Subject-driven image generation and editing using BLIP Diffusion and OpenVINO¶
This Jupyter notebook can be launched after a local installation only.
 BLIP-Diffusion is a
text-to-image diffusion model with built-in support for multimodal
subject-and-text condition. BLIP-Diffusion enables zero-shot
subject-driven generation, and efficient fine-tuning for customized
subjects with up to 20x speedup. In addition, BLIP-Diffusion can be
flexibly combined with ControlNet and prompt-to-prompt to enable novel
subject-driven generation and editing applications.
BLIP-Diffusion is a
text-to-image diffusion model with built-in support for multimodal
subject-and-text condition. BLIP-Diffusion enables zero-shot
subject-driven generation, and efficient fine-tuning for customized
subjects with up to 20x speedup. In addition, BLIP-Diffusion can be
flexibly combined with ControlNet and prompt-to-prompt to enable novel
subject-driven generation and editing applications.
Table of contents:¶
Prerequisites¶
%pip install -q "openvino>=2023.1.0" matplotlib Pillow gradio
%pip install -q --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu torch transformers accelerate controlnet_aux "diffusers>=0.23.0"
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
from pathlib import Path
import gc
from typing import List, Optional, Union
from functools import partial
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
import diffusers
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import ipywidgets
import PIL
import numpy as np
import gradio as gr
import controlnet_aux
import openvino as ov
/home/itrushkin/.virtualenvs/blip_diffusion/lib/python3.10/site-packages/controlnet_aux/mediapipe_face/mediapipe_face_common.py:7: UserWarning: The module 'mediapipe' is not installed. The package will have limited functionality. Please install it using the command: pip install 'mediapipe'
warnings.warn(
MODELS_DIR = Path("models")
QFORMER_PATH = MODELS_DIR / "qformer.xml"
TEXT_ENCODER_PATH = MODELS_DIR / "text_encoder.xml"
NEG_TEXT_ENCODER_PATH = MODELS_DIR / "neg_text_encoder.xml"
CONTROLNET_PATH = MODELS_DIR / "controlnet.xml"
UNET_PATH = MODELS_DIR / "unet.xml"
UNET_CONTROLNET_PATH = MODELS_DIR / "unet_controlnet.xml"
VAE_PATH = MODELS_DIR / "vae.xml"
DATA_DIR = Path("data")
DOG_IMG_URL = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/ayushtues/blipdiffusion_images/resolve/main/dog.jpg"
DOG_IMG_PATH = DATA_DIR / "dog.jpg"
KETTLE_IMG_URL = (
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/ayushtues/blipdiffusion_images/resolve/main/kettle.jpg"
)
KETTLE_IMG_PATH = DATA_DIR / "kettle.jpg"
FLOWER_IMG_URL = (
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/ayushtues/blipdiffusion_images/resolve/main/flower.jpg"
)
FLOWER_IMG_PATH = DATA_DIR / "flower.jpg"
BAG_IMG_URL = "https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-scribble/resolve/main/images/bag.png"
BAG_IMG_PATH = DATA_DIR / "bag.jpg"
MODELS_DIR.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
DATA_DIR.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
Load the model¶
We use Hugging Face diffusers library to load the model using
from_pretrained method.
pipe = diffusers.pipelines.BlipDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("ayushtues/blipdiffusion")
pipe_controlnet = diffusers.pipelines.BlipDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
"ayushtues/blipdiffusion-controlnet"
)
qformer/model.safetensors not found
Loading pipeline components...: 0%| | 0/7 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
qformer/model.safetensors not found
Loading pipeline components...: 0%| | 0/8 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
# Download images
urlretrieve(DOG_IMG_URL, DOG_IMG_PATH)
urlretrieve(KETTLE_IMG_URL, KETTLE_IMG_PATH)
urlretrieve(FLOWER_IMG_URL, FLOWER_IMG_PATH)
urlretrieve(BAG_IMG_URL, BAG_IMG_PATH);
Infer the original model¶
Zero-Shot subject-driven generation¶
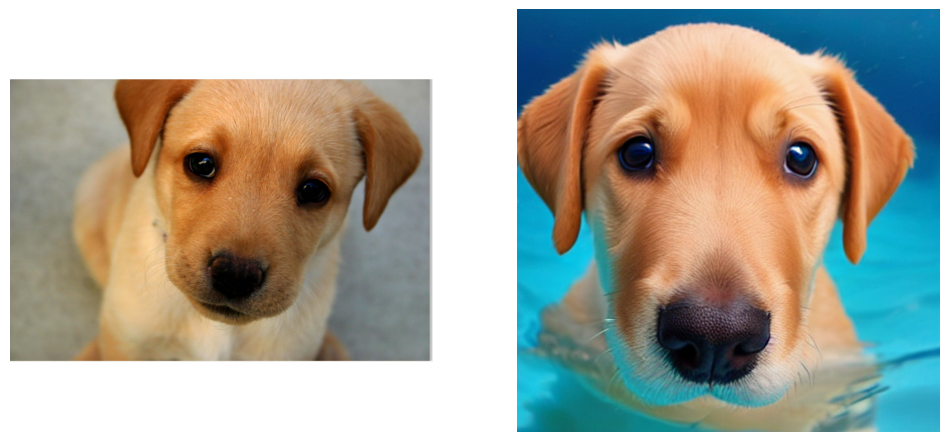
The pipeline takes a subject image and prompt text as input. The output is an image containing the subject with conditions from the prompt
dog_img = PIL.Image.open(DOG_IMG_PATH)
cond_subject = ["dog"]
tgt_subject = ["dog"]
text_prompt_input = ["swimming underwater"]
iter_seed = 88888
guidance_scale = 7.5
num_inference_steps = 50
negative_prompt = "over-exposure, under-exposure, saturated, duplicate, out of frame, lowres, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, ugly, bad anatomy, bad proportions, deformed, blurry, duplicate"
output = pipe(
text_prompt_input,
dog_img,
cond_subject,
tgt_subject,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
neg_prompt=negative_prompt,
height=512,
width=512,
)
0%| | 0/51 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(dog_img)
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(output["images"][0])
plt.axis("off");

Controlled subject-driven generation (Canny-edge)¶
The Canny edge detector is a popular edge detection algorithm that produces high-quality edge maps from images.
