Paint By Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models#
This Jupyter notebook can be launched after a local installation only.
Table of contents:
Installation Instructions#
This is a self-contained example that relies solely on its own code.
We recommend running the notebook in a virtual environment. You only need a Jupyter server to start. For details, please refer to Installation Guide.
Stable Diffusion in Diffusers library#
To work with Stable Diffusion,
we will use the Hugging Face
Diffusers library. To
experiment with in-painting we can use Diffusers which exposes the
StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
similar to the other Diffusers
pipelines.
The code below demonstrates how to create
StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline using
stable-diffusion-2-inpainting. To create the drawing tool we will
install Gradio for handling user interaction.
This is the overall flow of the application:
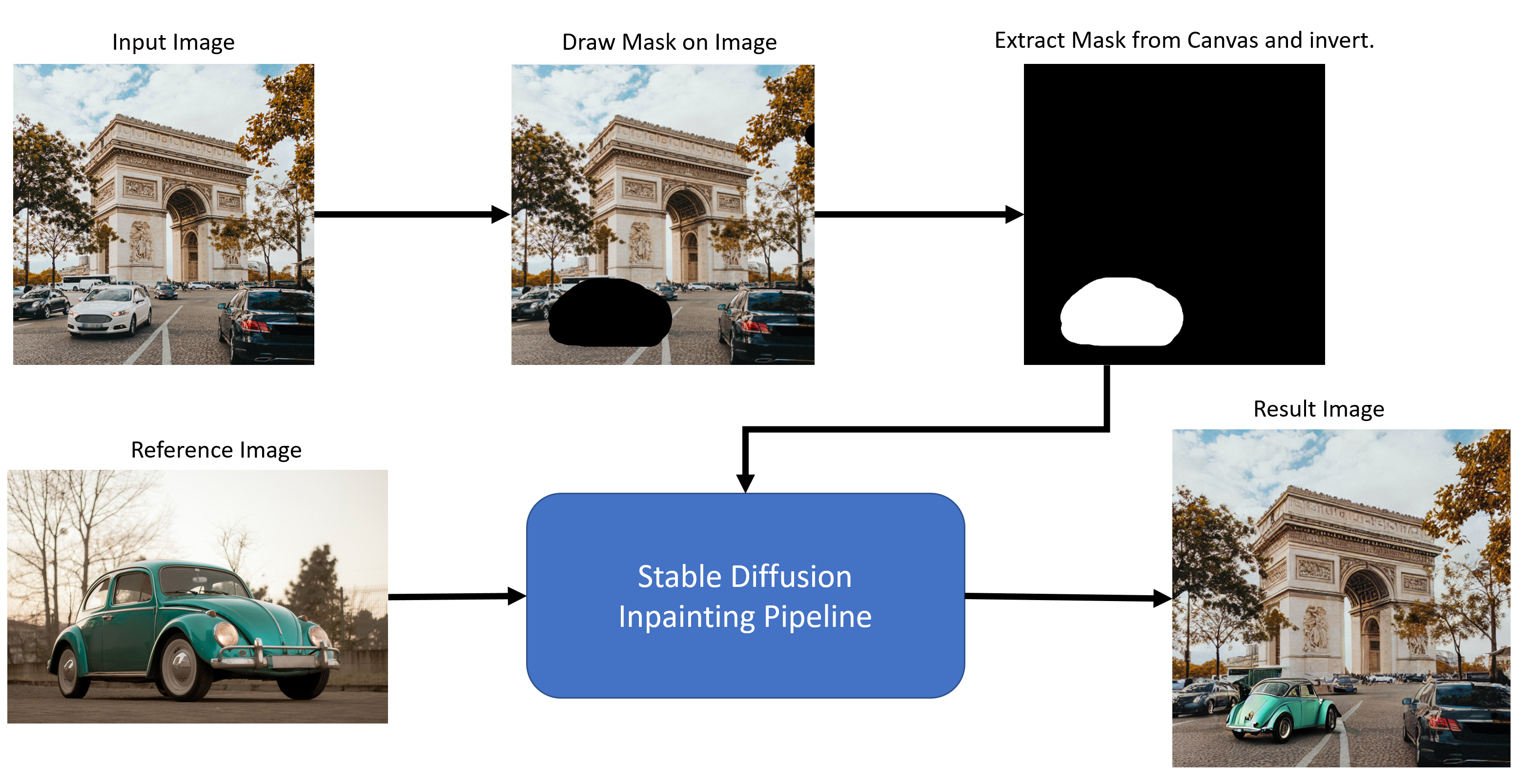
Flow Diagram#
%pip install -q "torch>=2.1" torchvision --extra-index-url "https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu"
%pip install -q "diffusers>=0.25.0" "peft>=0.6.2" "openvino>=2023.2.0" "transformers>=4.25.1" "matplotlib>=3.4" ipywidgets opencv-python pillow "nncf>=2.7.0" "gradio==3.44.1" tqdm
Download the model from HuggingFace Paint-by-Example. This might take several minutes because it is over 5GB
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
from diffusers.schedulers import DDIMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler, PNDMScheduler
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("Fantasy-Studio/Paint-By-Example")
scheduler_inpaint = DDIMScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
import gc
extractor = pipeline.feature_extractor
image_encoder = pipeline.image_encoder
image_encoder.eval()
unet_inpaint = pipeline.unet
unet_inpaint.eval()
vae_inpaint = pipeline.vae
vae_inpaint.eval()
del pipeline
gc.collect();
Download default images#
Download default images.
