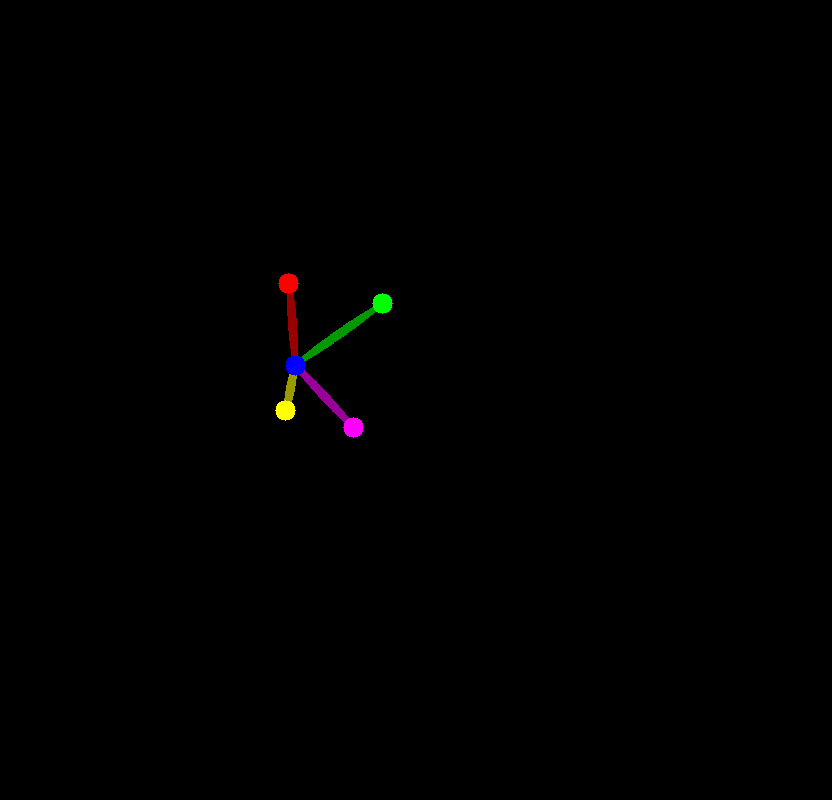
face_kps
Prepare InstantID pipeline#
The code below downloads InstantID pipeline parts - ControlNet for face pose and IP-Adapter for adding face embeddings to prompt
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
hf_hub_download(
repo_id="InstantX/InstantID",
filename="ControlNetModel/config.json",
local_dir="./checkpoints",
)
hf_hub_download(
repo_id="InstantX/InstantID",
filename="ControlNetModel/diffusion_pytorch_model.safetensors",
local_dir="./checkpoints",
)
hf_hub_download(repo_id="InstantX/InstantID", filename="ip-adapter.bin", local_dir="./checkpoints");
As it was discussed in model description, InstantID does not required diffusion model fine-tuning and can be applied on existing Stable Diffusion pipeline. We will use stable-diffusion-xl-bas-1-0 as basic text-to-image diffusion pipeline. We also apply LCM LoRA to speedup the generation process. Previously, we already considered how to convert and run SDXL model for Text-to-Image and Image-to-Image generation using Optimum-Intel library (please check out this notebook for details), now we will use it in combination with ControlNet and convert it using OpenVINO Model Conversion API.
from diffusers.models import ControlNetModel
from diffusers import LCMScheduler
from pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl_instantid import StableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline
import torch
from PIL import Image
import gc
ov_controlnet_path = MODELS_DIR / "controlnet.xml"
ov_unet_path = MODELS_DIR / "unet.xml"
ov_vae_decoder_path = MODELS_DIR / "vae_decoder.xml"
ov_text_encoder_path = MODELS_DIR / "text_encoder.xml"
ov_text_encoder_2_path = MODELS_DIR / "text_encoder_2.xml"
ov_image_proj_encoder_path = MODELS_DIR / "image_proj_model.xml"
required_pipeline_parts = [
ov_controlnet_path,
ov_unet_path,
ov_vae_decoder_path,
ov_text_encoder_path,
ov_text_encoder_2_path,
ov_image_proj_encoder_path,
]
def load_pytorch_pipeline(sdxl_id="stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"):
# prepare models under ./checkpoints
face_adapter = Path("checkpoints/ip-adapter.bin")
controlnet_path = Path("checkpoints/ControlNetModel")
# load IdentityNet
controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained(controlnet_path)
pipe = StableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline.from_pretrained(sdxl_id, controlnet=controlnet)
# load adapter
pipe.load_ip_adapter_instantid(face_adapter)
# load lcm lora
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdxl")
pipe.fuse_lora()
scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
pipe.set_ip_adapter_scale(0.8)
controlnet, unet, vae = pipe.controlnet, pipe.unet, pipe.vae
text_encoder, text_encoder_2, tokenizer, tokenizer_2 = (
pipe.text_encoder,
pipe.text_encoder_2,
pipe.tokenizer,
pipe.tokenizer_2,
)
image_proj_model = pipe.image_proj_model
return (
controlnet,
unet,
vae,
text_encoder,
text_encoder_2,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
image_proj_model,
scheduler,
)
load_torch_models = any([not path.exists() for path in required_pipeline_parts])
if load_torch_models:
(
controlnet,
unet,
vae,
text_encoder,
text_encoder_2,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
image_proj_model,
scheduler,
) = load_pytorch_pipeline()
tokenizer.save_pretrained(MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer")
tokenizer_2.save_pretrained(MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer_2")
scheduler.save_pretrained(MODELS_DIR / "scheduler")
else:
(
controlnet,
unet,
vae,
text_encoder,
text_encoder_2,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
image_proj_model,
scheduler,
) = (None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None)
gc.collect();
Convert InstantID pipeline components to OpenVINO Intermediate Representation format#
Starting from 2023.0 release, OpenVINO supports PyTorch models
conversion directly. We need to provide a model object, input data for
model tracing to ov.convert_model function to obtain OpenVINO
ov.Model object instance. Model can be saved on disk for next
deployment using ov.save_model function.
The pipeline consists of the following list of important parts:
Image Projection model for getting image prompt embeddings. It is similar with IP-Adapter approach described in this tutorial, but instead of image, it uses face embeddings as input for image prompt encoding.
Text Encoders for creating text embeddings to generate an image from a text prompt.
ControlNet for conditioning by face keypoints image for translation face pose on generated image.
Unet for step-by-step denoising latent image representation.
Autoencoder (VAE) for decoding latent space to image.
ControlNet#
ControlNet was introduced in Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models paper. It provides a framework that enables support for various spatial contexts such as a depth map, a segmentation map, a scribble, and key points that can serve as additional conditionings to Diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion. In this tutorial we already considered how to convert and use ControlNet with Stable Diffusion pipeline. The process of usage ControlNet for Stable Diffusion XL remains without changes.
import openvino as ov
from functools import partial
def cleanup_torchscript_cache():
"""
Helper for removing cached model representation
"""
torch._C._jit_clear_class_registry()
torch.jit._recursive.concrete_type_store = torch.jit._recursive.ConcreteTypeStore()
torch.jit._state._clear_class_state()
controlnet_example_input = {
"sample": torch.ones((2, 4, 100, 100)),
"timestep": torch.tensor(1, dtype=torch.float32),
"encoder_hidden_states": torch.randn((2, 77, 2048)),
"controlnet_cond": torch.randn((2, 3, 800, 800)),
"conditioning_scale": torch.tensor(0.8, dtype=torch.float32),
"added_cond_kwargs": {
"text_embeds": torch.zeros((2, 1280)),
"time_ids": torch.ones((2, 6), dtype=torch.int32),
},
}
if not ov_controlnet_path.exists():
controlnet.forward = partial(controlnet.forward, return_dict=False)
with torch.no_grad():
ov_controlnet = ov.convert_model(controlnet, example_input=controlnet_example_input)
ov_controlnet.inputs[-1].get_node().set_element_type(ov.Type.f32)
ov_controlnet.inputs[-1].get_node().set_partial_shape(ov.PartialShape([-1, 6]))
ov_controlnet.validate_nodes_and_infer_types()
ov.save_model(ov_controlnet, ov_controlnet_path)
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
del ov_controlnet
gc.collect()
if not ov_unet_path.exists():
out = controlnet(**controlnet_example_input)
down_block_res_samples, mid_block_res_sample = out[0], out[1]
else:
down_block_res_samples, mid_block_res_sample = None, None
del controlnet
gc.collect();
Unet#
Compared with Stable Diffusion, Stable Diffusion XL Unet has an
additional input for the time_ids condition. As we use ControlNet
and Image Projection Model, these models’ outputs also contribute to
preparing model input for Unet.