The approach is first to use the Canny edge detector to generate an edge map of the desired object. The edge map is then used to condition the diffusion model during image generation. This results in images that are more likely to contain the desired object and more faithful to the text description.
style_subject = ["flower"] # subject that defines the style
tgt_subject = ["teapot"] # subject to generate.
text_prompt = ["on a marble table"]
cond_image = PIL.Image.open(KETTLE_IMG_PATH).resize((512, 512))
canny = controlnet_aux.CannyDetector()
cldm_cond_image = canny(cond_image, 30, 70, output_type="pil")
cldm_cond_image = [cldm_cond_image]
style_image = PIL.Image.open(FLOWER_IMG_PATH)
guidance_scale = 7.5
num_inference_steps = 50
negative_prompt = "over-exposure, under-exposure, saturated, duplicate, out of frame, lowres, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, ugly, bad anatomy, bad proportions, deformed, blurry, duplicate"
output = pipe_controlnet(
text_prompt,
style_image,
cldm_cond_image,
style_subject,
tgt_subject,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
neg_prompt=negative_prompt,
height=512,
width=512,
)
0%| | 0/51 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
title2img = {
"Conditioning image": cond_image,
"Canny-edge mask": cldm_cond_image[0],
"Style image": style_image,
"Output": output[0][0]
}
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4), layout="tight")
for i, (title, img) in enumerate(title2img.items()):
ax = plt.subplot(1, len(title2img), i + 1)
ax.set_title(title)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis("off")

Controlled subject-driven generation (Scribble)¶
Holistically-Nested Edge Detection (HED) is a deep learning model for edge detection.
HED first uses the scribble to generate a seed map. The seed map is a binary image where the scribbled pixels are set to 1 and the other pixels are set to 0. Then, it uses the seed map to initialize a diffusion process. The diffusion process gradually spreads the edge information from the seed pixels to the other pixels in the image. The diffusion process is stopped when the edge map converges. The converged edge map is the final output of HED and input of our diffusion model.
style_subject = ["flower"] # subject that defines the style
tgt_subject = ["bag"] # subject to generate.
text_prompt = ["on a table"]
bag_img = PIL.Image.open(BAG_IMG_PATH)
cldm_cond_image = bag_img.resize((512, 512))
hed = controlnet_aux.HEDdetector.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/Annotators")
cldm_cond_image = hed(cldm_cond_image)
cldm_cond_image = [cldm_cond_image]
guidance_scale = 7.5
num_inference_steps = 50
negative_prompt = "over-exposure, under-exposure, saturated, duplicate, out of frame, lowres, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, ugly, bad anatomy, bad proportions, deformed, blurry, duplicate"
output = pipe_controlnet(
text_prompt,
style_image,
cldm_cond_image,
style_subject,
tgt_subject,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
neg_prompt=negative_prompt,
height=512,
width=512,
)
0%| | 0/51 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
title2img = {
"Conditioning image": bag_img,
"Scribble mask": cldm_cond_image[0],
"Style image": style_image,
"Output": output[0][0]
}
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4), layout="tight")
for i, (title, img) in enumerate(title2img.items()):
ax = plt.subplot(1, len(title2img), i + 1)
ax.set_title(title)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis("off")

Convert the model to OpenVINO Intermediate Representation (IR)¶
BLIP-Diffusion pipeline has the following structure:
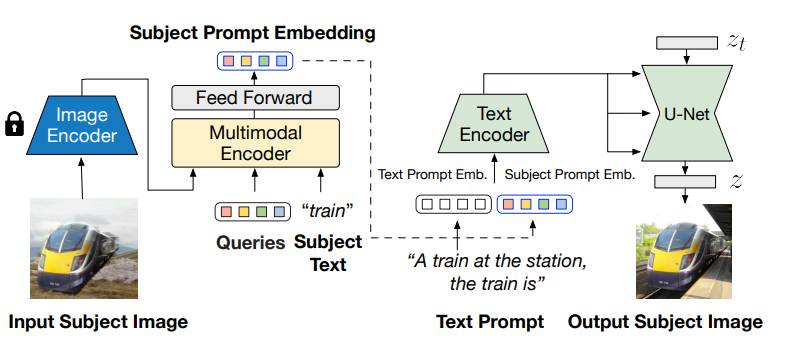
The output of the BLIP-2 multimodal encoder is connected to the input of the diffusion model’s text encoder. The multimodal encoder takes as input a subject image and a text of the subject category, and produces a category-aware subject visual representation. Then, the subject representation is transformed using a feed-forward layer consisting of two linear layers with GELU activation in-between. The projected features are appended to the text prompt token embeddings as a soft visual subject prompt. Specifically, when combining the text token and subject embeddings, “[text prompt], the [subject text] is [subject prompt]” template is used. Finally, the combined text and subject embeddings are passed through the CLIP text encoder, serving as guidance for the diffusion model to generate the output image.
