CLIP model with Jina CLIP and OpenVINO#
This Jupyter notebook can be launched after a local installation only.
jina-clip-v1 is a state-of-the-art English multimodal(text-image) embedding model trained by Jina AI. It bridges the gap between traditional text embedding models, which excel in text-to-text retrieval but are incapable of cross-modal tasks, and models that effectively align image and text embeddings but are not optimized for text-to-text retrieval. jina-clip-v1 offers robust performance in both domains. Its dual capability makes it an excellent tool for multimodal retrieval-augmented generation (MuRAG) applications, allowing seamless text-to-text and text-to-image searches within a single model. jina-clip-v1 can be used for a variety of multimodal applications, such as: image search by describing them in text, multimodal question answering, multimodal content generation. Jina AI has also provided the Embeddings API as an easy-to-use interface for working with jina-clip-v1 and their other embedding models.
In this notebook we will load the model with Hugging Face Transformers, convert it to OpenVINO IR format, optimize it with NNCF and show the life demo.
Table of contents:
Installation Instructions#
This is a self-contained example that relies solely on its own code.
We recommend running the notebook in a virtual environment. You only need a Jupyter server to start. For details, please refer to Installation Guide.
Prerequisites#
%pip install -q "openvino>=2024.2.0" "datasets>=2.20" "nncf>=2.11.0"
%pip install -q --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu "gradio>=4.19" "pillow" "einops" "timm" "transformers[torch]>=4.39" "torch>=2.1" "matplotlib>=3.4" "typing_extensions>=4.9"
Instantiate model#
Let’s load the
jinaai/jina-clip-v1
with Hugging Face Transformers. We creates PyTorch model class instance
with AutoModel, load and initialize it with model configuration and
weights, using from_pretrained method.
from transformers import AutoModel
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("jinaai/jina-clip-v1", trust_remote_code=True)
Prepare input data#
The model can encode meaningful sentences in English as text input. Image could be provided to model as local file path, URLs or directly passing in the PIL.Image objects.
from PIL import Image
import requests
from pathlib import Path
if not Path("notebook_utils.py").exists():
# image input data
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/notebook_utils.py",
)
open("notebook_utils.py", "w").write(r.text)
from notebook_utils import download_file, device_widget, quantization_widget
if not Path("data/furseal.png").exists():
download_file(
"https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/assets/29454499/3f779fc1-c1b2-4dec-915a-64dae510a2bb",
"furseal.png",
directory="data",
)
img_furseal = Image.open("./data/furseal.png")
if not Path("data/coco.jpg").exists():
image_path = download_file(
"https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/1c66a05d-7442-45c2-a34c-bb08b95af7a6",
"coco.jpg",
directory="data",
)
img_coco = Image.open("./data/coco.jpg")
IMAGE_INPUTS = [img_furseal, img_coco]
# text input data
TEXT_INPUTS = ["Seal", "Cobra", "Rat", "Penguin", "Dog"]
data/furseal.png: 0%| | 0.00/2.55M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
data/coco.jpg: 0%| | 0.00/202k [00:00<?, ?B/s]
from typing import List
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from scipy.special import softmax
def calc_simularity_softmax(embeddings1, embeddings2, apply_softmax=True):
simularity = []
for emb1 in embeddings1:
temp_simularity = []
for emb2 in embeddings2:
temp_simularity.append(emb1 @ emb2)
temp_simularity = softmax(temp_simularity) if apply_softmax else temp_simularity
simularity.append(temp_simularity)
return simularity
def visionize_result(image: Image, labels: List[str], probs: np.ndarray, top: int = 5):
"""
Utility function for visionization classification results
params:
image: input image
labels: list of classification labels
probs: model predicted softmaxed probabilities for each label
top: number of the highest probability results for visionization
returns:
None
"""
plt.figure(figsize=(64, 64))
top_labels = np.argsort(-probs)[: min(top, probs.shape[0])]
top_probs = probs[top_labels]
plt.subplot(8, 8, 1)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(8, 8, 2)
y = np.arange(top_probs.shape[-1])
plt.grid()
plt.barh(y, top_probs)
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
plt.gca().set_axisbelow(True)
plt.yticks(y, [labels[index] for index in top_labels])
plt.xlabel("simularity")
We will use tokenizer and preprocess from jina-clip model. We will take
tokenizer to encode text input data using model.get_tokenizer()
and take preprocess for image data using model.get_preprocess().
