[LEGACY] Troubleshooting Reshape Errors¶
Danger
The code described here has been deprecated! Do not use it to avoid working with a legacy solution. It will be kept for some time to ensure backwards compatibility, but you should not use it in contemporary applications.
How To Avoid Shape Collision¶
Operation semantics may impose restrictions on input shapes of the operation. Shape collision during shape propagation may be a sign that new shape does not satisfy the restrictions. Changing the model input shape may result in intermediate operations shape collision. For example, in the following:
The Reshape operation with a hard-coded output shape value,
The MatMul operation with the
Constsecond input and this input cannot be resized by spatial dimensions due to operation semantics.
Model structure and logic should not change significantly after model reshaping.
The Global Pooling operation is commonly used to reduce output feature map of classification models output. Having the input of the shape [N, C, H, W], Global Pooling returns the output of the shape [N, C, 1, 1]. Model architects usually express Global Pooling with the help of the
Poolingoperation with the fixed kernel size [H, W]. During spatial reshape, having the input of the shape [N, C, H1, W1],Poolingwith the fixed kernel size [H, W] returns the output of the shape [N, C, H2, W2], where H2 and W2 are commonly not equal to 1. It breaks the classification model structure. For example, the public Inception family models from TensorFlow have this issue.Changing the model input shape may significantly affect its accuracy. For example, Object Detection models from TensorFlow have resizing restrictions by design. To keep the model valid after the reshape, choose a new input shape that satisfies conditions listed in the
pipeline.configfile.
How To Fix Non-Reshape-able Model¶
To fix some operators which prevent normal shape propagation:
see if the issue can be fixed via changing the values of some operators’ input. For example, the most common problem of non-reshape-able models is a
Reshapeoperator with a hard-coded output shape. You can cut-off the hard-coded second input ofReshapeand fill it in with relaxed values. For the following example in the diagram below, the model conversion API command line should read:mo --input_model path/to/model --input data[8,3,224,224],1:reshaped[2]->[0,-1]`
With
1:reshaped[2], it is required to cut the second input (counting from zero, so1:means the second input) of the operation namedreshapedand replace it with aParameterwith shape[2]. With->[0 -1], this newParameteris replaced by aConstantoperator which has the[0, -1]value. Since theReshapeoperator has0and-1as specific values, it allows propagating shapes freely without losing the intended meaning ofReshape. For more information, see the specification.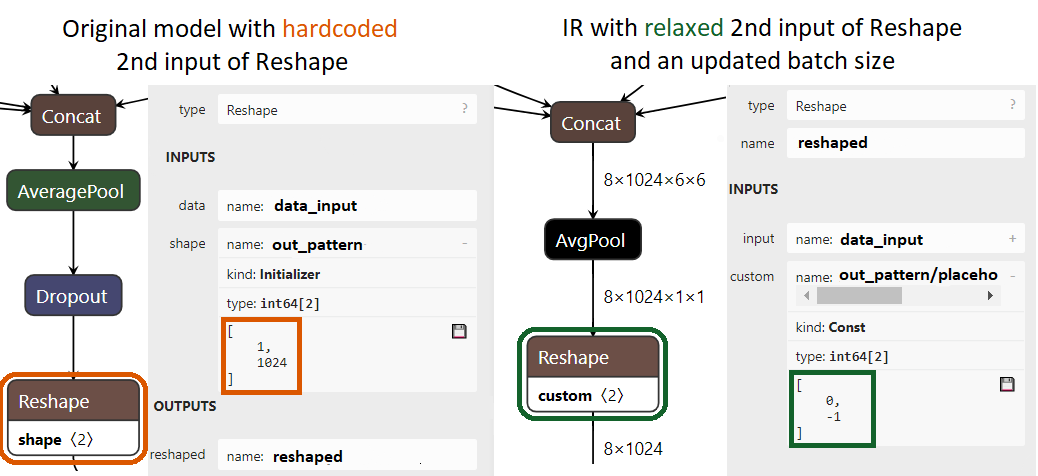
transform the model conversion on the back phase. For more information, see the How to Convert a Model,
transform OpenVINO Model during the runtime. For more information, see OpenVINO Runtime Transformations,
modify the original model with the help of the original framework.