# Extract all models from pipeline
qformer = pipe.qformer
qformer.eval()
text_encoder = pipe.text_encoder
text_encoder.eval()
unet = pipe.unet
unet.eval()
vae = pipe.vae
vae.eval()
controlnet = pipe_controlnet.controlnet
controlnet.eval()
# Extract additional instances
tokenizer = pipe.tokenizer
qformer_tokenizer = pipe.qformer.tokenizer
scheduler = pipe.scheduler
image_processor = pipe.image_processor
config = {
"mean": pipe.config.mean,
"std": pipe.config.std,
"text_encoder_max_position_embeddings": pipe.text_encoder.text_model.config.max_position_embeddings,
"qformer_num_query_tokens": pipe.qformer.config.num_query_tokens,
"ctx_begin_pos": pipe.config.ctx_begin_pos,
"unet_block_out_channels": pipe.unet.config.block_out_channels,
"unet_in_channels": pipe.unet.config.in_channels,
}
unet_sample_size = pipe.unet.config.sample_size
del pipe
del pipe_controlnet
gc.collect()
16237
We introduce the serialize_openvino helper function to convert all
pipeline parts that torch.nn.Modules. At first, we call the
ov.convert_model function to convert the model to OpenVINO
intermediate representation (IR). Then, we can save the model to XML
file with ov.save_model to clean up memory. For PyTorch modules
conversion, JIT tracing is used, which keeps some cache in memory that
we clean after every conversion.
def serialize_openvino(model: torch.nn.Module, xml_path: Path, **convert_kwargs):
if not xml_path.exists():
with torch.no_grad():
converted_model = ov.convert_model(model, **convert_kwargs)
ov.save_model(converted_model, xml_path)
del converted_model
# Clear torch.jit cache
torch._C._jit_clear_class_registry()
torch.jit._recursive.concrete_type_store = torch.jit._recursive.ConcreteTypeStore()
torch.jit._state._clear_class_state()
gc.collect()
Q-Former¶
Q-Former was introduced in BLIP-2 paper and is a transformer that accepts a fixed number a learnable query tokens and an input text. It is used in BLIP Diffusion pipeline as a multimodal encoder for image-text alignment. The query tokens interact with text through self-attention layers, and interact with frozen image features through cross-attention layers, and produces text-aligned image features as output. The output is of the same dimension as the number of query tokens.
Original QFormer model takes raw text as input, so we redefine the
forward function to accept tokenization result as input_ids and
attention_mask tensors.
class OVQFormer(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, qformer):
super().__init__()
self._qformer = qformer
def __getattr__(self, name):
if name == "_qformer":
return super().__getattr__(name)
return getattr(self._qformer, name)
def forward(
self,
text_input_ids,
text_attention_mask,
image_input,
):
batch_size = text_input_ids.shape[0]
query_atts = torch.ones((batch_size, self.query_tokens.size()[1]), dtype=torch.long)
attention_mask = torch.cat([query_atts, text_attention_mask], dim=1)
output_attentions = self.config.output_attentions
output_hidden_states = self.config.output_hidden_states
return_dict = self.config.use_return_dict
query_length = self.query_tokens.shape[1]
embedding_output = self.embeddings(input_ids=text_input_ids, query_embeds=self.query_tokens)
# embedding_output = self.layernorm(query_embeds)
# embedding_output = self.dropout(embedding_output)
input_shape = embedding_output.size()[:-1]
batch_size, seq_length = input_shape
device = embedding_output.device
image_embeds_frozen = self.visual_encoder(image_input).last_hidden_state
# image_embeds_frozen = torch.ones_like(image_embeds_frozen)
encoder_hidden_states = image_embeds_frozen
if attention_mask is None:
attention_mask = torch.ones(((batch_size, seq_length)), device=device)