tokenizer = model.get_tokenizer()
tokenizer_kwargs = dict()
tokenizer_kwargs["padding"] = "max_length"
tokenizer_kwargs["max_length"] = 512
tokenizer_kwargs["truncation"] = True
text_inputs = tokenizer(
TEXT_INPUTS,
return_tensors="pt",
**tokenizer_kwargs,
).to("cpu")
processor = model.get_preprocess()
vision_inputs = processor(images=IMAGE_INPUTS, return_tensors="pt")
Run PyTorch model inference#
text_embeddings = model.text_model(text_inputs["input_ids"])
image_embeddings = model.vision_model(vision_inputs["pixel_values"])
res = calc_simularity_softmax(image_embeddings.detach().numpy(), text_embeddings.detach().numpy())
visionize_result(img_furseal, TEXT_INPUTS, np.array(res[0]))
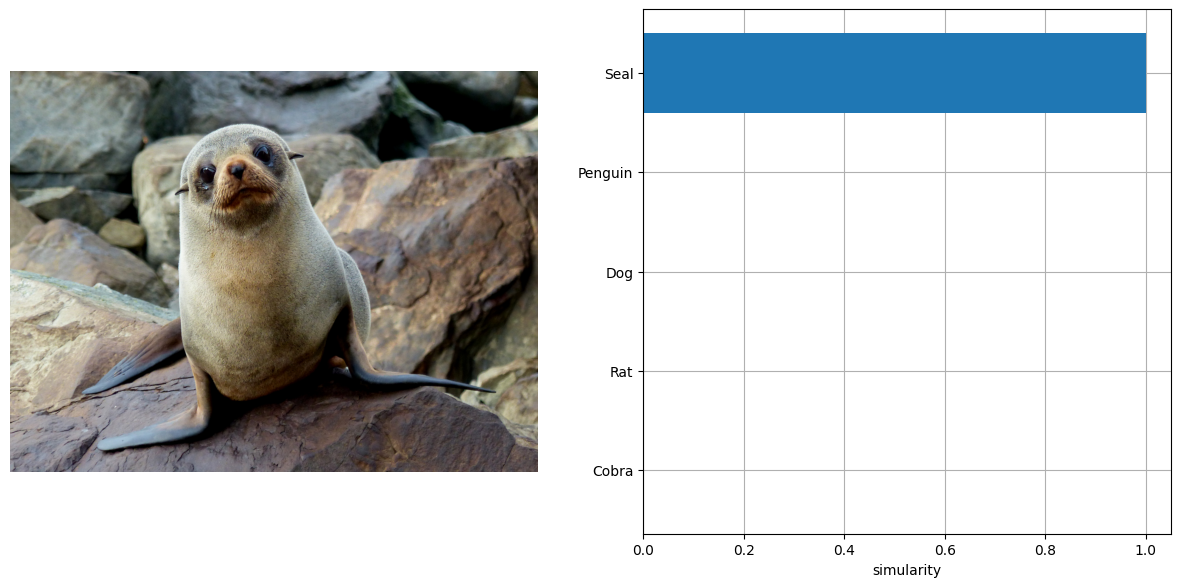
Run OpenVINO model inference#
Convert Model to OpenVINO IR format#
OpenVINO supports PyTorch models via conversion to OpenVINO Intermediate
Representation (IR). OpenVINO model conversion API should be used for
these purposes. ov.convert_model function accepts original PyTorch
model instance and example input for tracing and returns ov.Model
representing this model in OpenVINO framework. Converted model can be
used for saving on disk using ov.save_model function or directly
loading on device using core.complie_model.