# Fetch `notebook_utils` module
import requests
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/notebook_utils.py",
)
open("notebook_utils.py", "w").write(r.text)
from notebook_utils import download_file, device_widget, quantization_widget
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377210-edc98e97-0e43-4796-b771-dacd074c39ea.png",
"0.png",
"data/image",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377233-b2c2d902-d379-415a-8183-5bdd37c52429.png",
"1.png",
"data/image",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377248-da1db61e-3521-4cdb-85c8-1386d360ce22.png",
"2.png",
"data/image",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377279-fa496f17-e850-4351-87c5-2552dfbc4633.jpg",
"bird.jpg",
"data/reference",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377298-06a25ff2-84d8-4d46-95cd-8c25efa690d8.jpg",
"car.jpg",
"data/reference",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377318-8841a801-1933-4523-a433-7d2fb64c47e6.jpg",
"dog.jpg",
"data/reference",
)
Convert models to OpenVINO Intermediate representation (IR) format#
Adapted from Stable Diffusion v2 Infinite Zoom notebook
from pathlib import Path
import torch
import numpy as np
import openvino as ov
model_dir = Path("model")
model_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
sd2_inpainting_model_dir = Path("model/paint_by_example")
sd2_inpainting_model_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
Functions to convert to OpenVINO IR format
def cleanup_torchscript_cache():
"""
Helper for removing cached model representation
"""
torch._C._jit_clear_class_registry()
torch.jit._recursive.concrete_type_store = torch.jit._recursive.ConcreteTypeStore()
torch.jit._state._clear_class_state()
def convert_image_encoder(image_encoder: torch.nn.Module, ir_path: Path):
"""
Convert Image Encoder model to IR.
Function accepts pipeline, prepares example inputs for conversion
Parameters:
image_encoder (torch.nn.Module): image encoder PyTorch model
ir_path (Path): File for storing model
Returns:
None
"""
class ImageEncoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, image_encoder):
super().__init__()
self.image_encoder = image_encoder
def forward(self, image):
image_embeddings, negative_prompt_embeds = self.image_encoder(image, return_uncond_vector=True)
return image_embeddings, negative_prompt_embeds
if not ir_path.exists():
image_encoder = ImageEncoderWrapper(image_encoder)
image_encoder.eval()
input_ids = torch.randn((1, 3, 224, 224))
# switch model to inference mode
# disable gradients calculation for reducing memory consumption
with torch.no_grad():
ov_model = ov.convert_model(image_encoder, example_input=input_ids, input=([1, 3, 224, 224],))
ov.save_model(ov_model, ir_path)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
print("Image Encoder successfully converted to IR")
def convert_unet(
unet: torch.nn.Module,
ir_path: Path,
num_channels: int = 4,
width: int = 64,
height: int = 64,
):
"""
Convert Unet model to IR format.
Function accepts pipeline, prepares example inputs for conversion
Parameters:
unet (torch.nn.Module): UNet PyTorch model
ir_path (Path): File for storing model
num_channels (int, optional, 4): number of input channels
width (int, optional, 64): input width
height (int, optional, 64): input height
Returns:
None
"""
dtype_mapping = {torch.float32: ov.Type.f32, torch.float64: ov.Type.f64}
if not ir_path.exists():
# prepare inputs
encoder_hidden_state = torch.ones((2, 1, 768))
latents_shape = (2, num_channels, width, height)
latents = torch.randn(latents_shape)
t = torch.from_numpy(np.array(1, dtype=np.float32))
unet.eval()
dummy_inputs = (latents, t, encoder_hidden_state)
input_info = []
for input_tensor in dummy_inputs:
shape = ov.PartialShape(tuple(input_tensor.shape))
element_type = dtype_mapping[input_tensor.dtype]
input_info.append((shape, element_type))
with torch.no_grad():
ov_model = ov.convert_model(unet, example_input=dummy_inputs, input=input_info)
ov.save_model(ov_model, ir_path)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
print("U-Net successfully converted to IR")
def convert_vae_encoder(vae: torch.nn.Module, ir_path: Path, width: int = 512, height: int = 512):
"""
Convert VAE model to IR format.
