Photos to Anime with PaddleGAN and OpenVINO¶
This Jupyter notebook can be launched on-line, opening an interactive environment in a browser window. You can also make a local installation. Choose one of the following options:
This tutorial demonstrates converting a PaddlePaddle/PaddleGAN AnimeGAN model to OpenVINO IR format, and shows inference results on the PaddleGAN and OpenVINO IR models.
For more information about the model, see PaddleGAN’s AnimeGAN documentation

anime¶
Table of contents:¶
Preparation¶
Install requirements¶
%pip install -q "openvino>=2023.1.0"
%pip install -q "paddlepaddle>=2.5.1" "paddle2onnx>=0.6"
%pip install -q "git+https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleGAN.git" --no-deps
%pip install -q opencv-python matplotlib scikit-learn scikit-image
%pip install -q "imageio==2.9.0" "imageio-ffmpeg" "numba>=0.53.1" easydict munch natsort
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
ERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.
paddleclas 2.5.1 requires faiss-cpu==1.7.1.post2, but you have faiss-cpu 1.7.4 which is incompatible.
paddleclas 2.5.1 requires gast==0.3.3, but you have gast 0.4.0 which is incompatible.
ppgan 2.1.0 requires librosa==0.8.1, but you have librosa 0.10.1 which is incompatible.
ppgan 2.1.0 requires opencv-python<=4.6.0.66, but you have opencv-python 4.9.0.80 which is incompatible.
scikit-image 0.21.0 requires imageio>=2.27, but you have imageio 2.9.0 which is incompatible.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Imports¶
import sys
import time
import os
from pathlib import Path
import urllib.request
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import openvino as ov
from IPython.display import HTML, display
# PaddlePaddle requires a C++ compiler. If importing the paddle packages fails,
# install C++.
try:
import paddle
from paddle.static import InputSpec
from ppgan.apps import AnimeGANPredictor
except NameError:
if sys.platform == "win32":
install_message = (
"To use this notebook, please install the free Microsoft "
"Visual C++ redistributable from <a href='https://aka.ms/vs/16/release/vc_redist.x64.exe'>"
"https://aka.ms/vs/16/release/vc_redist.x64.exe</a>"
)
else:
install_message = (
"To use this notebook, please install a C++ compiler. On macOS, "
"`xcode-select --install` installs many developer tools, including C++. On Linux, "
"install gcc with your distribution's package manager."
)
display(
HTML(
f"""<div class="alert alert-danger" ><i>
<b>Error: </b>PaddlePaddle requires installation of C++. {install_message}"""
)
)
raise
Settings¶
MODEL_DIR = "model"
MODEL_NAME = "paddlegan_anime"
os.makedirs(MODEL_DIR, exist_ok=True)
# Create filenames of the models that will be converted in this notebook.
model_path = Path(f"{MODEL_DIR}/{MODEL_NAME}")
ir_path = model_path.with_suffix(".xml")
onnx_path = model_path.with_suffix(".onnx")
Functions¶
def resize_to_max_width(image, max_width):
"""
Resize `image` to `max_width`, preserving the aspect ratio of the image.
"""
if image.shape[1] > max_width:
hw_ratio = image.shape[0] / image.shape[1]
new_height = int(max_width * hw_ratio)
image = cv2.resize(image, (max_width, new_height))
return image
Inference on PaddleGAN Model¶
The PaddleGAN
documentation
explains how to run the model with .run() method. Find out what that
function does with Jupyter’s ?? shortcut to show the docstring and
source of the function.
# This cell will initialize the AnimeGANPredictor() and download the weights from PaddlePaddle.
# This may take a while. The weights are stored in a cache and are downloaded once.
predictor = AnimeGANPredictor()
[02/09 23:41:27] ppgan INFO: Found /opt/home/k8sworker/.cache/ppgan/animeganv2_hayao.pdparams
# In a Jupyter Notebook, ?? shows the source and docstring
predictor.run??
The AnimeGANPredictor.run() method works as follow:
Loads an image with OpenCV and converts it to RGB.
Transforms the image.
Propagates the transformed image through the generator model and postprocesses the results to return an array with a [0,255] range.
