Hello Image Segmentation#
This Jupyter notebook can be launched on-line, opening an interactive environment in a browser window. You can also make a local installation. Choose one of the following options:
A very basic introduction to using segmentation models with OpenVINO™.
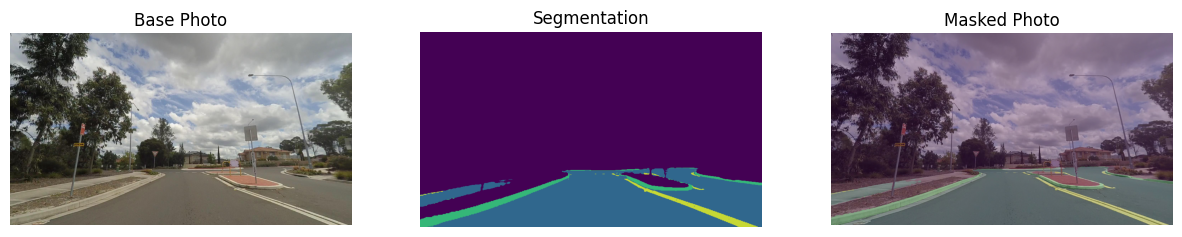
In this tutorial, a pre-trained road-segmentation-adas-0001 model from the Open Model Zoo is used. ADAS stands for Advanced Driver Assistance Services. The model recognizes four classes: background, road, curb and mark.
Table of contents:
Installation Instructions#
This is a self-contained example that relies solely on its own code.
We recommend running the notebook in a virtual environment. You only need a Jupyter server to start. For details, please refer to Installation Guide.
# Install required packages
%pip install -q "openvino>=2023.1.0" opencv-python tqdm "matplotlib>=3.4"
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Imports#
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import openvino as ov
# Fetch `notebook_utils` module
import requests
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/notebook_utils.py",
)
open("notebook_utils.py", "w").write(r.text)
from notebook_utils import segmentation_map_to_image, download_file, device_widget
Download model weights#
from pathlib import Path
base_model_dir = Path("./model").expanduser()
model_name = "road-segmentation-adas-0001"
model_xml_name = f"{model_name}.xml"
model_bin_name = f"{model_name}.bin"
model_xml_path = base_model_dir / model_xml_name
if not model_xml_path.exists():
model_xml_url = (
"https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/open_model_zoo/2023.0/models_bin/1/road-segmentation-adas-0001/FP32/road-segmentation-adas-0001.xml"
)
model_bin_url = (
"https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/open_model_zoo/2023.0/models_bin/1/road-segmentation-adas-0001/FP32/road-segmentation-adas-0001.bin"
)
download_file(model_xml_url, model_xml_name, base_model_dir)
download_file(model_bin_url, model_bin_name, base_model_dir)
else:
print(f"{model_name} already downloaded to {base_model_dir}")
road-segmentation-adas-0001.xml: 0%| | 0.00/389k [00:00<?, ?B/s]
road-segmentation-adas-0001.bin: 0%| | 0.00/720k [00:00<?, ?B/s]
Select inference device#
select device from dropdown list for running inference using OpenVINO
device = device_widget()
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
Load the Model#
core = ov.Core()
model = core.read_model(model=model_xml_path)
compiled_model = core.compile_model(model=model, device_name=device.value)
input_layer_ir = compiled_model.input(0)
output_layer_ir = compiled_model.output(0)
Load an Image#
A sample image from the Mapillary Vistas dataset is provided.
# Download the image from the openvino_notebooks storage
image_filename = download_file(
"https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/openvino_notebooks/data/data/image/empty_road_mapillary.jpg",
directory="data",
)
# The segmentation network expects images in BGR format.
image = cv2.imread(str(image_filename))
rgb_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image_h, image_w, _ = image.shape
# N,C,H,W = batch size, number of channels, height, width.
N, C, H, W = input_layer_ir.shape
# OpenCV resize expects the destination size as (width, height).
resized_image = cv2.resize(image, (W, H))
# Reshape to the network input shape.
input_image = np.expand_dims(resized_image.transpose(2, 0, 1), 0)
plt.imshow(rgb_image)
empty_road_mapillary.jpg: 0%| | 0.00/227k [00:00<?, ?B/s]
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f620b9afe50>
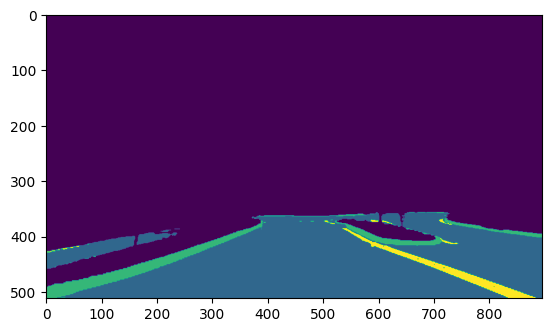
Do Inference#
# Run the inference.
result = compiled_model([input_image])[output_layer_ir]
# Prepare data for visualization.
segmentation_mask = np.argmax(result, axis=1)
plt.imshow(segmentation_mask.transpose(1, 2, 0))
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f61bc2f8a00>
Prepare Data for Visualization#
# Define colormap, each color represents a class.
colormap = np.array([[68, 1, 84], [48, 103, 141], [53, 183, 120], [199, 216, 52]])
# Define the transparency of the segmentation mask on the photo.
alpha = 0.3
# Use function from notebook_utils.py to transform mask to an RGB image.
mask = segmentation_map_to_image(segmentation_mask, colormap)
resized_mask = cv2.resize(mask, (image_w, image_h))
# Create an image with mask.
image_with_mask = cv2.addWeighted(resized_mask, alpha, rgb_image, 1 - alpha, 0)
Visualize data#
# Define titles with images.
data = {"Base Photo": rgb_image, "Segmentation": mask, "Masked Photo": image_with_mask}
# Create a subplot to visualize images.
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, len(data.items()), figsize=(15, 10))
# Fill the subplot.
for ax, (name, image) in zip(axs, data.items()):
ax.axis("off")
ax.set_title(name)
ax.imshow(image)
# Display an image.
plt.show(fig)