Function accepts VAE model, creates wrapper class for export only necessary for inference part,
prepares example inputs for conversion,
Parameters:
vae (torch.nn.Module): VAE PyTorch model
ir_path (Path): File for storing model
width (int, optional, 512): input width
height (int, optional, 512): input height
Returns:
None
"""
class VAEEncoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vae):
super().__init__()
self.vae = vae
def forward(self, image):
latents = self.vae.encode(image).latent_dist.sample()
return latents
if not ir_path.exists():
vae_encoder = VAEEncoderWrapper(vae)
vae_encoder.eval()
image = torch.zeros((1, 3, width, height))
with torch.no_grad():
ov_model = ov.convert_model(vae_encoder, example_input=image, input=([1, 3, width, height],))
ov.save_model(ov_model, ir_path)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
print("VAE encoder successfully converted to IR")
def convert_vae_decoder(vae: torch.nn.Module, ir_path: Path, width: int = 64, height: int = 64):
"""
Convert VAE decoder model to IR format.
Function accepts VAE model, creates wrapper class for export only necessary for inference part,
prepares example inputs for conversion,
Parameters:
vae (torch.nn.Module): VAE model
ir_path (Path): File for storing model
width (int, optional, 64): input width
height (int, optional, 64): input height
Returns:
None
"""
class VAEDecoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vae):
super().__init__()
self.vae = vae
def forward(self, latents):
latents = 1 / 0.18215 * latents
return self.vae.decode(latents)
if not ir_path.exists():
vae_decoder = VAEDecoderWrapper(vae)
latents = torch.zeros((1, 4, width, height))
vae_decoder.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
ov_model = ov.convert_model(vae_decoder, example_input=latents, input=([1, 4, width, height],))
ov.save_model(ov_model, ir_path)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
print("VAE decoder successfully converted to ")
Do the conversion of the in-painting model:
IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT = sd2_inpainting_model_dir / "image_encoder.xml"
if not IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT.exists():
convert_image_encoder(image_encoder, IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT)
else:
print(f"Image encoder will be loaded from {IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT}")
del image_encoder
gc.collect();
Do the conversion of the Unet model
UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT = sd2_inpainting_model_dir / "unet.xml"
if not UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT.exists():
convert_unet(unet_inpaint, UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT, num_channels=9, width=64, height=64)
del unet_inpaint
gc.collect()
else:
del unet_inpaint
print(f"U-Net will be loaded from {UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT}")
gc.collect();
Do the conversion of the VAE Encoder model
VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT = sd2_inpainting_model_dir / "vae_encoder.xml"
if not VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT.exists():
convert_vae_encoder(vae_inpaint, VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, 512, 512)
else:
print(f"VAE encoder will be loaded from {VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT}")
VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT = sd2_inpainting_model_dir / "vae_decoder.xml"
if not VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT.exists():
convert_vae_decoder(vae_inpaint, VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, 64, 64)
else:
print(f"VAE decoder will be loaded from {VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT}")
del vae_inpaint
gc.collect();
Prepare Inference pipeline#
Function to prepare the mask and masked image.
Adapted from Stable Diffusion v2 Infinite Zoom notebook
The main difference is that instead of encoding a text prompt it will now encode an image as the prompt.
This is the detailed flowchart for the pipeline:
pipeline-flowchart#
import inspect
from typing import Optional, Union, Dict
import PIL
import cv2
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor
from diffusers.pipelines.pipeline_utils import DiffusionPipeline
from openvino.runtime import Model
def prepare_mask_and_masked_image(image: PIL.Image.Image, mask: PIL.Image.Image):
"""
Prepares a pair (image, mask) to be consumed by the Stable Diffusion pipeline. This means that those inputs will be
converted to ``np.array`` with shapes ``batch x channels x height x width`` where ``channels`` is ``3`` for the
``image`` and ``1`` for the ``mask``.
The ``image`` will be converted to ``np.float32`` and normalized to be in ``[-1, 1]``. The ``mask`` will be
binarized (``mask > 0.5``) and cast to ``np.float32`` too.
Args:
image (Union[np.array, PIL.Image]): The image to inpaint.
It can be a ``PIL.Image``, or a ``height x width x 3`` ``np.array``
mask (_type_): The mask to apply to the image, i.e. regions to inpaint.