from typing import Tuple
class UnetWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
unet,
sample_dtype=torch.float32,
timestep_dtype=torch.int64,
encoder_hidden_states_dtype=torch.float32,
down_block_additional_residuals_dtype=torch.float32,
mid_block_additional_residual_dtype=torch.float32,
text_embeds_dtype=torch.float32,
time_ids_dtype=torch.int32,
):
super().__init__()
self.unet = unet
self.sample_dtype = sample_dtype
self.timestep_dtype = timestep_dtype
self.encoder_hidden_states_dtype = encoder_hidden_states_dtype
self.down_block_additional_residuals_dtype = down_block_additional_residuals_dtype
self.mid_block_additional_residual_dtype = mid_block_additional_residual_dtype
self.text_embeds_dtype = text_embeds_dtype
self.time_ids_dtype = time_ids_dtype
def forward(
self,
sample: torch.Tensor,
timestep: torch.Tensor,
encoder_hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
down_block_additional_residuals: Tuple[torch.Tensor],
mid_block_additional_residual: torch.Tensor,
text_embeds: torch.Tensor,
time_ids: torch.Tensor,
):
sample.to(self.sample_dtype)
timestep.to(self.timestep_dtype)
encoder_hidden_states.to(self.encoder_hidden_states_dtype)
down_block_additional_residuals = [res.to(self.down_block_additional_residuals_dtype) for res in down_block_additional_residuals]
mid_block_additional_residual.to(self.mid_block_additional_residual_dtype)
added_cond_kwargs = {
"text_embeds": text_embeds.to(self.text_embeds_dtype),
"time_ids": time_ids.to(self.time_ids_dtype),
}
return self.unet(
sample,
timestep,
encoder_hidden_states,
down_block_additional_residuals=down_block_additional_residuals,
mid_block_additional_residual=mid_block_additional_residual,
added_cond_kwargs=added_cond_kwargs,
)
if not ov_unet_path.exists():
unet_example_input = {
"sample": torch.ones((2, 4, 100, 100)),
"timestep": torch.tensor(1, dtype=torch.float32),
"encoder_hidden_states": torch.randn((2, 77, 2048)),
"down_block_additional_residuals": down_block_res_samples,
"mid_block_additional_residual": mid_block_res_sample,
"text_embeds": torch.zeros((2, 1280)),
"time_ids": torch.ones((2, 6), dtype=torch.int32),
}
unet = UnetWrapper(unet)
with torch.no_grad():
ov_unet = ov.convert_model(unet, example_input=unet_example_input)
for i in range(3, len(ov_unet.inputs) - 2):
ov_unet.inputs[i].get_node().set_element_type(ov.Type.f32)
ov_unet.validate_nodes_and_infer_types()
ov.save_model(ov_unet, ov_unet_path)
del ov_unet
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
gc.collect()
del unet
gc.collect();
VAE Decoder#
The VAE model has two parts, an encoder and a decoder. The encoder is used to convert the image into a low dimensional latent representation, which will serve as the input to the U-Net model. The decoder, conversely, transforms the latent representation back into an image. For InstantID pipeline we will use VAE only for decoding Unet generated image, it means that we can skip VAE encoder part conversion.
class VAEDecoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vae_decoder):
super().__init__()
self.vae = vae_decoder
def forward(self, latents):
return self.vae.decode(latents)
if not ov_vae_decoder_path.exists():
vae_decoder = VAEDecoderWrapper(vae)
with torch.no_grad():
ov_vae_decoder = ov.convert_model(vae_decoder, example_input=torch.zeros((1, 4, 64, 64)))
ov.save_model(ov_vae_decoder, ov_vae_decoder_path)
del ov_vae_decoder
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
del vae_decoder
gc.collect()
del vae
gc.collect();
Text Encoders#
The text-encoder is responsible for transforming the input prompt, for example, “a photo of an astronaut riding a horse” into an embedding space that can be understood by the U-Net. It is usually a simple transformer-based encoder that maps a sequence of input tokens to a sequence of latent text embeddings.
import types
inputs = {"input_ids": torch.ones((1, 77), dtype=torch.long)}
if not ov_text_encoder_path.exists():
text_encoder.eval()
text_encoder.config.output_hidden_states = True
text_encoder.config.return_dict = False
with torch.no_grad():
ov_text_encoder = ov.convert_model(text_encoder, example_input=inputs)
ov.save_model(ov_text_encoder, ov_text_encoder_path)
del ov_text_encoder
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
gc.collect()
del text_encoder
gc.collect()
def text_encoder_fwd_wrapper(self, input_ids):
res = self._orig_forward(input_ids, return_dict=True, output_hidden_states=True)
return tuple([v for v in res.values() if v is not None])
if not ov_text_encoder_2_path.exists():
text_encoder_2.eval()
text_encoder_2._orig_forward = text_encoder_2.forward
text_encoder_2.forward = types.MethodType(text_encoder_fwd_wrapper, text_encoder_2)
with torch.no_grad():
ov_text_encoder = ov.convert_model(text_encoder_2, example_input=inputs)
ov.save_model(ov_text_encoder, ov_text_encoder_2_path)
del ov_text_encoder
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
del text_encoder_2
gc.collect();
Image Projection Model#
Image projection model is responsible to transforming face embeddings to image prompt embeddings
if not ov_image_proj_encoder_path.exists():
with torch.no_grad():
ov_image_encoder = ov.convert_model(image_proj_model, example_input=torch.zeros((2, 1, 512)))
ov.save_model(ov_image_encoder, ov_image_proj_encoder_path)
del ov_image_encoder
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
del image_proj_model
gc.collect();
Prepare OpenVINO InstantID Pipeline#
import numpy as np
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline
from diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion_xl import StableDiffusionXLPipelineOutput
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
import torch
from diffusers.image_processor import PipelineImageInput, VaeImageProcessor
class OVStableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline(StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline):
def __init__(
self,
text_encoder,
text_encoder_2,
image_proj_model,
controlnet,
unet,
vae_decoder,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
scheduler,
):
self.text_encoder = text_encoder
self.text_encoder_2 = text_encoder_2
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.tokenizer_2 = tokenizer_2
self.image_proj_model = image_proj_model
self.controlnet = controlnet
self.unet = unet
self.vae_decoder = vae_decoder
self.scheduler = scheduler
self.image_proj_model_in_features = 512
self.vae_scale_factor = 8
self.vae_scaling_factor = 0.13025
self.image_processor = VaeImageProcessor(vae_scale_factor=self.vae_scale_factor, do_convert_rgb=True)
self.control_image_processor = VaeImageProcessor(
vae_scale_factor=self.vae_scale_factor,
do_convert_rgb=True,
do_normalize=False,
)
self._internal_dict = {}
self._progress_bar_config = {}
def _encode_prompt_image_emb(self, prompt_image_emb, num_images_per_prompt, do_classifier_free_guidance):
if isinstance(prompt_image_emb, torch.Tensor):
prompt_image_emb = prompt_image_emb.clone().detach()
else:
prompt_image_emb = torch.tensor(prompt_image_emb)
prompt_image_emb = prompt_image_emb.reshape([1, -1, self.image_proj_model_in_features])
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
prompt_image_emb = torch.cat([torch.zeros_like(prompt_image_emb), prompt_image_emb], dim=0)
else:
prompt_image_emb = torch.cat([prompt_image_emb], dim=0)
prompt_image_emb = self.image_proj_model(prompt_image_emb)[0]
bs_embed, seq_len, _ = prompt_image_emb.shape
prompt_image_emb = np.tile(prompt_image_emb, (1, num_images_per_prompt, 1))
prompt_image_emb = prompt_image_emb.reshape(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, seq_len, -1)
return prompt_image_emb
def __call__(
self,
prompt: Union[str, List[str]] = None,
prompt_2: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
image: PipelineImageInput = None,
height: Optional[int] = None,
width: Optional[int] = None,
num_inference_steps: int = 50,
guidance_scale: float = 5.0,
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
negative_prompt_2: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
num_images_per_prompt: Optional[int] = 1,
eta: float = 0.0,
generator: Optional[Union[torch.Generator, List[torch.Generator]]] = None,
latents: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
negative_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
pooled_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
image_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
return_dict: bool = True,
cross_attention_kwargs: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
controlnet_conditioning_scale: Union[float, List[float]] = 1.0,
guess_mode: bool = False,
control_guidance_start: Union[float, List[float]] = 0.0,
control_guidance_end: Union[float, List[float]] = 1.0,
original_size: Tuple[int, int] = None,
crops_coords_top_left: Tuple[int, int] = (0, 0),
target_size: Tuple[int, int] = None,
negative_original_size: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = None,
negative_crops_coords_top_left: Tuple[int, int] = (0, 0),
negative_target_size: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = None,
clip_skip: Optional[int] = None,
callback_on_step_end: Optional[Callable[[int, int, Dict], None]] = None,
callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs: List[str] = ["latents"],
# IP adapter
ip_adapter_scale=None,
**kwargs,
):
r"""
The call function to the pipeline for generation.
Args:
prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to guide image generation. If not defined, you need to pass `prompt_embeds`.
prompt_2 (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to be sent to `tokenizer_2` and `text_encoder_2`. If not defined, `prompt` is
used in both text-encoders.
image (`torch.FloatTensor`, `PIL.Image.Image`, `np.ndarray`, `List[torch.FloatTensor]`, `List[PIL.Image.Image]`, `List[np.ndarray]`,:
`List[List[torch.FloatTensor]]`, `List[List[np.ndarray]]` or `List[List[PIL.Image.Image]]`):
The ControlNet input condition to provide guidance to the `unet` for generation. If the type is
specified as `torch.FloatTensor`, it is passed to ControlNet as is. `PIL.Image.Image` can also be
accepted as an image. The dimensions of the output image defaults to `image`'s dimensions. If height__module.unet.up_blocks.0.upsamplers.0.conv.base_layer/aten::_convolu
and/or width are passed, `image` is resized accordingly. If multiple ControlNets are specified in
`init`, images must be passed as a list such that each element of the list can be correctly batched for
input to a single ControlNet.
height (`int`, *optional*, defaults to `self.unet.config.sample_size * self.vae_scale_factor`):
The height in pixels of the generated image. Anything below 512 pixels won't work well for
[stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0)
and checkpoints that are not specifically fine-tuned on low resolutions.
width (`int`, *optional*, defaults to `self.unet.config.sample_size * self.vae_scale_factor`):
The width in pixels of the generated image. Anything below 512 pixels won't work well for
[stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0)
and checkpoints that are not specifically fine-tuned on low resolutions.
num_inference_steps (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 50):
The number of denoising steps. More denoising steps usually lead to a higher quality image at the
expense of slower inference.
guidance_scale (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 5.0):
A higher guidance scale value encourages the model to generate images closely linked to the text
`prompt` at the expense of lower image quality. Guidance scale is enabled when `guidance_scale > 1`.