# We can provide a self-attention mask of dimensions [batch_size, from_seq_length, to_seq_length]
# ourselves in which case we just need to make it broadcastable to all heads.
extended_attention_mask = self.get_extended_attention_mask(
attention_mask, input_shape, device
)
# If a 2D or 3D attention mask is provided for the cross-attention
# we need to make broadcastable to [batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, seq_length]
if encoder_hidden_states is not None:
if isinstance(encoder_hidden_states, list):
encoder_batch_size, encoder_sequence_length, _ = encoder_hidden_states[0].size()
else:
encoder_batch_size, encoder_sequence_length, _ = encoder_hidden_states.size()
encoder_hidden_shape = (encoder_batch_size, encoder_sequence_length)
encoder_attention_mask = torch.ones(encoder_hidden_shape, device=device)
encoder_extended_attention_mask = self.invert_attention_mask(encoder_attention_mask)
else:
encoder_extended_attention_mask = None
head_mask = [None] * self.config.qformer_config.num_hidden_layers
encoder_outputs = self.encoder(
embedding_output,
attention_mask=extended_attention_mask,
head_mask=head_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_attention_mask=encoder_extended_attention_mask,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
return_dict=return_dict,
query_length=query_length,
)
sequence_output = encoder_outputs[0]
return self.proj_layer(sequence_output[:, :query_length, :])
serialize_openvino(
OVQFormer(qformer),
QFORMER_PATH,
example_input={
"image_input": torch.randn(1, 3, 16, 16),
"text_input_ids": torch.zeros((1, 3), dtype=torch.int64),
"text_attention_mask": torch.zeros((1, 3), dtype=torch.int64),
},
input={
"image_input": ((1, 3, 224, 224),),
"text_input_ids": ((1, ov.Dimension(3, 77)), np.int64),
"text_attention_mask": ((1, ov.Dimension(3, 77)), np.int64),
},
)
del qformer
gc.collect()
0
Text encoder¶
BLIP-Diffusion pipeline uses CLIP text encoder, the default encoder for Stable Diffusion-based models. The only difference is it allows for an extra input of “context embeddings”, which are the query embeddings used in Q-Former. They pass through the CLIP model, along with the text embeddings, and interact with them using self-attention.
serialize_openvino(
text_encoder,
TEXT_ENCODER_PATH,
example_input={
"input_ids": torch.zeros((1, 61), dtype=torch.int64),
"ctx_embeddings": torch.zeros((1, 16, 768)),
"ctx_begin_pos": torch.tensor([2]),
},
input={
"input_ids": ((1, 61), np.int64),
"ctx_embeddings": ((1, 16, 768),),
"ctx_begin_pos": ((1),),
},
)
# Convert 2nd instance for negative prompt encoding
serialize_openvino(
text_encoder,
NEG_TEXT_ENCODER_PATH,
example_input={
"input_ids": torch.zeros((1, 77), dtype=torch.int64),
},
input={
"input_ids": ((1, 77), np.int64),
},
)
del text_encoder
gc.collect()
0
ControlNet¶
The ControlNet model was introduced in Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models. It provides a greater degree of control over text-to-image generation by conditioning the model on additional inputs such as edge maps, depth maps, segmentation maps, and keypoints for pose detection.
controlnet.forward = partial(controlnet.forward, return_dict=False)
example_input = {
"sample": torch.randn(2, 4, 64, 64),
"timestep": torch.tensor(1),
"encoder_hidden_states": torch.randn(2, 77, 768),
"controlnet_cond": torch.randn(2, 3, 512, 512),
}
with torch.no_grad():
down_block_res_samples, mid_block_res_sample = controlnet(**example_input)
serialize_openvino(
controlnet,
CONTROLNET_PATH,
example_input=example_input,
input={
"sample": ((2, 4, 64, 64)),
"timestep": ((),),
"encoder_hidden_states": ((2, 77, 768),),
"controlnet_cond": ((2, 3, 512, 512)),
},
)
del controlnet
gc.collect()
4463
UNet¶
The UNet model is one of the most important components of a diffusion system because it facilitates the actual diffusion process.
from typing import Tuple
serialize_openvino(
unet,
UNET_PATH,
example_input={
"sample": torch.randn(2, 4, 32, 32),
"timestep": torch.tensor(1),
"encoder_hidden_states": torch.randn(2, 77, 768),
},
input={
"sample": ((2, 4, unet_sample_size, unet_sample_size),),
"timestep": ((),),
"encoder_hidden_states": ((2, 77, 768),),
},
)
dtype_mapping = {
torch.float32: ov.Type.f32,
torch.float64: ov.Type.f64,
torch.int32: ov.Type.i32,
torch.int64: ov.Type.i64,
}
class UnetWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
unet,
sample_dtype=torch.float32,
timestep_dtype=torch.int64,
encoder_hidden_states=torch.float32,
down_block_additional_residuals=torch.float32,
mid_block_additional_residual=torch.float32
):
super().__init__()
self.unet = unet
self.sample_dtype = sample_dtype
self.timestep_dtype = timestep_dtype
self.encoder_hidden_states_dtype = encoder_hidden_states
self.down_block_additional_residuals_dtype = down_block_additional_residuals
self.mid_block_additional_residual_dtype = mid_block_additional_residual
def forward(
self,
sample:torch.Tensor,
timestep:torch.Tensor,
encoder_hidden_states:torch.Tensor,
down_block_additional_residuals:Tuple[torch.Tensor],
mid_block_additional_residual:torch.Tensor
):
sample.to(self.sample_dtype)
timestep.to(self.timestep_dtype)
encoder_hidden_states.to(self.encoder_hidden_states_dtype)
down_block_additional_residuals = [res.to(self.down_block_additional_residuals_dtype) for res in down_block_additional_residuals]
mid_block_additional_residual.to(self.mid_block_additional_residual_dtype)