import openvino as ov
from pathlib import Path
core = ov.Core()
fp16_text_model_path = Path("jina-clip-text_v1_fp16.xml")
if not fp16_text_model_path.exists():
ov_text_model = ov.convert_model(model.text_model, example_input=text_inputs["input_ids"])
ov.save_model(ov_text_model, fp16_text_model_path)
fp16_vision_model_path = Path("jina-clip-vision_v1_fp16.xml")
if not fp16_vision_model_path.exists():
ov_vision_model = ov.convert_model(model.vision_model, example_input=vision_inputs["pixel_values"])
ov.save_model(ov_vision_model, fp16_vision_model_path)
Select inference device#
For starting work, please select inference device from dropdown list.
device = device_widget()
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
Compile model and run inference#
compiled_text_model = core.compile_model(fp16_text_model_path, device.value)
compiled_vision_model = core.compile_model(fp16_vision_model_path, device.value)
text_ov_res = compiled_text_model(text_inputs["input_ids"])
vis_ov_res = compiled_vision_model(vision_inputs["pixel_values"])
res = calc_simularity_softmax(vis_ov_res[0], text_ov_res[0])
visionize_result(img_furseal, TEXT_INPUTS, np.array(res[0]))
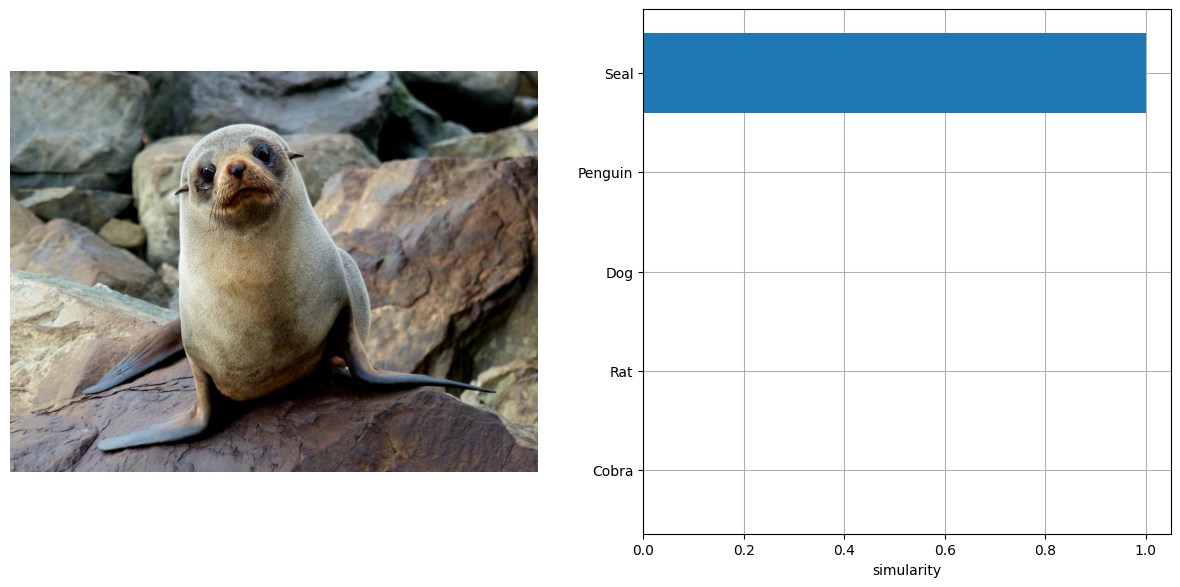
Quantize model to INT8 using NNCF#
Lets speed up the model by applying 8-bit post-training quantization
from NNCF (Neural Network
Compression Framework) and infer quantized model via OpenVINO™ Toolkit.
NNCF enables
post-training quantization by adding quantization layers into model
graph and then using a subset of the training dataset to initialize the
parameters of these additional quantization layers. Quantized operations
are executed in INT8 instead of FP32/FP16 making model
inference faster. The optimization process contains the following steps:
Prepare quantization dataset
Quantize the converted OpenVINO model with NNCF with
nncf.quantize().Save the
INT8model usingopenvino.save_model()function.Compare model size of converted and quantized models.