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to guide what to not include in image generation. If not defined, you need to
pass `negative_prompt_embeds` instead. Ignored when not using guidance (`guidance_scale < 1`).
negative_prompt_2 (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to guide what to not include in image generation. This is sent to `tokenizer_2`
and `text_encoder_2`. If not defined, `negative_prompt` is used in both text-encoders.
num_images_per_prompt (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
The number of images to generate per prompt.
eta (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 0.0):
Corresponds to parameter eta (η) from the [DDIM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502) paper. Only applies
to the [`~schedulers.DDIMScheduler`], and is ignored in other schedulers.
generator (`torch.Generator` or `List[torch.Generator]`, *optional*):
A [`torch.Generator`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html) to make
generation deterministic.
latents (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated noisy latents sampled from a Gaussian distribution, to be used as inputs for image
generation. Can be used to tweak the same generation with different prompts. If not provided, a latents
tensor is generated by sampling using the supplied random `generator`.
prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs (prompt weighting). If not
provided, text embeddings are generated from the `prompt` input argument.
negative_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated negative text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs (prompt weighting). If
not provided, `negative_prompt_embeds` are generated from the `negative_prompt` input argument.
pooled_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated pooled text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs (prompt weighting). If
not provided, pooled text embeddings are generated from `prompt` input argument.
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated negative pooled text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs (prompt
weighting). If not provided, pooled `negative_prompt_embeds` are generated from `negative_prompt` input
argument.
image_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated image embeddings.
output_type (`str`, *optional*, defaults to `"pil"`):
The output format of the generated image. Choose between `PIL.Image` or `np.array`.
return_dict (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
Whether or not to return a [`~pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput`] instead of a
plain tuple.
controlnet_conditioning_scale (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to 1.0):
The outputs of the ControlNet are multiplied by `controlnet_conditioning_scale` before they are added
to the residual in the original `unet`. If multiple ControlNets are specified in `init`, you can set
the corresponding scale as a list.
control_guidance_start (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to 0.0):
The percentage of total steps at which the ControlNet starts applying.
control_guidance_end (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to 1.0):
The percentage of total steps at which the ControlNet stops applying.
original_size (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (1024, 1024)):
If `original_size` is not the same as `target_size` the image will appear to be down- or upsampled.
`original_size` defaults to `(height, width)` if not specified. Part of SDXL's micro-conditioning as
explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952).
crops_coords_top_left (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (0, 0)):
`crops_coords_top_left` can be used to generate an image that appears to be "cropped" from the position
`crops_coords_top_left` downwards. Favorable, well-centered images are usually achieved by setting
`crops_coords_top_left` to (0, 0). Part of SDXL's micro-conditioning as explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952).
target_size (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (1024, 1024)):
For most cases, `target_size` should be set to the desired height and width of the generated image. If
not specified it will default to `(height, width)`. Part of SDXL's micro-conditioning as explained in
section 2.2 of [https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952).
negative_original_size (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (1024, 1024)):
To negatively condition the generation process based on a specific image resolution. Part of SDXL's
micro-conditioning as explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952). For more
information, refer toencode_pro this issue thread: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/4208.
negative_crops_coords_top_left (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (0, 0)):
To negatively condition the generation process based on a specific crop coordinates. Part of SDXL's
micro-conditioning as explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952). For more
information, refer to this issue thread: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/4208.
negative_target_size (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (1024, 1024)):
To negatively condition the generation process based on a target image resolution. It should be as same
as the `target_size` for most cases. Part of SDXL's micro-conditioning as explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952). For more
information, refer to this issue thread: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/4208.
clip_skip (`int`, *optional*):
Number of layers to be skipped from CLIP while computing the prompt embeddings. A value of 1 means that
the output of the pre-final layer will be used for computing the prompt embeddings.
Examples:
Returns:
[`~pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput`] or `tuple`:
If `return_dict` is `True`, [`~pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput`] is returned,
otherwise a `tuple` is returned containing the output images.
"""
do_classifier_free_guidance = guidance_scale >= 1.0
# align format for control guidance
if not isinstance(control_guidance_start, list) and isinstance(control_guidance_end, list):
control_guidance_start = len(control_guidance_end) * [control_guidance_start]
elif not isinstance(control_guidance_end, list) and isinstance(control_guidance_start, list):
control_guidance_end = len(control_guidance_start) * [control_guidance_end]
elif not isinstance(control_guidance_start, list) and not isinstance(control_guidance_end, list):
control_guidance_start, control_guidance_end = (
[control_guidance_start],
[control_guidance_end],
)
# 2. Define call parameters
if prompt is not None and isinstance(prompt, str):
batch_size = 1
elif prompt is not None and isinstance(prompt, list):
batch_size = len(prompt)
else:
batch_size = prompt_embeds.shape[0]
(
prompt_embeds,
negative_prompt_embeds,
pooled_prompt_embeds,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds,
) = self.encode_prompt(
prompt,
prompt_2,
num_images_per_prompt,
do_classifier_free_guidance,
negative_prompt,
negative_prompt_2,
prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds,
negative_prompt_embeds=negative_prompt_embeds,
pooled_prompt_embeds=pooled_prompt_embeds,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds=negative_pooled_prompt_embeds,
lora_scale=None,
clip_skip=clip_skip,
)
# 3.2 Encode image prompt
prompt_image_emb = self._encode_prompt_image_emb(image_embeds, num_images_per_prompt, do_classifier_free_guidance)
# 4. Prepare image
image = self.prepare_image(
image=image,
width=width,
height=height,
batch_size=batch_size * num_images_per_prompt,
num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt,
do_classifier_free_guidance=do_classifier_free_guidance,
guess_mode=guess_mode,
)
height, width = image.shape[-2:]
# 5. Prepare timesteps
self.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
timesteps = self.scheduler.timesteps
# 6. Prepare latent variables
num_channels_latents = 4
latents = self.prepare_latents(
int(batch_size) * int(num_images_per_prompt),
int(num_channels_latents),
int(height),
int(width),
dtype=torch.float32,
device=torch.device("cpu"),
generator=generator,
latents=latents,
)
# 7. Prepare extra step kwargs.
extra_step_kwargs = self.prepare_extra_step_kwargs(generator, eta)
# 7.1 Create tensor stating which controlnets to keep
controlnet_keep = []
for i in range(len(timesteps)):
keeps = [1.0 - float(i / len(timesteps) < s or (i + 1) / len(timesteps) > e) for s, e in zip(control_guidance_start, control_guidance_end)]
controlnet_keep.append(keeps)
# 7.2 Prepare added time ids & embeddings
if isinstance(image, list):
original_size = original_size or image[0].shape[-2:]
else:
original_size = original_size or image.shape[-2:]
target_size = target_size or (height, width)
add_text_embeds = pooled_prompt_embeds
if self.text_encoder_2 is None:
text_encoder_projection_dim = pooled_prompt_embeds.shape[-1]
else:
text_encoder_projection_dim = 1280
add_time_ids = self._get_add_time_ids(
original_size,
crops_coords_top_left,
target_size,
text_encoder_projection_dim=text_encoder_projection_dim,
)
if negative_original_size is not None and negative_target_size is not None:
negative_add_time_ids = self._get_add_time_ids(
negative_original_size,
negative_crops_coords_top_left,
negative_target_size,
text_encoder_projection_dim=text_encoder_projection_dim,
)
else:
negative_add_time_ids = add_time_ids
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
prompt_embeds = np.concatenate([negative_prompt_embeds, prompt_embeds], axis=0)
add_text_embeds = np.concatenate([negative_pooled_prompt_embeds, add_text_embeds], axis=0)
add_time_ids = np.concatenate([negative_add_time_ids, add_time_ids], axis=0)
add_time_ids = np.tile(add_time_ids, (batch_size * num_images_per_prompt, 1))
encoder_hidden_states = np.concatenate([prompt_embeds, prompt_image_emb], axis=1)
# 8. Denoising loop
with self.progress_bar(total=num_inference_steps) as progress_bar:
for i, t in enumerate(timesteps):
# expand the latents if we are doing classifier free guidance
latent_model_input = torch.cat([latents] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else latents
latent_model_input = self.scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, t)
# controlnet(s) inference
control_model_input = latent_model_input
cond_scale = controlnet_conditioning_scale
controlnet_outputs = self.controlnet(
[
control_model_input,
t,
prompt_image_emb,
image,
cond_scale,
add_text_embeds,
add_time_ids,
]
)
controlnet_additional_blocks = list(controlnet_outputs.values())
# predict the noise residual
noise_pred = self.unet(
[
latent_model_input,
t,
encoder_hidden_states,
*controlnet_additional_blocks,
add_text_embeds,
add_time_ids,
]
)[0]
# perform guidance
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred[0], noise_pred[1]
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
# compute the previous noisy sample x_t -> x_t-1
latents = self.scheduler.step(
torch.from_numpy(noise_pred),
t,
latents,
**extra_step_kwargs,
return_dict=False,
)[0]
progress_bar.update()
if not output_type == "latent":
image = self.vae_decoder(latents / self.vae_scaling_factor)[0]
else:
image = latents
if not output_type == "latent":
image = self.image_processor.postprocess(torch.from_numpy(image), output_type=output_type)
if not return_dict:
return (image,)
return StableDiffusionXLPipelineOutput(images=image)
def encode_prompt(
self,
prompt: str,
prompt_2: Optional[str] = None,
num_images_per_prompt: int = 1,
do_classifier_free_guidance: bool = True,
negative_prompt: Optional[str] = None,
negative_prompt_2: Optional[str] = None,
prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
negative_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
pooled_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
lora_scale: Optional[float] = None,
clip_skip: Optional[int] = None,
):
r"""
Encodes the prompt into text encoder hidden states.
Args:
prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
prompt to be encoded
prompt_2 (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to be sent to the `tokenizer_2` and `text_encoder_2`. If not defined, `prompt` is
used in both text-encoders
num_images_per_prompt (`int`):
number of images that should be generated per prompt
do_classifier_free_guidance (`bool`):
whether to use classifier free guidance or not
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. If not defined, one has to pass
`negative_prompt_embeds` instead. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored if `guidance_scale` is
less than `1`).
negative_prompt_2 (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation to be sent to `tokenizer_2` and
`text_encoder_2`. If not defined, `negative_prompt` is used in both text-encoders
prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt weighting. If not
provided, text embeddings will be generated from `prompt` input argument.
negative_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated negative text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt
weighting. If not provided, negative_prompt_embeds will be generated from `negative_prompt` input
argument.
pooled_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated pooled text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt weighting.