return self.unet(
sample,
timestep,
encoder_hidden_states,
down_block_additional_residuals=down_block_additional_residuals,
mid_block_additional_residual=mid_block_additional_residual
)
def flatten_inputs(inputs):
flat_inputs = []
for input_data in inputs:
if input_data is None:
continue
if isinstance(input_data, (list, tuple)):
flat_inputs.extend(flatten_inputs(input_data))
else:
flat_inputs.append(input_data)
return flat_inputs
# convert 2nd time for stylization task
example_input = {
"sample": torch.randn(2, 4, unet_sample_size, unet_sample_size),
"timestep": torch.tensor(1),
"encoder_hidden_states": torch.randn(2, 77, 768),
"down_block_additional_residuals": down_block_res_samples,
"mid_block_additional_residual": mid_block_res_sample,
}
if not UNET_CONTROLNET_PATH.exists():
with torch.no_grad():
ov_unet = ov.convert_model(UnetWrapper(unet), example_input=example_input)
flat_inputs = flatten_inputs(example_input.values())
for input_data, input_tensor in zip(flat_inputs, ov_unet.inputs):
input_tensor.get_node().set_partial_shape(ov.PartialShape(input_data.shape))
input_tensor.get_node().set_element_type(dtype_mapping[input_data.dtype])
ov_unet.validate_nodes_and_infer_types()
ov.save_model(ov_unet, UNET_CONTROLNET_PATH)
del ov_unet
del unet
gc.collect()
0
Variational Autoencoder (VAE)¶
The variational autoencoder (VAE) model with KL loss was introduced in
Auto-Encoding Variational
Bayes. The model is used to
encode images into latents and to decode latent representations into
images. For inference we use only decoding part of the VAE. We wrap the
decoder in separate torch.nn.Module.
class VaeDecoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vae: torch.nn.Module):
super().__init__()
self.vae = vae
def forward(self, z: torch.FloatTensor):
return self.vae.decode(z / self.vae.config.scaling_factor, return_dict=False)[0]
serialize_openvino(
VaeDecoderWrapper(vae),
VAE_PATH,
example_input=torch.randn(1, 4, 64, 64),
input=((1, 4, 64, 64)),
)
del vae
gc.collect()
0
Select inference device¶
select device from dropdown list for running inference using OpenVINO
core = ov.Core()
device = ipywidgets.Dropdown(
options=core.available_devices + ["AUTO"],
value="AUTO",
description="Device:",
disabled=False,
)
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=4, options=('CPU', 'GPU.0', 'GPU.1', 'GPU.2', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
qformer = core.compile_model(QFORMER_PATH, device_name=device.value)
text_encoder = core.compile_model(TEXT_ENCODER_PATH, device_name=device.value)
neg_text_encoder = core.compile_model(NEG_TEXT_ENCODER_PATH, device_name=device.value)
controlnet = core.compile_model(CONTROLNET_PATH, device_name=device.value)
unet = core.compile_model(UNET_PATH, device_name=device.value)
unet_controlnet = core.compile_model(UNET_CONTROLNET_PATH, device_name=device.value)
vae = core.compile_model(VAE_PATH, device_name=device.value)
Inference¶
def call(compiled_model, *args, **kwargs):
if len(args) and not kwargs:
result = compiled_model([np.array(a) for a in args])[0]
elif kwargs and not len(args):
result = compiled_model({k: np.array(v) for k, v in kwargs.items()})[0]
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"{args=},{kwargs=}")
result = torch.tensor(result)
return result
class OvBlipDiffusionPipeline(diffusers.DiffusionPipeline):
def __init__(self):
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.qformer_tokenizer = qformer_tokenizer
self.text_encoder = partial(call, text_encoder)
self.neg_text_encoder = partial(call, neg_text_encoder)
self.vae = partial(call, vae)
self.unet = partial(call, unet)
self.unet_controlnet = partial(call, unet_controlnet)
self.controlnet = controlnet
self.scheduler = scheduler
self.qformer = partial(call, qformer)
self.image_processor = image_processor
self.register_to_config(**config)
def __call__(
self,
prompt: List[str],
reference_image: PIL.Image.Image,
source_subject_category: List[str],
target_subject_category: List[str],
conditioning_image: Optional[PIL.Image.Image] = None,
latents: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
guidance_scale: float = 7.5,
num_inference_steps: int = 50,
generator: Optional[Union[torch.Generator, List[torch.Generator]]] = None,
neg_prompt: Optional[str] = "",
prompt_strength: float = 1.0,
prompt_reps: int = 20,
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
):
"""
Function invoked when calling the pipeline for generation.
Args:
prompt (`List[str]`):
The prompt or prompts to guide the image generation.
reference_image (`PIL.Image.Image`):
The reference image to condition the generation on.
source_subject_category (`List[str]`):
The source subject category.
target_subject_category (`List[str]`):
The target subject category.
conditioning_image (`PIL.Image.Image`):
The conditioning canny edge image to condition the generation on.
latents (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated noisy latents, sampled from a Gaussian distribution, to be used as inputs for image
generation. Can be used to tweak the same generation with different prompts. If not provided, a latents
tensor will ge generated by random sampling.
guidance_scale (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 7.5):
Guidance scale as defined in [Classifier-Free Diffusion Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.12598).