Compare performance of converted and quantized models.
Note: quantization process may require additional time and memory for performing. You can disable it using widget below:
to_quantize = quantization_widget()
to_quantize
Checkbox(value=True, description='Quantization')
if not Path("skip_kernel_extension.py").exists():
# Fetch `skip_kernel_extension` module
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/skip_kernel_extension.py",
)
open("skip_kernel_extension.py", "w").write(r.text)
int8_text_model_path = Path("jina-clip-text_v1_int8.xml")
int8_vision_model_path = Path("jina-clip-vision_v1_int8.xml")
%load_ext skip_kernel_extension
Prepare datasets#
The Conceptual Captions dataset consisting of ~3.3M images annotated with captions is used to quantize model.
Dataset with text data#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import torch
from datasets import load_dataset
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
import requests
from io import BytesIO
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning)
def check_text_data(data):
"""
Check if the given data is text-based.
"""
if isinstance(data, str):
return True
if isinstance(data, list):
return all(isinstance(x, str) for x in data)
return False
def collate_fn_text(example, text_column="caption"):
"""
Preprocesses an example by loading and transforming text data.
Checks if the text data in the example is valid by calling the `check_text_data` function.
If there is any error during the download process, returns None.
Returns the preprocessed inputs with transformed image and text data.
"""
assert len(example) == 1
example = example[0]
if not check_text_data(example[text_column]):
raise ValueError("Text data is not valid")
text_input = tokenizer(
example[text_column],
return_tensors='pt',
**tokenizer_kwargs)
return text_input
def prepare_calibration_data_text(dataloader, init_steps):
"""
This function prepares calibration data from a dataloader for a specified number of initialization steps.
It iterates over the dataloader, fetching batches and storing the relevant data.
"""
data = []
print(f"Fetching {init_steps} samples for the initialization...")
with tqdm(total=init_steps) as pbar:
for batch in dataloader:
if len(data) == init_steps:
break
if batch:
pbar.update(1)
with torch.no_grad():
data.append(batch["input_ids"].to("cpu"))
return data
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import logging
import nncf
if not int8_text_model_path.exists():
dataset = load_dataset("google-research-datasets/conceptual_captions", trust_remote_code=True)
train_dataset = dataset["train"].shuffle(seed=42)
dataloader_text = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, collate_fn=collate_fn_text, batch_size=1)
calibration_data_text = prepare_calibration_data_text(dataloader_text, 50)
INFO:nncf:NNCF initialized successfully. Supported frameworks detected: torch, openvino
Fetching 50 samples for the initialization...
0%| | 0/50 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Dataset with image data#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
def get_pil_from_url(url):
"""
Downloads and converts an image from a URL to a PIL Image object.
"""
response = requests.get(url, verify=False, timeout=20)
image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content))
return image.convert("RGB")
def collate_fn_vision(example, image_column="image_url"):
"""
Preprocesses an example by loading and transforming image data.
Downloads the image specified by the URL in the image_column by calling the `get_pil_from_url` function.
If there is any error during the download process, returns None.
Returns the preprocessed inputs with transformed image and text data.
"""
assert len(example) == 1
example = example[0]
url = example[image_column]
try:
image = get_pil_from_url(url)
h, w = image.size
if h == 1 or w == 1:
return None
except Exception:
return None
vision_input = processor(images=[image])
return vision_input
def prepare_calibration_data_vis(dataloader, init_steps):
"""
This function prepares calibration data from a dataloader for a specified number of initialization steps.
It iterates over the dataloader, fetching batches and storing the relevant data.