If not provided, pooled text embeddings will be generated from `prompt` input argument.
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated negative pooled text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt
weighting. If not provided, pooled negative_prompt_embeds will be generated from `negative_prompt`
input argument.
lora_scale (`float`, *optional*):
A lora scale that will be applied to all LoRA layers of the text encoder if LoRA layers are loaded.
clip_skip (`int`, *optional*):
Number of layers to be skipped from CLIP while computing the prompt embeddings. A value of 1 means that
the output of the pre-final layer will be used for computing the prompt embeddings.
"""
prompt = [prompt] if isinstance(prompt, str) else prompt
if prompt is not None:
batch_size = len(prompt)
else:
batch_size = prompt_embeds.shape[0]
# Define tokenizers and text encoders
tokenizers = [self.tokenizer, self.tokenizer_2] if self.tokenizer is not None else [self.tokenizer_2]
text_encoders = [self.text_encoder, self.text_encoder_2] if self.text_encoder is not None else [self.text_encoder_2]
if prompt_embeds is None:
prompt_2 = prompt_2 or prompt
prompt_2 = [prompt_2] if isinstance(prompt_2, str) else prompt_2
# textual inversion: procecss multi-vector tokens if necessary
prompt_embeds_list = []
prompts = [prompt, prompt_2]
for prompt, tokenizer, text_encoder in zip(prompts, tokenizers, text_encoders):
text_inputs = tokenizer(
prompt,
padding="max_length",
max_length=tokenizer.model_max_length,
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
text_input_ids = text_inputs.input_ids
prompt_embeds = text_encoder(text_input_ids)
# We are only ALWAYS interested in the pooled output of the final text encoder
pooled_prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds[0]
hidden_states = list(prompt_embeds.values())[1:]
if clip_skip is None:
prompt_embeds = hidden_states[-2]
else:
# "2" because SDXL always indexes from the penultimate layer.
prompt_embeds = hidden_states[-(clip_skip + 2)]
prompt_embeds_list.append(prompt_embeds)
prompt_embeds = np.concatenate(prompt_embeds_list, axis=-1)
# get unconditional embeddings for classifier free guidance
zero_out_negative_prompt = negative_prompt is None
if do_classifier_free_guidance and negative_prompt_embeds is None and zero_out_negative_prompt:
negative_prompt_embeds = np.zeros_like(prompt_embeds)
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds = np.zeros_like(pooled_prompt_embeds)
elif do_classifier_free_guidance and negative_prompt_embeds is None:
negative_prompt = negative_prompt or ""
negative_prompt_2 = negative_prompt_2 or negative_prompt
# normalize str to list
negative_prompt = batch_size * [negative_prompt] if isinstance(negative_prompt, str) else negative_prompt
negative_prompt_2 = batch_size * [negative_prompt_2] if isinstance(negative_prompt_2, str) else negative_prompt_2
uncond_tokens: List[str]
if prompt is not None and type(prompt) is not type(negative_prompt):
raise TypeError(f"`negative_prompt` should be the same type to `prompt`, but got {type(negative_prompt)} !=" f" {type(prompt)}.")
elif batch_size != len(negative_prompt):
raise ValueError(
f"`negative_prompt`: {negative_prompt} has batch size {len(negative_prompt)}, but `prompt`:"
f" {prompt} has batch size {batch_size}. Please make sure that passed `negative_prompt` matches"
" the batch size of `prompt`."
)
else:
uncond_tokens = [negative_prompt, negative_prompt_2]
negative_prompt_embeds_list = []
for negative_prompt, tokenizer, text_encoder in zip(uncond_tokens, tokenizers, text_encoders):
max_length = prompt_embeds.shape[1]
uncond_input = tokenizer(
negative_prompt,
padding="max_length",
max_length=max_length,
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
negative_prompt_embeds = text_encoder(uncond_input.input_ids)
# We are only ALWAYS interested in the pooled output of the final text encoder
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds = negative_prompt_embeds[0]
hidden_states = list(negative_prompt_embeds.values())[1:]
negative_prompt_embeds = hidden_states[-2]
negative_prompt_embeds_list.append(negative_prompt_embeds)
negative_prompt_embeds = np.concatenate(negative_prompt_embeds_list, axis=-1)
bs_embed, seq_len, _ = prompt_embeds.shape
# duplicate text embeddings for each generation per prompt, using mps friendly method
prompt_embeds = np.tile(prompt_embeds, (1, num_images_per_prompt, 1))
prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.reshape(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, seq_len, -1)
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
# duplicate unconditional embeddings for each generation per prompt, using mps friendly method
seq_len = negative_prompt_embeds.shape[1]
negative_prompt_embeds = np.tile(negative_prompt_embeds, (1, num_images_per_prompt, 1))
negative_prompt_embeds = negative_prompt_embeds.reshape(batch_size * num_images_per_prompt, seq_len, -1)
pooled_prompt_embeds = np.tile(pooled_prompt_embeds, (1, num_images_per_prompt)).reshape(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, -1)
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds = np.tile(negative_pooled_prompt_embeds, (1, num_images_per_prompt)).reshape(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, -1)
return (
prompt_embeds,
negative_prompt_embeds,
pooled_prompt_embeds,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds,
)
def prepare_image(
self,
image,
width,
height,
batch_size,
num_images_per_prompt,
do_classifier_free_guidance=False,
guess_mode=False,
):
image = self.control_image_processor.preprocess(image, height=height, width=width).to(dtype=torch.float32)
image_batch_size = image.shape[0]
if image_batch_size == 1:
repeat_by = batch_size
else:
# image batch size is the same as prompt batch size
repeat_by = num_images_per_prompt
image = image.repeat_interleave(repeat_by, dim=0)
if do_classifier_free_guidance and not guess_mode:
image = torch.cat([image] * 2)
return image
def _get_add_time_ids(
self,
original_size,
crops_coords_top_left,
target_size,
text_encoder_projection_dim,
):
add_time_ids = list(original_size + crops_coords_top_left + target_size)
add_time_ids = torch.tensor([add_time_ids])
return add_time_ids
Run OpenVINO pipeline inference#
Select inference device for InstantID#
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
Create pipeline#
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
def create_ov_pipe(
text_encoder_path,
text_encoder_2_path,
image_proj_encoder_path,
controlnet_path,
unet_path,
vae_decoder_path,
tokenizer_path,
tokenizer_2_path,
scheduler_path,
):
return OVStableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline(
core.compile_model(text_encoder_path, device.value),
core.compile_model(text_encoder_2_path, device.value),
core.compile_model(image_proj_encoder_path, device.value),
core.compile_model(controlnet_path, device.value),
core.compile_model(unet_path, device.value),
core.compile_model(vae_decoder_path, device.value),
AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(tokenizer_path),
AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(tokenizer_2_path),
LCMScheduler.from_pretrained(scheduler_path),
)
ov_pipe = create_ov_pipe(
ov_text_encoder_path,
ov_text_encoder_2_path,
ov_image_proj_encoder_path,
ov_controlnet_path,
ov_unet_path,
ov_vae_decoder_path,
MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer",
MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer_2",
MODELS_DIR / "scheduler",
)
Run inference#
prompt = "Anime girl"
negative_prompt = ""
image = ov_pipe(
prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
num_inference_steps=4,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
guidance_scale=0.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(1749781188),
).images[0]
0%| | 0/4 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
image
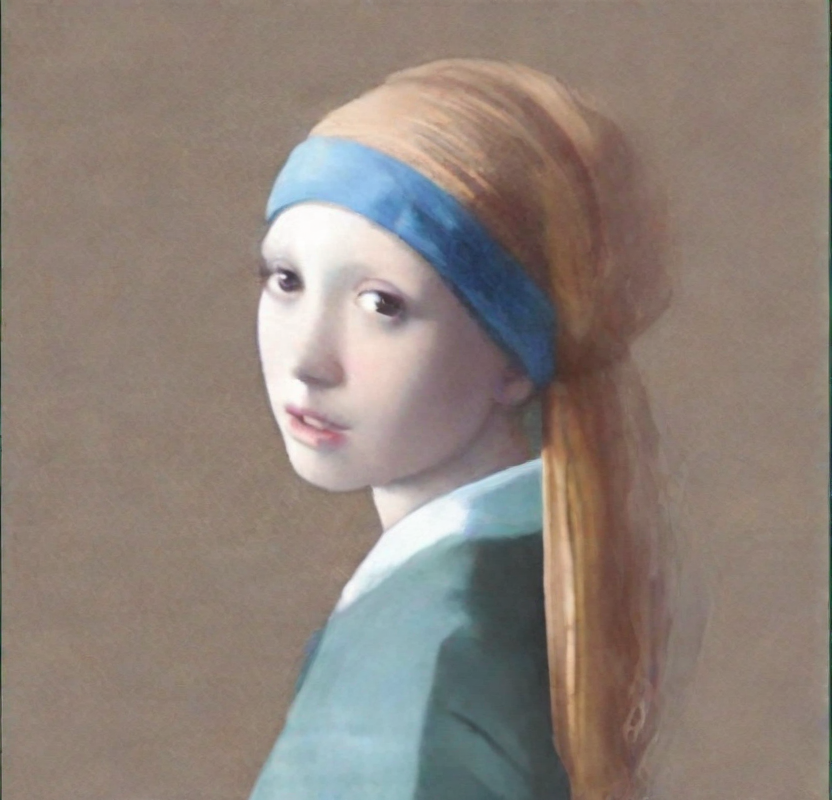

Quantization#
NNCF enables
post-training quantization by adding quantization layers into model
graph and then using a subset of the training dataset to initialize the
parameters of these additional quantization layers. Quantized operations
are executed in INT8 instead of FP32/FP16 making model
inference faster.