Transposes the result from (C,H,W) to (H,W,C) shape.
Resizes the result image to the original image size.
(optional) Adjusts the brightness of the result image.
Saves the image.
You can execute these steps manually and confirm that the result looks
correct. To speed up inference time, resize large images before
propagating them through the network. The inference step in the next
cell will still take some time to execute. If you want to skip this
step, set PADDLEGAN_INFERENCE = False in the first line of the next
cell.
PADDLEGAN_INFERENCE = True
OUTPUT_DIR = "output"
os.makedirs(OUTPUT_DIR, exist_ok=True)
# Step 1. Load the image and convert to RGB.
image_path = Path("./data/coco_bricks.png")
# fetch the image from the web
image_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
urllib.request.urlretrieve(
"https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/openvino_notebooks/data/data/image/coco_bricks.png",
image_path
)
image = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(str(image_path), flags=cv2.IMREAD_COLOR), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
## Inference takes a long time on large images. Resize to a max width of 600.
image = resize_to_max_width(image, 600)
# Step 2. Transform the image.
transformed_image = predictor.transform(image)
input_tensor = paddle.to_tensor(transformed_image[None, ::])
if PADDLEGAN_INFERENCE:
# Step 3. Do inference.
predictor.generator.eval()
with paddle.no_grad():
result = predictor.generator(input_tensor)
# Step 4. Convert the inference result to an image, following the same steps as
# PaddleGAN's predictor.run() function.
result_image_pg = (result * 0.5 + 0.5)[0].numpy() * 255
result_image_pg = result_image_pg.transpose((1, 2, 0))
# Step 5. Resize the result image.
result_image_pg = cv2.resize(result_image_pg, image.shape[:2][::-1])
# Step 6. Adjust the brightness.
result_image_pg = predictor.adjust_brightness(result_image_pg, image)
# Step 7. Save the result image.
anime_image_path_pg = Path(f"{OUTPUT_DIR}/{image_path.stem}_anime_pg").with_suffix(".jpg")
if cv2.imwrite(str(anime_image_path_pg), result_image_pg[:, :, (2, 1, 0)]):
print(f"The anime image was saved to {anime_image_path_pg}")
The anime image was saved to output/coco_bricks_anime_pg.jpg
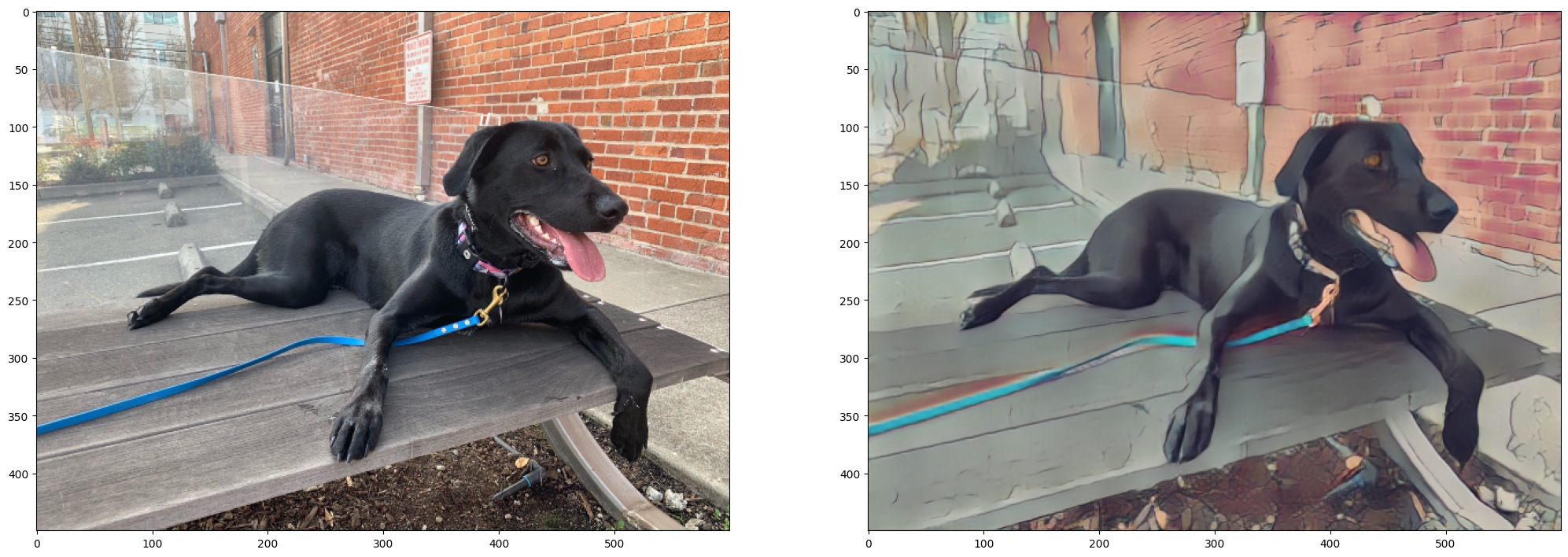
Show Inference Results on PaddleGAN model¶
if PADDLEGAN_INFERENCE:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(25, 15))
ax[0].imshow(image)
ax[1].imshow(result_image_pg)
else:
print("PADDLEGAN_INFERENCE is not enabled. Set PADDLEGAN_INFERENCE = True in the previous cell and run that cell to show inference results.")