"""
data = []
print(f"Fetching {init_steps} samples for the initialization...")
with tqdm(total=init_steps) as pbar:
for batch in dataloader:
if len(data) == init_steps:
break
if batch:
pbar.update(1)
with torch.no_grad():
data.append(batch["pixel_values"].to("cpu"))
return data
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not int8_vision_model_path.exists():
dataset = load_dataset("google-research-datasets/conceptual_captions", trust_remote_code=True)
train_dataset = dataset["train"].shuffle(seed=42)
dataloader_vis = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, collate_fn=collate_fn_vision, batch_size=1)
calibration_data_vision = prepare_calibration_data_vis(dataloader_vis, 50)
Fetching 50 samples for the initialization...
0%| | 0/50 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Perform quantization#
Create a quantized model from the pre-trained FP16 model.
NOTE: Quantization is time and memory consuming operation. Running quantization code below may take a long time.
Quantization of text model#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not int8_text_model_path.exists():
if len(calibration_data_text) == 0:
raise RuntimeError(
'Calibration dataset is empty. Please check internet connection and try to download images manually.'
)
ov_model_text = core.read_model(fp16_text_model_path)
calibration_dataset = nncf.Dataset(calibration_data_text)
quantized_model = nncf.quantize(
model=ov_model_text,
calibration_dataset=calibration_dataset
)
ov.save_model(quantized_model, int8_text_model_path)
Quantization of image model#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not int8_vision_model_path.exists():
if len(calibration_data_vision) == 0:
raise RuntimeError(
'Calibration dataset is empty. Please check internet connection and try to download images manually.'
)
ov_model_vision = core.read_model(fp16_vision_model_path)
calibration_dataset = nncf.Dataset(calibration_data_vision)
quantized_model = nncf.quantize(
model=ov_model_vision,
calibration_dataset=calibration_dataset
)
ov.save_model(quantized_model, int8_vision_model_path)
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
compiled_text_model_int8 = core.compile_model(int8_text_model_path, device.value)
compiled_vision_model_int8 = core.compile_model(int8_vision_model_path, device.value)
text_ov_res_int8 = compiled_text_model_int8(text_inputs["input_ids"])
vis_ov_res_int8 = compiled_vision_model_int8(vision_inputs["pixel_values"])
res = calc_simularity_softmax(vis_ov_res_int8[0], text_ov_res_int8[0])
visionize_result(img_furseal, TEXT_INPUTS, np.array(res[0]))
Compare File Size#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
from pathlib import Path
fp16_ir_model_size = Path(fp16_text_model_path).with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024 / 1024
quantized_model_size = Path(int8_text_model_path).with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024 / 1024
print(
f"Text model: FP16 model size - {fp16_ir_model_size:.2f} MB; INT8 model size - {quantized_model_size:.2f} MB; Model compression rate: {fp16_ir_model_size / quantized_model_size:.3f}"
)
fp16_ir_model_size = Path(fp16_vision_model_path).with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024 / 1024
quantized_model_size = Path(int8_vision_model_path).with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024 / 1024
print(
f"Vision model: FP16 model size - {fp16_ir_model_size:.2f} MB; INT8 model size - {quantized_model_size:.2f} MB; Model compression rate: {fp16_ir_model_size / quantized_model_size:.3f}"
)
Text model: FP16 model size - 266.88 MB; INT8 model size - 136.98 MB; Model compression rate: 1.948
Vision model: FP16 model size - 163.83 MB; INT8 model size - 82.64 MB; Model compression rate: 1.983
Compare inference time of the FP16 IR and quantized models#
To measure the inference performance of the FP16 and INT8
models, we use median inference time on calibration dataset. So we can
approximately estimate the speed up of the dynamic quantized models.