According to OVStableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline structure,
ControlNet and UNet models are used in the cycle repeating inference on
each diffusion step, while other parts of pipeline take part only once.
Now we will show you how to optimize pipeline using
NNCF to reduce memory and
computation cost.
Please select below whether you would like to run quantization to improve model inference speed.
NOTE: Quantization is time and memory consuming operation. Running quantization code below may take some time.
from notebook_utils import quantization_widget
skip_for_device = "GPU" in device.value or (device.value == "AUTO" and any("GPU" in device_name for device_name in core.available_devices))
to_quantize = quantization_widget(not skip_for_device)
to_quantize
Checkbox(value=True, description='Quantization')
Let’s load skip magic extension to skip quantization if
to_quantize is not selected
# Fetch `skip_kernel_extension` module
import requests
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/skip_kernel_extension.py",
)
open("skip_kernel_extension.py", "w").write(r.text)
int8_pipe = None
%load_ext skip_kernel_extension
Prepare calibration datasets#
We use a portion of wider_face dataset from Hugging Face as calibration data. We use prompts below to guide image generation and to determine what not to include in the resulting image.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
negative_prompts = [
"blurry unreal occluded",
"low contrast disfigured uncentered mangled",
"amateur out of frame low quality nsfw",
"ugly underexposed jpeg artifacts",
"low saturation disturbing content",
"overexposed severe distortion",
"amateur NSFW",
"ugly mutilated out of frame disfigured",
]
prompts = [
"a Naruto-style image of a young boy, incorporating dynamic action lines, intense energy effects, and a sense of movement and power",
"an anime-style girl, with vibrant, otherworldly colors, fantastical elements, and a sense of awe",
"analog film photo of a man. faded film, desaturated, 35mm photo, grainy, vignette, vintage, Kodachrome, Lomography, stained, highly detailed, found footage, masterpiece, best quality",
"Apply a staining filter to give the impression of aged, worn-out film while maintaining sharp detail on a portrait of a woman",
"a modern picture of a boy an antique feel through selective desaturation, grain addition, and a warm tone, mimicking the style of old photographs",
"a dreamy, ethereal portrait of a young girl, featuring soft, pastel colors, a blurred background, and a touch of bokeh",
"a dynamic, action-packed image of a boy in motion, using motion blur, panning, and other techniques to convey a sense of speed and energy",
"a dramatic, cinematic image of a boy, using color grading, contrast adjustments, and a widescreen aspect ratio, to create a sense of epic scale and grandeur",
"a portrait of a woman in the style of Picasso's cubism, featuring fragmented shapes, bold lines, and a vibrant color palette",
"an artwork in the style of Picasso's Blue Period, featuring a somber, melancholic portrait of a person, with muted colors, elongated forms, and a sense of introspection and contemplation",
]
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import datasets
num_inference_steps = 4
subset_size = 200
ov_int8_unet_path = MODELS_DIR / 'unet_optimized.xml'
ov_int8_controlnet_path = MODELS_DIR / 'controlnet_optimized.xml'
num_samples = int(np.ceil(subset_size / num_inference_steps))
dataset = datasets.load_dataset("wider_face", split="train", streaming=True, trust_remote_code=True).shuffle(seed=42)
face_info = []
for batch in dataset:
try:
face_info.append(get_face_info(batch["image"]))
except RuntimeError:
continue
if len(face_info) > num_samples:
break
To collect intermediate model inputs for calibration we should customize
CompiledModel.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
from transformers import set_seed
set_seed(42)
class CompiledModelDecorator(ov.CompiledModel):
def __init__(self, compiled_model: ov.CompiledModel, keep_prob: float = 1.0):
super().__init__(compiled_model)
self.data_cache = []
self.keep_prob = np.clip(keep_prob, 0, 1)
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
if np.random.rand() <= self.keep_prob:
self.data_cache.append(*args)
return super().__call__(*args, **kwargs)
def collect_calibration_data(pipeline, face_info, subset_size):
original_unet = pipeline.unet
pipeline.unet = CompiledModelDecorator(original_unet)
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=True)
pbar = tqdm(total=subset_size)
for face_emb, face_kps in face_info:
negative_prompt = np.random.choice(negative_prompts)
prompt = np.random.choice(prompts)
_ = pipeline(
prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
guidance_scale=0.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(1749781188)
)
collected_subset_size = len(pipeline.unet.data_cache)
pbar.update(collected_subset_size - pbar.n)
calibration_dataset = pipeline.unet.data_cache[:subset_size]
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=False)
pipeline.unet = original_unet
return calibration_dataset
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not (ov_int8_unet_path.exists() and ov_int8_controlnet_path.exists()):
unet_calibration_data = collect_calibration_data(ov_pipe, face_info, subset_size=subset_size)
0%| | 0/200 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
def prepare_controlnet_dataset(pipeline, face_info, unet_calibration_data):
controlnet_calibration_data = []
i = 0
for face_emb, face_kps in face_info:
prompt_image_emb = pipeline._encode_prompt_image_emb(
face_emb, num_images_per_prompt=1, do_classifier_free_guidance=False
)
image = pipeline.prepare_image(
image=face_kps,
width=None,
height=None,
batch_size=1,
num_images_per_prompt=1,
do_classifier_free_guidance=False,
guess_mode=False,
)
for data in unet_calibration_data[i:i+num_inference_steps]:
controlnet_inputs = [data[0], data[1], prompt_image_emb, image, 1.0, data[-2], data[-1]]
controlnet_calibration_data.append(controlnet_inputs)
i += num_inference_steps
return controlnet_calibration_data
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not ov_int8_controlnet_path.exists():
controlnet_calibration_data = prepare_controlnet_dataset(ov_pipe, face_info, unet_calibration_data)
Run Quantization#
Quantization of the first Convolution layer impacts the generation
results. We recommend using IgnoredScope to keep accuracy sensitive
layers in FP16 precision.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
# Delete loaded full precision pipeline before quantization to lower peak memory footprint.
ov_pipe = None
gc.collect()
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import nncf
if not ov_int8_controlnet_path.exists():
controlnet = core.read_model(ov_controlnet_path)
quantized_controlnet = nncf.quantize(
model=controlnet,
calibration_dataset=nncf.Dataset(controlnet_calibration_data),
subset_size=subset_size,
ignored_scope=nncf.IgnoredScope(names=["__module.model.conv_in/aten::_convolution/Convolution"]),
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
)
ov.save_model(quantized_controlnet, ov_int8_controlnet_path)
INFO:nncf:NNCF initialized successfully. Supported frameworks detected: torch, onnx, openvino
Output()
Output()
INFO:nncf:1 ignored nodes were found by names in the NNCFGraph
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 8 __module.model.conv_in/aten::_convolution/Convolution
27 __module.model.conv_in/aten::_convolution/Add
Output()
Output()
On the one hand, post-training quantization of the UNet model requires more than ~100Gb and leads to accuracy drop. On the other hand, the weight compression doesn’t improve performance when applying to Stable Diffusion models, because the size of activations is comparable to weights. That is why the proposal is to apply quantization in hybrid mode which means that we quantize: (1) weights of MatMul and Embedding layers and (2) activations of other layers. The steps are the following:
Create a calibration dataset for quantization.
Collect operations with weights.