Model Conversion to ONNX and OpenVINO IR¶
Convert the PaddleGAN model to OpenVINO IR by first converting PaddleGAN
to ONNX with paddle2onnx and then converting the ONNX model to
OpenVINO IR with model conversion API.
Convert to ONNX¶
Exporting to ONNX requires specifying an input shape with PaddlePaddle
InputSpec and calling paddle.onnx.export. Then, check the input
shape of the transformed image and use that as the input shape for the
ONNX model. Exporting to ONNX should not take long. If the export
succeeds, the output of the next cell will include
ONNX model saved in paddlegan_anime.onnx.
target_height, target_width = transformed_image.shape[1:]
target_height, target_width
(448, 576)
predictor.generator.eval()
x_spec = InputSpec([None, 3, target_height, target_width], "float32", "x")
paddle.onnx.export(predictor.generator, str(model_path), input_spec=[x_spec], opset_version=11)
2024-02-09 23:41:36 [INFO] Static PaddlePaddle model saved in model/paddle_model_static_onnx_temp_dir.
[Paddle2ONNX] Start to parse PaddlePaddle model...
[Paddle2ONNX] Model file path: model/paddle_model_static_onnx_temp_dir/model.pdmodel
[Paddle2ONNX] Paramters file path: model/paddle_model_static_onnx_temp_dir/model.pdiparams
[Paddle2ONNX] Start to parsing Paddle model...
[Paddle2ONNX] Use opset_version = 11 for ONNX export.
[Paddle2ONNX] PaddlePaddle model is exported as ONNX format now.
2024-02-09 23:41:36 [INFO] ONNX model saved in model/paddlegan_anime.onnx.
I0209 23:41:36.202327 2843665 program_interpreter.cc:212] New Executor is Running.
Convert to OpenVINO IR¶
The OpenVINO IR format enables storing the preprocessing normalization
in the model file. It is then no longer necessary to normalize input
images manually. See the transforms that the .run() method used:
predictor.__init__??
t = predictor.transform.transforms[0]
t.params
{'taget_size': (448, 576)}
## Uncomment the line below to see the documentation and code of the ResizeToScale transformation
# t??
There are three transformations: resize, transpose, and normalize, where
normalize uses a mean and scale of [127.5, 127.5, 127.5].
The ResizeToScale class is called with (256,256) as the argument
for size. Further analysis shows that this is the minimum size to resize
to. The ResizeToScale class transform resizes images to the size
specified in the ResizeToScale parameters, with width and height as
multiples of 32. We will preprocess the images the same way before
feeding them to the converted model.
Now we use model conversion API and convert the model to OpenVINO IR.
Convert ONNX Model to OpenVINO IR withModel Conversion Python API
print("Exporting ONNX model to OpenVINO IR... This may take a few minutes.")
model = ov.convert_model(
onnx_path,
input=[1, 3, target_height, target_width],
)
# Serialize model in IR format
ov.save_model(model, str(ir_path))
Exporting ONNX model to OpenVINO IR... This may take a few minutes.