`guidance_scale` is defined as `w` of equation 2. of [Imagen
Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.11487.pdf). Guidance scale is enabled by setting `guidance_scale >
1`. Higher guidance scale encourages to generate images that are closely linked to the text `prompt`,
usually at the expense of lower image quality.
num_inference_steps (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 50):
The number of denoising steps. More denoising steps usually lead to a higher quality image at the
expense of slower inference.
generator (`torch.Generator` or `List[torch.Generator]`, *optional*):
One or a list of [torch generator(s)](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html)
to make generation deterministic.
neg_prompt (`str`, *optional*, defaults to ""):
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored
if `guidance_scale` is less than `1`).
prompt_strength (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 1.0):
The strength of the prompt. Specifies the number of times the prompt is repeated along with prompt_reps
to amplify the prompt.
prompt_reps (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 20):
The number of times the prompt is repeated along with prompt_strength to amplify the prompt.
output_type (`str`, *optional*, defaults to `"pil"`):
The output format of the generate image. Choose between: `"pil"` (`PIL.Image.Image`), `"np"`
(`np.array`) or `"pt"` (`torch.Tensor`).
"""
width = 512
height = 512
reference_image = self.image_processor.preprocess(
reference_image,
image_mean=self.config.mean,
image_std=self.config.std,
return_tensors="pt",
)["pixel_values"]
if isinstance(prompt, str):
prompt = [prompt]
if isinstance(source_subject_category, str):
source_subject_category = [source_subject_category]
if isinstance(target_subject_category, str):
target_subject_category = [target_subject_category]
batch_size = len(prompt)
prompt = self._build_prompt(
prompts=prompt,
tgt_subjects=target_subject_category,
prompt_strength=prompt_strength,
prompt_reps=prompt_reps,
)
qformer_input = self.qformer_tokenizer(
source_subject_category, return_tensors="pt", padding=True
)
query_embeds = self.qformer(
image_input=reference_image,
text_input_ids=qformer_input.input_ids,
text_attention_mask=qformer_input.attention_mask,
)
text_embeddings = self.encode_prompt(query_embeds, prompt, device)
do_classifier_free_guidance = guidance_scale > 1.0
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
max_length = self.config.text_encoder_max_position_embeddings
uncond_input = self.tokenizer(
[neg_prompt] * batch_size,
padding="max_length",
max_length=max_length,
return_tensors="pt",
)
uncond_embeddings = self.neg_text_encoder(input_ids=uncond_input.input_ids)
# For classifier free guidance, we need to do two forward passes.
# Here we concatenate the unconditional and text embeddings into a single batch
# to avoid doing two forward passes
text_embeddings = torch.cat([uncond_embeddings, text_embeddings])
scale_down_factor = 2 ** (len(self.config.unet_block_out_channels) - 1)
latents = self.prepare_latents(
batch_size=batch_size,
num_channels=self.config.unet_in_channels,
height=height // scale_down_factor,
width=width // scale_down_factor,
generator=generator,
latents=latents,
device=None,
dtype=None,
)
# set timesteps
extra_set_kwargs = {}
self.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps, **extra_set_kwargs)
if conditioning_image:
cond_image = self.prepare_control_image(
image=conditioning_image,
width=width,
height=height,
batch_size=batch_size,
num_images_per_prompt=1,
device=None,
dtype=None,
do_classifier_free_guidance=do_classifier_free_guidance,
)
for i, t in enumerate(self.progress_bar(self.scheduler.timesteps)):
# expand the latents if we are doing classifier free guidance
do_classifier_free_guidance = guidance_scale > 1.0
latent_model_input = (
torch.cat([latents] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else latents
)
if conditioning_image:
controlnet_output = self.controlnet(
[
latent_model_input,
t,
text_embeddings,
cond_image,
]
)
noise_pred = (
self.unet(
sample=latent_model_input, timestep=t, encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings
)
if not conditioning_image
else self.unet_controlnet(
latent_model_input,
t,
text_embeddings,
*[v for _, v in controlnet_output.items()],
)
)
# perform guidance
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred.chunk(2)
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (
noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond
)
latents = self.scheduler.step(
noise_pred,
t,
latents,
)["prev_sample"]
image = self.vae(latents)
image = self.image_processor.postprocess(image, output_type=output_type)
return image
def encode_prompt(self, query_embeds, prompt, device=None):
# embeddings for prompt, with query_embeds as context
max_len = self.config.text_encoder_max_position_embeddings
max_len -= self.config.qformer_num_query_tokens