Run
nncf.compress_model()to compress only the model weights.Run
nncf.quantize()on the compressed model with weighted operations ignored by providingignored_scopeparameter.Save the
INT8model usingopenvino.save_model()function.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
from collections import deque
def get_operation_const_op(operation, const_port_id: int):
node = operation.input_value(const_port_id).get_node()
queue = deque([node])
constant_node = None
allowed_propagation_types_list = ["Convert", "FakeQuantize", "Reshape"]
while len(queue) != 0:
curr_node = queue.popleft()
if curr_node.get_type_name() == "Constant":
constant_node = curr_node
break
if len(curr_node.inputs()) == 0:
break
if curr_node.get_type_name() in allowed_propagation_types_list:
queue.append(curr_node.input_value(0).get_node())
return constant_node
def is_embedding(node) -> bool:
allowed_types_list = ["f16", "f32", "f64"]
const_port_id = 0
input_tensor = node.input_value(const_port_id)
if input_tensor.get_element_type().get_type_name() in allowed_types_list:
const_node = get_operation_const_op(node, const_port_id)
if const_node is not None:
return True
return False
def collect_ops_with_weights(model):
ops_with_weights = []
for op in model.get_ops():
if op.get_type_name() == "MatMul":
constant_node_0 = get_operation_const_op(op, const_port_id=0)
constant_node_1 = get_operation_const_op(op, const_port_id=1)
if constant_node_0 or constant_node_1:
ops_with_weights.append(op.get_friendly_name())
if op.get_type_name() == "Gather" and is_embedding(op):
ops_with_weights.append(op.get_friendly_name())
return ops_with_weights
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not ov_int8_unet_path.exists():
unet = core.read_model(ov_unet_path)
unet_ignored_scope = collect_ops_with_weights(unet)
compressed_unet = nncf.compress_weights(unet, ignored_scope=nncf.IgnoredScope(types=['Convolution']))
quantized_unet = nncf.quantize(
model=compressed_unet,
calibration_dataset=nncf.Dataset(unet_calibration_data),
subset_size=subset_size,
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
ignored_scope=nncf.IgnoredScope(names=unet_ignored_scope),
advanced_parameters=nncf.AdvancedQuantizationParameters(smooth_quant_alpha=-1)
)
ov.save_model(quantized_unet, ov_int8_unet_path)
INFO:nncf:51 ignored nodes were found by types in the NNCFGraph
INFO:nncf:Statistics of the bitwidth distribution:
┍━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┑
│ Num bits (N) │ % all parameters (layers) │ % ratio-defining parameters (layers) │
┝━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┥
│ 8 │ 100% (883 / 883) │ 100% (883 / 883) │
┕━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┙
Output()
/home/ea/work/py3.11/lib/python3.11/site-packages/nncf/quantization/algorithms/post_training/pipeline.py:87: FutureWarning: AdvancedQuantizationParameters(smooth_quant_alpha=..) is deprecated.Please, use AdvancedQuantizationParameters(smooth_quant_alphas) option with AdvancedSmoothQuantParameters(convolution=.., matmul=..) as value instead. warning_deprecated(
INFO:nncf:883 ignored nodes were found by names in the NNCFGraph
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 100 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 101 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 102 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 103 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 104 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 105 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 106 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 107 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 108 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 109 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 110 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 111 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 112 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 113 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 114 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 115 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 116 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 117 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 118 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 119 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 120 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 121 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 122 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 123 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 124 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 125 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 126 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 127 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 128 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 129 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 130 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 131 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 132 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 133 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 134 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 135 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 136 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 137 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 138 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 139 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 140 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 141 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 142 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 143 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 144 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 145 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 146 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 147 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 148 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 149 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 150 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 151 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 152 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 153 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 154 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 155 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 156 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 157 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 158 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 159 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 160 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 161 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 162 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 163 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 164 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 165 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 166 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 167 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 168 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 169 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 170 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 171 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 172 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 173 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 174 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 175 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 176 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 177 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 178 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 179 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 180 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 181 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 182 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 183 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 184 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 185 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 186 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 187 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 188 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 189 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 190 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 191 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 192 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 193 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 194 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 195 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 196 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 197 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 198 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 199 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 200 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 201 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 202 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 203 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 204 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 205 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 206 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 207 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 208 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 209 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 210 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 211 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 212 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 213 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 214 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 215 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 216 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 217 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 218 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 219 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 220 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 221 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 222 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 223 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 224 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 225 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 226 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 227 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 228 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 229 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 230 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 231 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 232 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 233 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 234 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 235 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 236 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 237 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 238 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 239 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 240 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 241 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 242 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 243 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 244 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 245 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 246 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 247 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 248 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 249 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 250 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 251 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 252 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 253 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 254 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 255 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 256 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 257 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 258 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 259 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 260 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 261 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 262 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 263 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 264 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 265 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 266 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 267 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 268 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 269 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 270 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 271 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 272 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 273 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 274 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 275 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 276 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 277 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 278 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 279 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 280 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 281 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 282 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 283 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 284 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 285 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 286 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 287 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 288 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 289 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 290 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 291 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 292 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 293 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 294 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 295 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 296 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 297 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 298 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 299 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 300 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 301 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 302 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 303 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 304 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 305 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 306 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 307 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 308 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 309 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 310 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 311 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 312 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 313 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 314 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 315 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 316 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 317 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_k_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 318 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.processor.to_v_ip/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 39 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 40 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 41 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 42 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 43 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 44 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 45 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 46 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 47 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 48 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 49 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 50 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 51 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 52 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 53 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 54 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 55 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 56 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 57 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 58 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 59 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 60 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 61 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 62 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 63 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 64 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 65 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 66 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 67 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 68 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 69 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 70 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 71 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 72 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 73 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 74 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 75 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 76 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 77 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 78 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 79 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 80 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 81 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 82 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 83 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 84 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 85 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 86 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 87 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 88 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 89 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 90 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 91 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 92 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 93 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 94 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 95 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 96 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 97 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 98 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 99 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1809 __module.unet.time_embedding.linear_1/aten::linear/MatMul
1928 __module.unet.time_embedding.linear_1/aten::linear/Add
2048 __module.unet.conv_act/aten::silu/Swish_1
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2174 __module.unet.time_embedding.linear_2/aten::linear/MatMul
2368 __module.unet.time_embedding.linear_2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 329 __module.unet.add_embedding.linear_1/aten::linear/MatMul
646 __module.unet.add_embedding.linear_1/aten::linear/Add
1032 __module.unet.conv_act/aten::silu/Swish_2
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1268 __module.unet.add_embedding.linear_2/aten::linear/MatMul
1450 __module.unet.add_embedding.linear_2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1904 __module.unet.down_blocks.0.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2021 __module.unet.down_blocks.0.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1905 __module.unet.down_blocks.0.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2022 __module.unet.down_blocks.0.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1906 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2023 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1907 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2024 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1908 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2025 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1909 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2026 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1910 __module.unet.mid_block.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2027 __module.unet.mid_block.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1911 __module.unet.mid_block.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2028 __module.unet.mid_block.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1912 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2029 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1913 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2030 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1914 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.resnets.2.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2031 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.resnets.2.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1915 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2032 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1916 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2033 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1917 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.resnets.2.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2034 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.resnets.2.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1918 __module.unet.up_blocks.2.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2035 __module.unet.up_blocks.2.resnets.0.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1919 __module.unet.up_blocks.2.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2036 __module.unet.up_blocks.2.resnets.1.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1920 __module.unet.up_blocks.2.resnets.2.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/MatMul
2037 __module.unet.up_blocks.2.resnets.2.time_emb_proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3065 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
3410 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4876 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4877 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4878 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5281 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5289 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5099 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1810 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1929 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2839 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3072 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4276 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4588 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3073 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3074 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3075 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5103 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5181 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3420 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1811 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1930 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2842 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3077 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4280 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4592 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2373 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2602 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3836 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
4269 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5176 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5177 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5178 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5297 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5306 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5255 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1812 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1931 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2843 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3078 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4283 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4595 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3079 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3080 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3081 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5104 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5182 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3428 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1813 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1932 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2846 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3083 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4287 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4599 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2378 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2607 __module.unet.down_blocks.1.attentions.1.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5256 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
5272 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5298 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5299 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5300 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5343 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5346 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5310 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1814 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1933 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2847 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3084 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4290 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4602 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3085 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3086 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3087 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5105 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5183 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3436 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1815 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1934 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2850 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3089 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4294 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4606 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3090 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3091 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3092 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5106 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5184 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3442 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1816 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1935 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2853 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3094 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4298 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4610 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3095 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3096 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3097 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5107 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5185 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3448 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1817 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1936 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2856 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3099 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4302 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4614 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3100 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3101 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3102 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5108 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5186 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3454 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1818 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1937 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2859 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3104 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4306 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4618 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3105 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3106 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3107 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5109 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5187 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3460 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1819 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1938 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2862 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3109 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4310 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4622 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3110 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3111 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3112 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5110 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5188 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3466 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1820 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1939 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2865 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3114 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4314 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4626 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3115 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3116 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3117 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5111 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5189 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3472 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1821 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1940 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2868 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3119 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4318 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4630 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3120 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3121 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3122 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5112 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5190 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3478 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1822 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1941 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2871 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3124 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4322 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4634 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3125 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3126 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3127 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5113 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5191 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3484 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1823 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1942 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2874 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3129 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4326 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4638 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2407 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2636 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5273 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
5279 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5311 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5312 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5313 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5347 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5349 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5325 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1824 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1943 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2876 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3131 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4334 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4645 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3132 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3133 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3134 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5116 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5194 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3493 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1825 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1944 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2879 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3136 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4338 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4649 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3137 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3138 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3139 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5117 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5195 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3499 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1826 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1945 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2882 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3141 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4342 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4653 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3142 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3143 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3144 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5118 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5196 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3505 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1827 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1946 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2885 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3146 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4346 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4657 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3147 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3148 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3149 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5119 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5197 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3511 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1828 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1947 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2888 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3151 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4350 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4661 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3152 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3153 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3154 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5120 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5198 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3517 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1829 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1948 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2891 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3156 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4354 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4665 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3157 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3158 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3159 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5121 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5199 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3523 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1830 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1949 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2894 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3161 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4358 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4669 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3162 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3163 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3164 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5122 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5200 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3529 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1831 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1950 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2897 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3166 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4362 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4673 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3167 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3168 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3169 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5123 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5201 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3535 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1832 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1951 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2900 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3171 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4366 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4677 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3172 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3173 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3174 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5124 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5202 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3541 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1833 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1952 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2903 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3176 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4370 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4681 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2436 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2665 __module.unet.down_blocks.2.attentions.1.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5274 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