It can be a ``PIL.Image``, or a ``height x width`` ``np.array``.
Returns:
tuple[np.array]: The pair (mask, masked_image) as ``torch.Tensor`` with 4
dimensions: ``batch x channels x height x width``.
"""
if isinstance(image, (PIL.Image.Image, np.ndarray)):
image = [image]
if isinstance(image, list) and isinstance(image[0], PIL.Image.Image):
image = [np.array(i.convert("RGB"))[None, :] for i in image]
image = np.concatenate(image, axis=0)
elif isinstance(image, list) and isinstance(image[0], np.ndarray):
image = np.concatenate([i[None, :] for i in image], axis=0)
image = image.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
image = image.astype(np.float32) / 127.5 - 1.0
# preprocess mask
if isinstance(mask, (PIL.Image.Image, np.ndarray)):
mask = [mask]
if isinstance(mask, list) and isinstance(mask[0], PIL.Image.Image):
mask = np.concatenate([np.array(m.convert("L"))[None, None, :] for m in mask], axis=0)
mask = mask.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
elif isinstance(mask, list) and isinstance(mask[0], np.ndarray):
mask = np.concatenate([m[None, None, :] for m in mask], axis=0)
mask = 1 - mask
mask[mask < 0.5] = 0
mask[mask >= 0.5] = 1
masked_image = image * mask
return mask, masked_image
Class for the pipeline which will connect all the models together: VAE decode –> image encode –> tokenizer –> Unet –> VAE model –> scheduler
class OVStableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
def __init__(
self,
vae_decoder: Model,
image_encoder: Model,
image_processor: CLIPImageProcessor,
unet: Model,
scheduler: Union[DDIMScheduler, PNDMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler],
vae_encoder: Model = None,
):
"""
Pipeline for text-to-image generation using Stable Diffusion.
Parameters:
vae_decoder (Model):
Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) Model to decode images to and from latent representations.
image_encoder (Model):
https://huggingface.co/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/image_encoder/config.json
tokenizer (CLIPTokenizer):
Tokenizer of class CLIPTokenizer(https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/v4.21.0/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPTokenizer).
unet (Model): Conditional U-Net architecture to denoise the encoded image latents.
vae_encoder (Model):
Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) Model to encode images to latent representation.
scheduler (SchedulerMixin):
A scheduler to be used in combination with unet to denoise the encoded image latents. Can be one of
DDIMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler, or PNDMScheduler.
"""
super().__init__()
self.scheduler = scheduler
self.vae_decoder = vae_decoder
self.vae_encoder = vae_encoder
self.image_encoder = image_encoder
self.unet = unet
self.register_to_config(unet=unet)
self._unet_output = unet.output(0)
self._vae_d_output = vae_decoder.output(0)
self._vae_e_output = vae_encoder.output(0) if vae_encoder is not None else None
self.height = self.unet.input(0).shape[2] * 8
self.width = self.unet.input(0).shape[3] * 8
self.image_processor = image_processor
def prepare_mask_latents(
self,
mask,
masked_image,
height=512,
width=512,
do_classifier_free_guidance=True,
):
"""
Prepare mask as Unet nput and encode input masked image to latent space using vae encoder
Parameters:
mask (np.array): input mask array
masked_image (np.array): masked input image tensor
heigh (int, *optional*, 512): generated image height
width (int, *optional*, 512): generated image width
do_classifier_free_guidance (bool, *optional*, True): whether to use classifier free guidance or not
Returns:
mask (np.array): resized mask tensor
masked_image_latents (np.array): masked image encoded into latent space using VAE
"""
mask = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(torch.from_numpy(mask), size=(height // 8, width // 8))
mask = mask.numpy()
# encode the mask image into latents space so we can concatenate it to the latents
masked_image_latents = self.vae_encoder(masked_image)[self._vae_e_output]
masked_image_latents = 0.18215 * masked_image_latents
mask = np.concatenate([mask] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else mask
masked_image_latents = np.concatenate([masked_image_latents] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else masked_image_latents
return mask, masked_image_latents
def __call__(
self,
image: PIL.Image.Image,
mask_image: PIL.Image.Image,
reference_image: PIL.Image.Image,
num_inference_steps: Optional[int] = 50,
guidance_scale: Optional[float] = 7.5,
eta: Optional[float] = 0,
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
seed: Optional[int] = None,
):
"""
Function invoked when calling the pipeline for generation.