tokenized_prompt = self.tokenizer(
prompt,
padding="max_length",
truncation=True,
max_length=max_len,
return_tensors="pt",
)
batch_size = query_embeds.shape[0]
ctx_begin_pos = [self.config.ctx_begin_pos] * batch_size
text_embeddings = self.text_encoder(
input_ids=tokenized_prompt.input_ids,
ctx_embeddings=query_embeds,
ctx_begin_pos=ctx_begin_pos,
)
return text_embeddings
OvBlipDiffusionPipeline.prepare_control_image = (
diffusers.pipelines.BlipDiffusionControlNetPipeline.prepare_control_image
)
OvBlipDiffusionPipeline._build_prompt = diffusers.pipelines.BlipDiffusionPipeline._build_prompt
OvBlipDiffusionPipeline.prepare_latents = diffusers.pipelines.BlipDiffusionPipeline.prepare_latents
ov_pipe = OvBlipDiffusionPipeline()
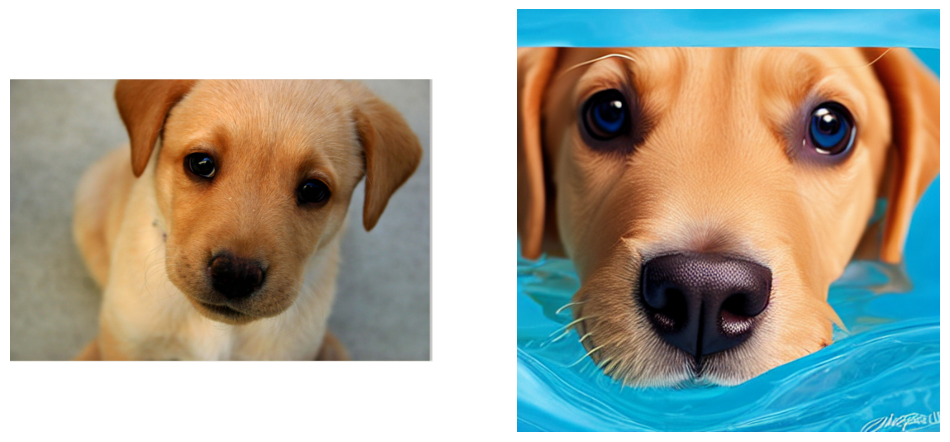
Zero-Shot subject-driven generation¶
output = ov_pipe(
text_prompt_input,
dog_img,
cond_subject,
tgt_subject,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
neg_prompt=negative_prompt
)
0%| | 0/51 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(dog_img)
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(output[0])
plt.axis("off");

Controlled subject-driven generation (Canny-edge)¶
style_subject = ["flower"] # subject that defines the style
tgt_subject = ["teapot"] # subject to generate.
text_prompt = ["on a marble table"]
cond_image = PIL.Image.open(KETTLE_IMG_PATH).resize((512, 512))
canny = controlnet_aux.CannyDetector()
cldm_cond_image = canny(cond_image, 30, 70, output_type="pil")
cldm_cond_image = [cldm_cond_image]
style_image = PIL.Image.open(FLOWER_IMG_PATH)
guidance_scale = 7.5
num_inference_steps = 50
negative_prompt = "over-exposure, under-exposure, saturated, duplicate, out of frame, lowres, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, ugly, bad anatomy, bad proportions, deformed, blurry, duplicate"
output = ov_pipe(
text_prompt,
style_image,
style_subject,
tgt_subject,
cldm_cond_image,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
neg_prompt=negative_prompt,
)
0%| | 0/51 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
title2img = {
"Conditioning image": cond_image,
"Canny-edge mask": cldm_cond_image[0],
"Style image": style_image,
"Output": output[0]
}
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4), layout="tight")
for i, (title, img) in enumerate(title2img.items()):
ax = plt.subplot(1, len(title2img), i + 1)
ax.set_title(title)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis("off")

Controlled subject-driven generation (Scribble)¶
style_subject = ["flower"] # subject that defines the style
tgt_subject = ["bag"] # subject to generate.
text_prompt = ["on a table"]
cldm_cond_image = bag_img
hed = controlnet_aux.HEDdetector.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/Annotators")
cldm_cond_image = hed(cldm_cond_image)
cldm_cond_image = [cldm_cond_image]
guidance_scale = 7.5
num_inference_steps = 50
negative_prompt = "over-exposure, under-exposure, saturated, duplicate, out of frame, lowres, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, ugly, bad anatomy, bad proportions, deformed, blurry, duplicate"
output = ov_pipe(
text_prompt,
style_image,
style_subject,
tgt_subject,
cldm_cond_image,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
neg_prompt=negative_prompt,
)
0%| | 0/51 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
title2img = {
"Conditioning image": bag_img,
"Scribble mask": cldm_cond_image[0],
"Style image": style_image,
"Output": output[0]
}
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4), layout="tight")
for i, (title, img) in enumerate(title2img.items()):
ax = plt.subplot(1, len(title2img), i + 1)
ax.set_title(title)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis("off")

Interactive inference¶
def generate(
prompt,
reference_img,
src_subject_category,
tgt_subject_category,
guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps,
seed,
neg_prompt,
_=gr.Progress(track_tqdm=True),
):
generator = torch.Generator().manual_seed(seed)
output = ov_pipe(
prompt=prompt,
reference_image=reference_img,
source_subject_category=src_subject_category,
target_subject_category=tgt_subject_category,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
generator=generator,
neg_prompt=neg_prompt,
)
return output[0]
def generate_canny(
prompt,
reference_img,
src_subject_category,
tgt_subject_category,
conditioning_image,
guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps,
seed,
neg_prompt,
_=gr.Progress(track_tqdm=True),
):
conditioning_image = conditioning_image.resize((512, 512))
canny = controlnet_aux.CannyDetector()
cldm_cond_image = canny(conditioning_image, 30, 70, output_type="pil")
cldm_cond_image = [cldm_cond_image]
generator = torch.Generator().manual_seed(seed)
output = ov_pipe(
prompt=prompt,
reference_image=reference_img,
source_subject_category=src_subject_category,
target_subject_category=tgt_subject_category,
conditioning_image=cldm_cond_image,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