5280 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5315 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5316 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5317 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5348 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5350 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5329 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1834 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1953 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2905 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3178 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4378 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4688 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3179 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3180 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3181 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5127 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5205 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3550 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1835 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1954 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2908 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3183 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4382 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4692 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3184 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3185 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3186 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5128 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5206 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3556 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1836 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1955 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2911 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3188 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4386 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4696 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3189 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3190 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3191 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5129 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5207 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3562 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1837 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1956 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2914 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3193 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4390 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4700 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3194 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3195 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3196 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5130 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5208 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3568 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1838 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1957 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2917 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3198 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4394 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4704 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3199 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3200 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3201 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5131 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5209 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3574 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1839 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1958 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2920 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3203 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4398 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4708 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3204 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3205 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3206 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5132 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5210 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3580 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1840 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1959 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2923 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3208 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4402 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4712 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3209 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3210 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3211 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5133 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5211 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3586 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1841 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1960 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2926 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3213 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4406 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4716 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3214 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3215 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3216 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5134 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5212 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3592 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1842 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1961 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2929 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3218 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4410 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4720 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3219 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3220 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3221 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5135 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5213 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3598 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1843 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1962 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2932 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3223 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4414 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4724 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2465 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2694 __module.unet.mid_block.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2337 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
2582 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3822 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3823 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3824 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5250 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5267 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4260 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1844 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1963 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2934 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3225 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4419 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4728 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3226 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3227 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3228 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5137 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5215 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3607 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1845 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1964 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2937 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3230 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4423 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4732 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3231 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3232 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3233 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5138 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5216 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3613 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1846 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1965 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2940 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3235 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4427 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4736 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3236 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3237 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3238 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5139 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5217 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3619 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1847 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1966 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2943 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3240 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4431 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4740 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3241 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3242 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3243 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5140 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5218 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3625 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1848 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1967 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2946 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3245 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4435 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4744 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3246 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3247 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3248 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5141 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5219 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3631 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1849 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1968 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2949 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3250 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4439 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4748 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3251 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3252 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3253 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5142 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5220 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3637 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1850 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1969 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2952 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3255 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4443 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4752 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3256 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3257 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3258 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5143 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5221 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3643 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1851 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1970 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2955 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3260 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4447 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4756 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3261 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3262 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3263 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5144 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5222 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3649 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1852 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1971 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2958 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3265 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4451 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4760 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3266 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3267 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3268 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5145 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5223 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3655 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1853 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1972 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2961 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3270 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4455 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4764 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2494 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2723 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2334 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
2580 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3817 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3818 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3819 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5249 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5266 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4256 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1854 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1973 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2962 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3271 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4458 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4767 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3272 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3273 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3274 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5146 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5224 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3663 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1855 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1974 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2965 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3276 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4462 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4771 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3277 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3278 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3279 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5147 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5225 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3669 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1856 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1975 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2968 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3281 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4466 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4775 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3282 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3283 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3284 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5148 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5226 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3675 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1857 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1976 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2971 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3286 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4470 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4779 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3287 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3288 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3289 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5149 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5227 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3681 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1858 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1977 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2974 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3291 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4474 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4783 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3292 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3293 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3294 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5150 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5228 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3687 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1859 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1978 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2977 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3296 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4478 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4787 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3297 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3298 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3299 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5151 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5229 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3693 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1860 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1979 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2980 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3301 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4482 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4791 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3302 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3303 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3304 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5152 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5230 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3699 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1861 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1980 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2983 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3306 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4486 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4795 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3307 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3308 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3309 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5153 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5231 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3705 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1862 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1981 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2986 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3311 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4490 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4799 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3312 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3313 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3314 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5154 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5232 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3711 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1863 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1982 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2989 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3316 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4494 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4803 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2523 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2752 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.1.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2331 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
2578 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3812 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3813 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3814 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5248 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5265 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4252 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1864 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1983 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2990 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3317 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4497 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4806 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3318 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3319 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3320 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5155 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5233 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3719 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1865 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1984 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2993 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3322 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4501 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4810 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3323 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3324 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3325 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5156 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5234 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3725 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1866 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1985 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2996 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3327 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4505 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4814 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.2.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3328 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3329 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3330 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5157 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5235 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3731 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1867 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1986 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2999 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3332 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4509 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4818 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.3.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3333 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3334 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3335 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5158 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5236 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3737 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1868 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1987 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3002 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3337 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4513 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4822 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.4.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3338 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3339 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3340 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5159 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5237 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3743 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1869 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1988 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3005 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3342 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4517 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4826 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.5.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3343 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3344 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3345 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5160 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5238 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3749 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1870 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1989 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3008 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3347 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4521 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4830 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.6.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3348 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3349 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3350 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5161 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5239 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3755 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1871 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1990 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3011 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3352 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4525 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4834 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.7.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3353 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3354 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3355 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5162 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5240 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3761 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1872 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1991 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3014 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3357 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4529 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4838 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.8.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3358 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3359 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3360 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5163 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5241 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3767 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1873 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1992 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3017 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3362 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4533 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4842 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.9.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2552 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2781 __module.unet.up_blocks.0.attentions.2.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2328 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
2576 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3807 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3808 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3809 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5247 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5264 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4248 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1874 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1993 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3018 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3363 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4536 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4845 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3364 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3365 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3366 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5164 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5242 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3775 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1875 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1994 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3021 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3368 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4540 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4849 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2557 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2786 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.0.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2325 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
2574 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3802 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3803 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3804 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5246 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5263 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4244 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1876 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1995 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3022 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3369 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4543 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4852 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3370 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3371 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3372 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5165 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5243 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3783 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1877 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1996 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3025 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3374 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4547 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4856 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2562 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2791 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.1.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2322 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.proj_in/aten::linear/MatMul
2572 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.proj_in/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3797 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3798 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3799 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5245 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5262 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4240 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1878 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1997 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3026 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3375 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4550 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4859 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.0.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3376 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_k/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3377 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3378 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_v/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 5166 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
5244 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn1.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3791 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_q/aten::linear/MatMul
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 1879 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/MatMul
1998 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.attn2.to_out.0/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 3029 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/MatMul
3380 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.0.proj/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 4554 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/MatMul
4863 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.transformer_blocks.1.ff.net.2/aten::linear/Add
INFO:nncf:Not adding activation input quantizer for operation: 2567 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.proj_out/aten::linear/MatMul
2796 __module.unet.up_blocks.1.attentions.2.proj_out/aten::linear/Add
Output()
Output()
Quantizing of the Text Encoders and VAE Decoder does not
significantly improve inference performance but can lead to a
substantial degradation of accuracy. The weight compression will be
applied to footprint reduction.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
ov_int8_text_encoder_path = MODELS_DIR / 'text_encoder_optimized.xml'
ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path = MODELS_DIR / 'text_encoder_2_optimized.xml'
ov_int8_vae_decoder_path = MODELS_DIR / 'vae_decoder_optimized.xml'
if not ov_int8_text_encoder_path.exists():
text_encoder = core.read_model(ov_text_encoder_path)
compressed_text_encoder = nncf.compress_weights(text_encoder)
ov.save_model(compressed_text_encoder, ov_int8_text_encoder_path)
if not ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path.exists():
text_encoder_2 = core.read_model(ov_text_encoder_2_path)
compressed_text_encoder_2 = nncf.compress_weights(text_encoder_2)
ov.save_model(compressed_text_encoder_2, ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path)
if not ov_int8_vae_decoder_path.exists():
vae_decoder = core.read_model(ov_vae_decoder_path)
compressed_vae_decoder = nncf.compress_weights(vae_decoder)
ov.save_model(compressed_vae_decoder, ov_int8_vae_decoder_path)
INFO:nncf:Statistics of the bitwidth distribution:
┍━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┑
│ Num bits (N) │ % all parameters (layers) │ % ratio-defining parameters (layers) │
┝━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┥
│ 8 │ 100% (74 / 74) │ 100% (74 / 74) │
┕━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┙
Output()
INFO:nncf:Statistics of the bitwidth distribution:
┍━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┑
│ Num bits (N) │ % all parameters (layers) │ % ratio-defining parameters (layers) │
┝━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┥
│ 8 │ 100% (195 / 195) │ 100% (195 / 195) │
┕━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┙
Output()
INFO:nncf:Statistics of the bitwidth distribution:
┍━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┑
│ Num bits (N) │ % all parameters (layers) │ % ratio-defining parameters (layers) │
┝━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┥
│ 8 │ 100% (40 / 40) │ 100% (40 / 40) │
┕━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┙
Output()
Let’s compare the images generated by the original and optimized pipelines.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
int8_pipe = create_ov_pipe(
ov_int8_text_encoder_path,
ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path,
ov_image_proj_encoder_path,
ov_int8_controlnet_path,
ov_int8_unet_path,
ov_int8_vae_decoder_path,
MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer",
MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer_2",
MODELS_DIR / "scheduler"
)
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
int8_image = int8_pipe(
prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
num_inference_steps=4,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
guidance_scale=0.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(1749781188)
).images[0]
0%| | 0/4 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def visualize_results(orig_img: Image, optimized_img: Image):
"""
Helper function for results visualization
Parameters:
orig_img (Image.Image): generated image using FP16 models
optimized_img (Image.Image): generated image using quantized models
Returns:
fig (matplotlib.pyplot.Figure): matplotlib generated figure contains drawing result
"""
orig_title = "FP16 pipeline"
control_title = "INT8 pipeline"
figsize = (20, 20)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=figsize, sharex="all", sharey="all")
list_axes = list(axs.flat)
for a in list_axes:
a.set_xticklabels([])
a.set_yticklabels([])
a.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
a.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
a.grid(False)
list_axes[0].imshow(np.array(orig_img))
list_axes[1].imshow(np.array(optimized_img))
list_axes[0].set_title(orig_title, fontsize=15)
list_axes[1].set_title(control_title, fontsize=15)
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.01, hspace=0.01)
fig.tight_layout()
return fig
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
visualize_results(image, int8_image)
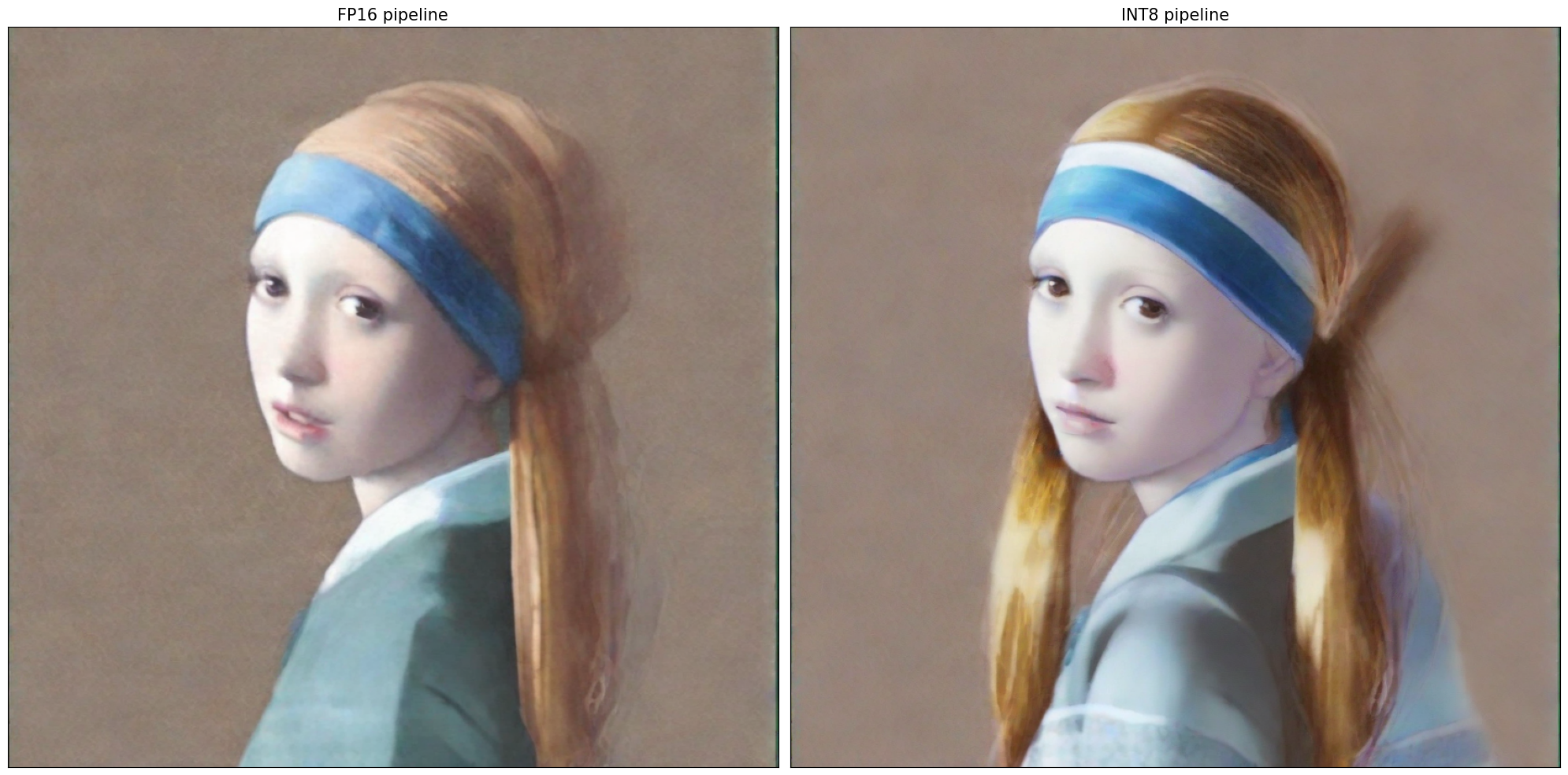

Compare model file sizes#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
fp16_model_paths = [ov_unet_path, ov_controlnet_path, ov_text_encoder_path, ov_text_encoder_2_path, ov_vae_decoder_path]
int8_model_paths = [ov_int8_unet_path, ov_int8_controlnet_path, ov_int8_text_encoder_path, ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path, ov_int8_vae_decoder_path]
for fp16_path, int8_path in zip(fp16_model_paths, int8_model_paths):
fp16_ir_model_size = fp16_path.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size
int8_model_size = int8_path.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size
print(f"{fp16_path.stem} compression rate: {fp16_ir_model_size / int8_model_size:.3f}")
unet compression rate: 1.995
controlnet compression rate: 1.992
text_encoder compression rate: 1.992
text_encoder_2 compression rate: 1.995
vae_decoder compression rate: 1.997
Compare inference time of the FP16 and INT8 pipelines#
To measure the inference performance of the FP16 and INT8
pipelines, we use mean inference time on 5 samples.