Parameters:
image (PIL.Image.Image):
Source image for inpainting.
mask_image (PIL.Image.Image):
Mask area for inpainting
reference_image (PIL.Image.Image):
Reference image to inpaint in mask area
num_inference_steps (int, *optional*, defaults to 50):
The number of denoising steps. More denoising steps usually lead to a higher quality image at the
expense of slower inference.
guidance_scale (float, *optional*, defaults to 7.5):
Guidance scale as defined in Classifier-Free Diffusion Guidance(https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.12598).
guidance_scale is defined as `w` of equation 2.
Higher guidance scale encourages to generate images that are closely linked to the text prompt,
usually at the expense of lower image quality.
eta (float, *optional*, defaults to 0.0):
Corresponds to parameter eta (η) in the DDIM paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502. Only applies to
[DDIMScheduler], will be ignored for others.
output_type (`str`, *optional*, defaults to "pil"):
The output format of the generate image. Choose between
[PIL](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/): PIL.Image.Image or np.array.
seed (int, *optional*, None):
Seed for random generator state initialization.
Returns:
Dictionary with keys:
sample - the last generated image PIL.Image.Image or np.array
"""
if seed is not None:
np.random.seed(seed)
# here `guidance_scale` is defined analog to the guidance weight `w` of equation (2)
# of the Imagen paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.11487.pdf . `guidance_scale = 1`
# corresponds to doing no classifier free guidance.
do_classifier_free_guidance = guidance_scale > 1.0
# get reference image embeddings
image_embeddings = self._encode_image(reference_image, do_classifier_free_guidance=do_classifier_free_guidance)
# prepare mask
mask, masked_image = prepare_mask_and_masked_image(image, mask_image)
# set timesteps
accepts_offset = "offset" in set(inspect.signature(self.scheduler.set_timesteps).parameters.keys())
extra_set_kwargs = {}
if accepts_offset:
extra_set_kwargs["offset"] = 1
self.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps, **extra_set_kwargs)
timesteps, num_inference_steps = self.get_timesteps(num_inference_steps, 1)
latent_timestep = timesteps[:1]
# get the initial random noise unless the user supplied it
latents, meta = self.prepare_latents(latent_timestep)
mask, masked_image_latents = self.prepare_mask_latents(
mask,
masked_image,
do_classifier_free_guidance=do_classifier_free_guidance,
)
# prepare extra kwargs for the scheduler step, since not all schedulers have the same signature
# eta (η) is only used with the DDIMScheduler, it will be ignored for other schedulers.
# eta corresponds to η in DDIM paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502
# and should be between [0, 1]
accepts_eta = "eta" in set(inspect.signature(self.scheduler.step).parameters.keys())
extra_step_kwargs = {}
if accepts_eta:
extra_step_kwargs["eta"] = eta
for t in self.progress_bar(timesteps):
# expand the latents if we are doing classifier free guidance
latent_model_input = np.concatenate([latents] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else latents
latent_model_input = self.scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, t)
latent_model_input = np.concatenate([latent_model_input, masked_image_latents, mask], axis=1)
# predict the noise residual
noise_pred = self.unet([latent_model_input, np.array(t, dtype=np.float32), image_embeddings])[self._unet_output]
# perform guidance
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred[0], noise_pred[1]
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
# compute the previous noisy sample x_t -> x_t-1
latents = self.scheduler.step(
torch.from_numpy(noise_pred),
t,
torch.from_numpy(latents),
**extra_step_kwargs,
)["prev_sample"].numpy()
# scale and decode the image latents with vae
image = self.vae_decoder(latents)[self._vae_d_output]
image = self.postprocess_image(image, meta, output_type)
return {"sample": image}
def _encode_image(self, image: PIL.Image.Image, do_classifier_free_guidance: bool = True):
"""
Encodes the image into image encoder hidden states.