generator=generator,
neg_prompt=neg_prompt,
)
return output[0]
def generate_scribble(
prompt,
reference_img,
src_subject_category,
tgt_subject_category,
conditioning_image,
guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps,
seed,
neg_prompt,
_=gr.Progress(track_tqdm=True),
):
conditioning_image = conditioning_image.resize((512, 512))
hed = controlnet_aux.HEDdetector.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/Annotators")
cldm_cond_image = hed(conditioning_image)
cldm_cond_image = [cldm_cond_image]
generator = torch.Generator().manual_seed(seed)
output = ov_pipe(
prompt=prompt,
reference_image=reference_img,
source_subject_category=src_subject_category,
target_subject_category=tgt_subject_category,
conditioning_image=cldm_cond_image,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
generator=generator,
neg_prompt=neg_prompt,
)
return output[0]
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
with gr.Tab("Zero-shot subject-driven generation"):
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column():
inputs = [
gr.Textbox(label="Prompt"),
gr.Image(label="Reference image", type="pil"),
gr.Textbox(label="Source subject category", info="String description of a subject that defines the style"),
gr.Textbox(label="Target subject category", info="String description of a subject to generate"),
gr.Slider(1.1, 10, value=7.5, label="Guidance scale", info="Higher guidance scale encourages to generate images that are closely linked to the text `prompt`, usually at the expense of lower image quality"),
gr.Slider(1, 100, value=50, label="Number of inference steps"),
gr.Slider(0, 1_000_000, value=0, label="Random seed"),
gr.Textbox(label="Negative prompt"),
]
btn = gr.Button()
with gr.Column():
output = gr.Image(type="pil")
btn.click(generate, inputs, output)
gr.Examples(
[
[
"swimming underwater",
DOG_IMG_PATH,
"dog",
"dog",
7.5,
50,
88888,
"over-exposure, under-exposure, saturated, duplicate, out of frame, lowres, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, ugly, bad anatomy, bad proportions, deformed, blurry, duplicate",
]
],
inputs,
)
with gr.Tab("Controlled subject-driven generation (Canny-edge)"):
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column():
inputs = [
gr.Textbox(label="Prompt"),
gr.Image(label="Reference image", type="pil"),
gr.Textbox(label="Source subject category", info="String description of a subject that defines the style"),
gr.Textbox(label="Target subject category", info="String description of a subject to generate"),
gr.Image(label="Conditioning image", type="pil"),
gr.Slider(1.1, 10, value=7.5, label="Guidance scale", info="Higher guidance scale encourages to generate images that are closely linked to the text `prompt`, usually at the expense of lower image quality"),
gr.Slider(1, 100, value=50, label="Number of inference steps"),
gr.Slider(0, 1_000_000, value=0, label="Random seed"),
gr.Textbox(label="Negative prompt"),
]
btn = gr.Button()
with gr.Column():
output = gr.Image(type="pil")
btn.click(generate_canny, inputs, output)
gr.Examples(
[
[
"on a marble table",
FLOWER_IMG_PATH,
"flower",
"teapot",
KETTLE_IMG_PATH,
7.5,
50,
88888,
"over-exposure, under-exposure, saturated, duplicate, out of frame, lowres, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, ugly, bad anatomy, bad proportions, deformed, blurry, duplicate",
]
],
inputs,
)
with gr.Tab("Controlled subject-driven generation (Scribble)"):
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column():
inputs = [
gr.Textbox(label="Prompt"),
gr.Image(label="Reference image", type="pil"),
gr.Textbox(label="Source subject category", info="String description of a subject that defines the style"),
gr.Textbox(label="Target subject category", info="String description of a subject to generate"),
gr.Image(label="Conditioning image", type="pil"),
gr.Slider(1.1, 10, value=7.5, label="Guidance scale", info="Higher guidance scale encourages to generate images that are closely linked to the text `prompt`, usually at the expense of lower image quality"),
gr.Slider(1, 100, value=50, label="Number of inference steps"),
gr.Slider(0, 1_000_000, value=0, label="Random seed"),
gr.Textbox(label="Negative prompt"),
]
btn = gr.Button()
with gr.Column():
output = gr.Image(type="pil")
btn.click(generate_scribble, inputs, output)
gr.Examples(
[
[
"on a table",
FLOWER_IMG_PATH,
"flower",
"bag",
BAG_IMG_PATH,
7.5,
50,
88888,
"over-exposure, under-exposure, saturated, duplicate, out of frame, lowres, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, ugly, bad anatomy, bad proportions, deformed, blurry, duplicate",
]
],
inputs,
)
try:
demo.queue().launch(debug=False)
except Exception:
demo.queue().launch(share=True, debug=False)
# if you are launching remotely, specify server_name and server_port
# demo.launch(server_name='your server name', server_port='server port in int')
# Read more in the docs: https://gradio.app/docs/