NOTE: For the most accurate performance estimation, it is recommended to run
benchmark_appin a terminal/command prompt after closing other applications with static shapes.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import time
def calculate_inference_time(model_path, calibration_data):
model = core.compile_model(model_path, device.value)
inference_time = []
for batch in calibration_data:
start = time.perf_counter()
_ = model(batch)[0]
end = time.perf_counter()
delta = end - start
inference_time.append(delta)
return np.median(inference_time)
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
fp16_latency = calculate_inference_time(fp16_text_model_path, calibration_data_text)
int8_latency = calculate_inference_time(int8_text_model_path, calibration_data_text)
print(f"Performance speed up for text model: {fp16_latency / int8_latency:.3f}")
fp16_latency = calculate_inference_time(fp16_vision_model_path, calibration_data_vision)
int8_latency = calculate_inference_time(int8_vision_model_path, calibration_data_vision)
print(f"Performance speed up for vision model: {fp16_latency / int8_latency:.3f}")
Performance speed up for text model: 1.610
Performance speed up for vision model: 1.489
Gradio demo#
You can provide your own image and comma-separated list of labels for zero-shot classification.
Feel free to upload an image, using the file upload window and type
label names into the text field, using comma as the separator (for
example, cat,dog,bird)
core = ov.Core()
compiled_text_model_int8 = None
compiled_vision_model_int8 = None
if Path(int8_text_model_path).exists() and Path(int8_vision_model_path).exists():
compiled_text_model_int8 = core.compile_model(int8_text_model_path, device.value)
compiled_vision_model_int8 = core.compile_model(int8_vision_model_path, device.value)
compiled_text_model_f16 = core.compile_model(fp16_text_model_path, device.value)
compiled_vision_model_f16 = core.compile_model(fp16_vision_model_path, device.value)
def image_text_sim(text, image, quantized_model):
compiled_text_model = compiled_text_model_int8 if quantized_model else compiled_text_model_f16
text = text.split(",")
text_inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt", **tokenizer_kwargs)
emb1_res = compiled_text_model(text_inputs["input_ids"])
compiled_vision_model = compiled_vision_model_int8 if quantized_model else compiled_vision_model_f16
vision_input = processor(images=[image])
emb2_res = compiled_vision_model(vision_input["pixel_values"])
text_description = "Simularity: "
simularity = calc_simularity_softmax(emb2_res[0], emb1_res[0], False)
if len(text) == 1:
text_description += f"{simularity[0]}"
else:
simularity_text = "\n".join([f"{text[i]} {sim:.4f}" for i, sim in enumerate(simularity[0])])
text_description += f"\n{simularity_text}"
return text_description
def text_text_sim(text1, text2, quantized_model):
compiled_text_model = compiled_text_model_int8 if quantized_model else compiled_text_model_f16
text_inputs = tokenizer(text1, return_tensors="pt", **tokenizer_kwargs)
emb1_res = compiled_text_model(text_inputs["input_ids"])
text_inputs = tokenizer(text2, return_tensors="pt", **tokenizer_kwargs)
emb2_res = compiled_text_model(text_inputs["input_ids"])
return f"Simularity: {calc_simularity_softmax(emb1_res[0], emb2_res[0], False)[0][0]:.4f}"
def image_image_sim(image1, image2, quantized_model):
compiled_vision_model = compiled_vision_model_int8 if quantized_model else compiled_vision_model_f16
vision_input = processor(images=[image1])
emb1_res = compiled_vision_model(vision_input["pixel_values"])
vision_input = processor(images=[image2])
emb2_res = compiled_vision_model(vision_input["pixel_values"])
return f"Simularity: {calc_simularity_softmax(emb1_res[0], emb2_res[0], False)[0][0]:.4f}"
if not Path("gradio_helper.py").exists():
r = requests.get(url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/notebooks/jina-clip/gradio_helper.py")
open("gradio_helper.py", "w").write(r.text)
from gradio_helper import make_demo
model_choice_visible = Path(int8_text_model_path).exists() and Path(int8_vision_model_path).exists()
demo = make_demo(image_text_fn=image_text_sim, text_text_fn=text_text_sim, image_image_fn=image_image_sim, model_choice_visible=model_choice_visible)
try:
demo.queue().launch(debug=True)
except Exception:
demo.queue().launch(share=True, debug=True)
# if you are launching remotely, specify server_name and server_port
# demo.launch(server_name='your server name', server_port='server port in int')
# Read more in the docs: https://gradio.app/docs/