Parameters:
image (PIL.Image.Image): base image to encode
do_classifier_free_guidance (bool): whether to use classifier free guidance or not
Returns:
image_embeddings (np.ndarray): image encoder hidden states
"""
processed_image = self.image_processor(image)
processed_image = processed_image["pixel_values"][0]
processed_image = np.expand_dims(processed_image, axis=0)
output = self.image_encoder(processed_image)
image_embeddings = output[self.image_encoder.output(0)]
negative_embeddings = output[self.image_encoder.output(1)]
image_embeddings = np.concatenate([negative_embeddings, image_embeddings])
return image_embeddings
def prepare_latents(self, latent_timestep: torch.Tensor = None):
"""
Function for getting initial latents for starting generation
Parameters:
latent_timestep (torch.Tensor, *optional*, None):
Predicted by scheduler initial step for image generation, required for latent image mixing with nosie
Returns:
latents (np.ndarray):
Image encoded in latent space
"""
latents_shape = (1, 4, self.height // 8, self.width // 8)
noise = np.random.randn(*latents_shape).astype(np.float32)
# if we use LMSDiscreteScheduler, let's make sure latents are mulitplied by sigmas
if isinstance(self.scheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler):
noise = noise * self.scheduler.sigmas[0].numpy()
return noise, {}
def postprocess_image(self, image: np.ndarray, meta: Dict, output_type: str = "pil"):
"""
Postprocessing for decoded image. Takes generated image decoded by VAE decoder, unpad it to initila image size (if required),
normalize and convert to [0, 255] pixels range. Optionally, convertes it from np.ndarray to PIL.Image format
Parameters:
image (np.ndarray):
Generated image
meta (Dict):
Metadata obtained on latents preparing step, can be empty
output_type (str, *optional*, pil):
Output format for result, can be pil or numpy
Returns:
image (List of np.ndarray or PIL.Image.Image):
Postprocessed images
"""
if "padding" in meta:
pad = meta["padding"]
(_, end_h), (_, end_w) = pad[1:3]
h, w = image.shape[2:]
unpad_h = h - end_h
unpad_w = w - end_w
image = image[:, :, :unpad_h, :unpad_w]
image = np.clip(image / 2 + 0.5, 0, 1)
image = np.transpose(image, (0, 2, 3, 1))
# 9. Convert to PIL
if output_type == "pil":
image = self.numpy_to_pil(image)
if "src_height" in meta:
orig_height, orig_width = meta["src_height"], meta["src_width"]
image = [img.resize((orig_width, orig_height), PIL.Image.Resampling.LANCZOS) for img in image]
else:
if "src_height" in meta:
orig_height, orig_width = meta["src_height"], meta["src_width"]
image = [cv2.resize(img, (orig_width, orig_width)) for img in image]
return image
def get_timesteps(self, num_inference_steps: int, strength: float):
"""
Helper function for getting scheduler timesteps for generation
In case of image-to-image generation, it updates number of steps according to strength
Parameters:
num_inference_steps (int):
number of inference steps for generation
strength (float):
value between 0.0 and 1.0, that controls the amount of noise that is added to the input image.
Values that approach 1.0 allow for lots of variations but will also produce images that are not semantically consistent with the input.
"""
# get the original timestep using init_timestep
init_timestep = min(int(num_inference_steps * strength), num_inference_steps)
t_start = max(num_inference_steps - init_timestep, 0)
timesteps = self.scheduler.timesteps[t_start:]
return timesteps, num_inference_steps - t_start
Select inference device#
select device from dropdown list for running inference using OpenVINO
device = device_widget()
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=4, options=('CPU', 'GPU.0', 'GPU.1', 'GPU.2', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
Configure Inference Pipeline#
Configuration steps: 1. Load models on device 2. Configure tokenizer and scheduler 3. Create instance of OvStableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline class
This can take a while to run.
ov_config = {"INFERENCE_PRECISION_HINT": "f32"} if device.value != "CPU" else {}
core = ov.Core()
def get_ov_pipeline():
image_encoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value)
unet_model_inpaint = core.compile_model(UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value)
vae_decoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value, ov_config)
vae_encoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value, ov_config)
ov_pipe_inpaint = OVStableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline(
image_processor=extractor,
image_encoder=image_encoder_inpaint,
unet=unet_model_inpaint,
vae_encoder=vae_encoder_inpaint,
vae_decoder=vae_decoder_inpaint,
scheduler=scheduler_inpaint,
)
return ov_pipe_inpaint
ov_pipe_inpaint = get_ov_pipeline()
Quantization#
NNCF enables
post-training quantization by adding quantization layers into model
graph and then using a subset of the training dataset to initialize the
parameters of these additional quantization layers. Quantized operations
are executed in INT8 instead of FP32/FP16 making model
inference faster.
According to StableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline structure, UNet used
for iterative denoising of input. It means that model runs in the cycle
repeating inference on each diffusion step, while other parts of
pipeline take part only once. That is why computation cost and speed of
UNet denoising becomes the critical path in the pipeline. Quantizing the
rest of the SD pipeline does not significantly improve inference
performance but can lead to a substantial degradation of accuracy.
The optimization process contains the following steps:
Create a calibration dataset for quantization.
Run
nncf.quantize()to obtain quantized model.Save the
INT8model usingopenvino.save_model()function.
Please select below whether you would like to run quantization to improve model inference speed.