Please select below whether you would like to run inference time comparison.
NOTE: For the most accurate performance estimation, it is recommended to run
benchmark_appin a terminal/command prompt after closing other applications.
NOTE: This is a memory consuming step because two pipelines need to be loaded at the same time.
import ipywidgets as widgets
run_inference_time_comparison = widgets.Checkbox(
value=False,
description="Inference time comparison",
disabled=not to_quantize.value,
)
run_inference_time_comparison
%%skip (not $to_quantize.value or not $run_inference_time_comparison.value)
import time
def calculate_inference_time(pipeline, face_info):
inference_time = []
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=True)
for i in range(5):
face_emb, face_kps = face_info[i]
prompt = np.random.choice(prompts)
negative_prompt = np.random.choice(negative_prompts)
start = time.perf_counter()
_ = pipeline(
prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
num_inference_steps=4,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
guidance_scale=0.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(1749781188)
)
end = time.perf_counter()
delta = end - start
inference_time.append(delta)
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=False)
return np.mean(inference_time)
%%skip (not $to_quantize.value or not $run_inference_time_comparison.value)
# Load full precision pipeline
ov_pipe = create_ov_pipe(
ov_text_encoder_path,
ov_text_encoder_2_path,
ov_image_proj_encoder_path,
ov_controlnet_path,
ov_unet_path,
ov_vae_decoder_path,
MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer",
MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer_2",
MODELS_DIR / "scheduler",
)
%%skip (not $to_quantize.value or not $run_inference_time_comparison.value)
fp_latency = calculate_inference_time(ov_pipe, face_info)
print(f"FP16 pipeline: {fp_latency:.3f} seconds")
int8_latency = calculate_inference_time(int8_pipe, face_info)
print(f"INT8 pipeline: {int8_latency:.3f} seconds")
print(f"Performance speed-up: {fp_latency / int8_latency:.3f}")
FP16 pipeline: 20.018 seconds
INT8 pipeline: 20.372 seconds
Performance speed-up: 0.983
Interactive demo#
Please select below whether you would like to use the quantized models to launch the interactive demo.
import ipywidgets as widgets
quantized_models_present = int8_pipe is not None
use_quantized_models = widgets.Checkbox(
value=quantized_models_present,
description="Use quantized models",
disabled=not quantized_models_present,
)
use_quantized_models
Checkbox(value=True, description='Use quantized models')
if use_quantized_models.value:
if ov_pipe is not None:
del ov_pipe
gc.collect()
elif ov_pipe is None:
ov_pipe = create_ov_pipe(
ov_text_encoder_path,
ov_text_encoder_2_path,
ov_image_proj_encoder_path,
ov_controlnet_path,
ov_unet_path,
ov_vae_decoder_path,
MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer",
MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer_2",
MODELS_DIR / "scheduler",
)
import gradio as gr
from typing import Tuple
import PIL
import shutil
orig_style_template_path = Path("InstantID/gradio_demo/style_template.py")
style_template_path = Path(orig_style_template_path.name)
if not style_template_path.exists():
shutil.copy(orig_style_template_path, style_template_path)
from style_template import styles
# global variables
DEFAULT_STYLE_NAME = "Watercolor"
pipeline = int8_pipe if use_quantized_models.value else ov_pipe
def convert_from_cv2_to_image(img: np.ndarray) -> PIL.Image:
return Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
def convert_from_image_to_cv2(img: PIL.Image) -> np.ndarray:
return cv2.cvtColor(np.array(img), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
def resize_img(
input_image,
max_side=1024,
min_side=800,
size=None,
pad_to_max_side=False,
mode=PIL.Image.BILINEAR,
base_pixel_number=64,
):
w, h = input_image.size
if size is not None:
w_resize_new, h_resize_new = size
else:
ratio = min_side / min(h, w)
w, h = round(ratio * w), round(ratio * h)
ratio = max_side / max(h, w)
input_image = input_image.resize([round(ratio * w), round(ratio * h)], mode)
w_resize_new = (round(ratio * w) // base_pixel_number) * base_pixel_number
h_resize_new = (round(ratio * h) // base_pixel_number) * base_pixel_number
input_image = input_image.resize([w_resize_new, h_resize_new], mode)
if pad_to_max_side:
res = np.ones([max_side, max_side, 3], dtype=np.uint8) * 255
offset_x = (max_side - w_resize_new) // 2
offset_y = (max_side - h_resize_new) // 2
res[offset_y : offset_y + h_resize_new, offset_x : offset_x + w_resize_new] = np.array(input_image)
input_image = Image.fromarray(res)
return input_image
def apply_style(style_name: str, positive: str, negative: str = "") -> Tuple[str, str]:
p, n = styles.get(style_name, styles[DEFAULT_STYLE_NAME])
return p.replace("{prompt}", positive), n + " " + negative
def generate_image(
face_image,
pose_image,
prompt,
negative_prompt,
style_name,
num_steps,
identitynet_strength_ratio,
guidance_scale,
seed,
progress=gr.Progress(track_tqdm=True),
):
if prompt is None:
prompt = "a person"
# apply the style template
prompt, negative_prompt = apply_style(style_name, prompt, negative_prompt)
# face_image = load_image(face_image_path)
face_image = resize_img(face_image)
face_image_cv2 = convert_from_image_to_cv2(face_image)
height, width, _ = face_image_cv2.shape
# Extract face features
face_info = app.get(face_image_cv2)
if len(face_info) == 0:
raise gr.Error("Cannot find any face in the image! Please upload another person image")
face_info = sorted(
face_info,
key=lambda x: (x["bbox"][2] - x["bbox"][0]) * x["bbox"][3] - x["bbox"][1],
)[
-1
] # only use the maximum face
face_emb = face_info["embedding"]
face_kps = draw_kps(convert_from_cv2_to_image(face_image_cv2), face_info["kps"])
if pose_image is not None:
# pose_image = load_image(pose_image_path)
pose_image = resize_img(pose_image)
pose_image_cv2 = convert_from_image_to_cv2(pose_image)
face_info = app.get(pose_image_cv2)
if len(face_info) == 0:
raise gr.Error("Cannot find any face in the reference image! Please upload another person image")
face_info = face_info[-1]
face_kps = draw_kps(pose_image, face_info["kps"])
width, height = face_kps.size
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(seed)
print("Start inference...")
print(f"[Debug] Prompt: {prompt}, \n[Debug] Neg Prompt: {negative_prompt}")
images = pipeline(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
controlnet_conditioning_scale=float(identitynet_strength_ratio),
num_inference_steps=num_steps,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
height=height,
width=width,
generator=generator,
).images
return images[0]
if not Path("gradio_helper.py").exists():
r = requests.get(url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/notebooks/instant-id/gradio_helper.py")
open("gradio_helper.py", "w").write(r.text)
from gradio_helper import make_demo
demo = make_demo(fn=generate_image)
try:
demo.launch(debug=False)
except Exception:
demo.launch(share=True, debug=False)
# if you are launching remotely, specify server_name and server_port
# demo.launch(server_name='your server name', server_port='server port in int')
# Read more in the docs: https://gradio.app/docs/
# please uncomment and run this cell for stopping gradio interface
# demo.close()