UNET_INT8_OV_PATH = Path("model/unet_int8.xml")
int8_ov_pipe_inpaint = None
to_quantize = quantization_widget()
to_quantize
Checkbox(value=True, description='Quantization')
Let’s load skip magic extension to skip quantization if
to_quantize is not selected
# Fetch `skip_kernel_extension` module
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/skip_kernel_extension.py",
)
open("skip_kernel_extension.py", "w").write(r.text)
if to_quantize.value and "GPU" in device.value:
to_quantize.value = False
%load_ext skip_kernel_extension
Prepare calibration dataset#
We use 3 examples from Paint-by-Example to create a calibration dataset.
import PIL
import requests
from io import BytesIO
def download_image(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return PIL.Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
example1 = [
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/image/example_1.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/mask/example_1.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/reference/example_1.jpg?raw=true",
]
example2 = [
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/image/example_2.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/mask/example_2.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/reference/example_2.jpg?raw=true",
]
example3 = [
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/image/example_3.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/mask/example_3.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/reference/example_3.jpg?raw=true",
]
examples = [example1, example2, example3]
img_examples = []
for init_image_url, mask_image_url, example_image_url in examples:
init_image = download_image(init_image_url).resize((512, 512))
mask_image = download_image(mask_image_url).resize((512, 512))
example_image = download_image(example_image_url).resize((512, 512))
img_examples.append((init_image, mask_image, example_image))
To collect intermediate model inputs for calibration we should customize
CompiledModel.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
from transformers import set_seed
from typing import Any, Dict, List
class CompiledModelDecorator(ov.CompiledModel):
def __init__(self, compiled_model, data_cache: List[Any] = None):
super().__init__(compiled_model)
self.data_cache = data_cache if data_cache else []
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.data_cache.append(*args)
return super().__call__(*args, **kwargs)
def collect_calibration_data(pipeline) -> List[Dict]:
original_unet = pipeline.unet
pipeline.unet = CompiledModelDecorator(original_unet)
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=True)
prev_example_image = None
for init_image, mask_image, example_image in img_examples:
_ = pipeline(
image=init_image,
mask_image=mask_image,
reference_image=example_image,
)
if prev_example_image:
_ = pipeline(
image=init_image,
mask_image=mask_image,
reference_image=prev_example_image,
)
prev_example_image = example_image
calibration_dataset = pipeline.unet.data_cache
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=False)
pipeline.unet = original_unet
return calibration_dataset
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
UNET_INT8_OV_PATH = Path("model/unet_int8.xml")
if not UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
unet_calibration_data = collect_calibration_data(ov_pipe_inpaint)
Run quantization#
Create a quantized model from the pre-trained converted OpenVINO model.
NOTE: Quantization is time and memory consuming operation. Running quantization code below may take some time.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import nncf
def get_quantized_pipeline():
if UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
print("Loading quantized model")
quantized_unet = core.read_model(UNET_INT8_OV_PATH)
else:
unet = core.read_model(UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT)
quantized_unet = nncf.quantize(
model=unet,
preset=nncf.QuantizationPreset.MIXED,
calibration_dataset=nncf.Dataset(unet_calibration_data),
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
)
ov.save_model(quantized_unet, UNET_INT8_OV_PATH)
unet_optimized = core.compile_model(UNET_INT8_OV_PATH, device.value)
image_encoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value)
vae_decoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value, ov_config)
vae_encoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value, ov_config)
int8_ov_pipe_inpaint = OVStableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline(
image_processor=extractor,
image_encoder=image_encoder_inpaint,
unet=unet_optimized,
vae_encoder=vae_encoder_inpaint,
vae_decoder=vae_decoder_inpaint,
scheduler=scheduler_inpaint,
)
return int8_ov_pipe_inpaint
int8_ov_pipe_inpaint = get_quantized_pipeline()
INFO:nncf:NNCF initialized successfully. Supported frameworks detected: torch, openvino
Output()
Output()
INFO:nncf:121 ignored nodes were found by name in the NNCFGraph
Output()
Output()
Run inference and compare inference time#
OV pipeline:
init_image, mask_image, example_image = img_examples[1]
ov_image = ov_pipe_inpaint(image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image, reference_image=example_image, seed=2)
Quantized pipeline:
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
int8_image = int8_ov_pipe_inpaint(image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image, reference_image=example_image, seed=2)
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
def visualize_results(orig_img:Image.Image, optimized_img:Image.Image):
"""
Helper function for results visualization
Parameters:
orig_img (Image.Image): generated image using FP16 models
optimized_img (Image.Image): generated image using quantized models
Returns:
fig (matplotlib.pyplot.Figure): matplotlib generated figure contains drawing result
"""
orig_title = "FP16 pipeline"
control_title = "INT8 pipeline"
figsize = (20, 20)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=figsize, sharex='all', sharey='all')
list_axes = list(axs.flat)
for a in list_axes:
a.set_xticklabels([])
a.set_yticklabels([])
a.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
a.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
a.grid(False)
list_axes[0].imshow(np.array(orig_img))
list_axes[1].imshow(np.array(optimized_img))
list_axes[0].set_title(orig_title, fontsize=15)
list_axes[1].set_title(control_title, fontsize=15)
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.01, hspace=0.01)
fig.tight_layout()
return fig
visualize_results(ov_image["sample"][0], int8_image["sample"][0])

%%skip $to_quantize.value
display(ov_image["sample"][0])
Compare UNet file size#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
fp16_ir_model_size = UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024
quantized_model_size = UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024
print(f"FP16 model size: {fp16_ir_model_size:.2f} KB")
print(f"INT8 model size: {quantized_model_size:.2f} KB")
print(f"Model compression rate: {fp16_ir_model_size / quantized_model_size:.3f}")
FP16 model size: 1678780.62 KB
INT8 model size: 840725.98 KB
Model compression rate: 1.997
Interactive inference#
Choose what model do you want to use in the interactive interface. You can choose both, FP16 and INT8.
import ipywidgets as widgets
available_models = ["FP16"]
if UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
available_models.append("INT8")
model_to_use = widgets.Select(
options=available_models,
value="FP16",
description="Select model:",
disabled=False,
)
model_to_use
Select(description='Select model:', options=('FP16', 'INT8'), value='FP16')
if "INT8" == model_to_use.value:
chosen_pipeline = int8_ov_pipe_inpaint or get_quantized_pipeline()
ov_pipe_inpaint = None
else:
chosen_pipeline = ov_pipe_inpaint or get_ov_pipeline()
int8_ov_pipe_inpaint = None
gc.collect()
# Code adapated from https://huggingface.co/spaces/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/app.py
import os
def predict(input_dict, reference, seed, steps):
"""
This function runs when the 'paint' button is pressed. It takes 3 input images. Takes generated image decoded by VAE decoder, unpad it to initila image size (if required),
normalize and convert to [0, 255] pixels range. Optionally, convertes it from np.ndarray to PIL.Image format
Parameters:
input_dict (Dict):
Contains two images in a dictionary
'image' is the image that will be painted on
'mask' is the black/white image specifying where to paint (white) and not to paint (black)
image (PIL.Image.Image):
Reference image that will be used by the model to know what to paint in the specified area
seed (int):
Used to initialize the random number generator state
steps (int):
The number of denoising steps to run during inference. Low = fast/low quality, High = slow/higher quality
use_quantize_model (bool):
Use fp16 or int8 model
Returns:
image (PIL.Image.Image):
Postprocessed images
"""
width, height = input_dict["image"].size
# If the image is not 512x512 then resize
if width < height:
factor = width / 512.0
width = 512
height = int((height / factor) / 8.0) * 8
else:
factor = height / 512.0
height = 512
width = int((width / factor) / 8.0) * 8
init_image = input_dict["image"].convert("RGB").resize((width, height))
mask = input_dict["mask"].convert("RGB").resize((width, height))
# If the image is not a 512x512 square then crop
if width > height:
buffer = (width - height) / 2
input_image = init_image.crop((buffer, 0, width - buffer, 512))
mask = mask.crop((buffer, 0, width - buffer, 512))
elif width < height:
buffer = (height - width) / 2
input_image = init_image.crop((0, buffer, 512, height - buffer))
mask = mask.crop((0, buffer, 512, height - buffer))
else:
input_image = init_image
if not os.path.exists("output"):
os.mkdir("output")
input_image.save("output/init.png")
mask.save("output/mask.png")
reference.save("output/ref.png")
mask = [mask]
result = chosen_pipeline(
image=input_image,
mask_image=mask,
reference_image=reference,
seed=seed,
num_inference_steps=steps,
)[
"sample"
][0]
out_dir = Path("output")
out_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
result.save("output/result.png")
return result
Choose a source image and a reference image, draw a mask in source image and push “Paint!”
if not Path("gradio_helper.py").exists():
r = requests.get(url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/notebooks/paint-by-example/gradio_helper.py")
open("gradio_helper.py", "w").write(r.text)
from gradio_helper import make_demo
demo = make_demo(fn=predict)
# Launching the Gradio app
try:
demo.launch(debug=False, height=680)
except Exception:
demo.queue().launch(share=True, debug=False, height=680)
# if you are launching remotely, specify server_name and server_port
# image_blocks.launch(server_name='your server name', server_port='server port in int')
# Read more in the docs: https://gradio.app/docs/
# please uncomment and run this cell for stopping gradio interface
# demo.close()