Show Inference Results on OpenVINO IR and PaddleGAN Models¶
If the conversion is successful, the output of model conversion API in the cell above will show SUCCESS, and the OpenVINO IR model will be generated.
Now, use the model for inference with the adjust_brightness() method
from the PaddleGAN model. However, in order to use the OpenVINO IR model
without installing PaddleGAN, it is useful to check what these functions
do and extract them.
Create Postprocessing Functions¶
predictor.adjust_brightness??
predictor.calc_avg_brightness??
The average brightness is computed by a standard formula. To adjust the brightness, the difference in brightness between the source and destination (anime) image is computed and the brightness of the destination image is adjusted based on that. Then, the image is converted to an 8-bit image.
Copy these functions to the next cell, use them for inference on the OpenVINO IR model
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0
def calc_avg_brightness(img):
R = img[..., 0].mean()
G = img[..., 1].mean()
B = img[..., 2].mean()
brightness = 0.299 * R + 0.587 * G + 0.114 * B
return brightness, B, G, R
def adjust_brightness(dst, src):
brightness1, B1, G1, R1 = AnimeGANPredictor.calc_avg_brightness(src)
brightness2, B2, G2, R2 = AnimeGANPredictor.calc_avg_brightness(dst)
brightness_difference = brightness1 / brightness2
dstf = dst * brightness_difference
dstf = np.clip(dstf, 0, 255)
dstf = np.uint8(dstf)
return dstf
Do Inference on OpenVINO IR Model¶
Load the OpenVINO IR model and do inference, following the same steps as for the PaddleGAN model. For more information about inference on OpenVINO IR models, see the OpenVINO Runtime API notebook.
The OpenVINO IR model is generated with an input shape that is computed based on the input image. If you do inference on images with different input shapes, results may differ from the PaddleGAN results.
Select inference device¶
select device from dropdown list for running inference using OpenVINO
import ipywidgets as widgets
core = ov.Core()
device = widgets.Dropdown(
options=core.available_devices + ["AUTO"],
value='AUTO',
description='Device:',
disabled=False,
)
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
# Load and prepare the IR model.
core = ov.Core()
model = core.read_model(model=ir_path)
compiled_model = core.compile_model(model=model, device_name=device.value)
input_key = compiled_model.input(0)
output_key = compiled_model.output(0)
# Step 1. Load an image and convert it to RGB.
image_path = Path("./data/coco_bricks.png")
image = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(str(image_path), flags=cv2.IMREAD_COLOR), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Step 2. Do preprocess transformations.
# Resize the image
resized_image = cv2.resize(image, (target_width, target_height))
input_image = resized_image.transpose(2, 0, 1)[None, :, :, :]
# Normalize the image
input_mean = np.array([127.5,127.5,127.5]).reshape(1, 3, 1, 1)
input_scale = np.array([127.5,127.5,127.5]).reshape(1, 3, 1, 1)
input_image = (input_image - input_mean) / input_scale
# Step 3. Do inference.
result_ir = compiled_model([input_image])[output_key]
# Step 4. Convert the inference result to an image, following the same steps as
# PaddleGAN's predictor.run() function.
result_image_ir = (result_ir * 0.5 + 0.5)[0] * 255
result_image_ir = result_image_ir.transpose((1, 2, 0))
# Step 5. Resize the result image.
result_image_ir = cv2.resize(result_image_ir, image.shape[:2][::-1])
# Step 6. Adjust the brightness.
result_image_ir = adjust_brightness(result_image_ir, image)
# Step 7. Save the result image.
anime_fn_ir = Path(f"{OUTPUT_DIR}/{image_path.stem}_anime_ir").with_suffix(".jpg")
if cv2.imwrite(str(anime_fn_ir), result_image_ir[:, :, (2, 1, 0)]):
print(f"The anime image was saved to {anime_fn_ir}")
The anime image was saved to output/coco_bricks_anime_ir.jpg
Show Inference Results
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(25, 15))
ax[0].imshow(image)
ax[1].imshow(result_image_ir)
ax[0].set_title("Image")
ax[1].set_title("OpenVINO IR result");
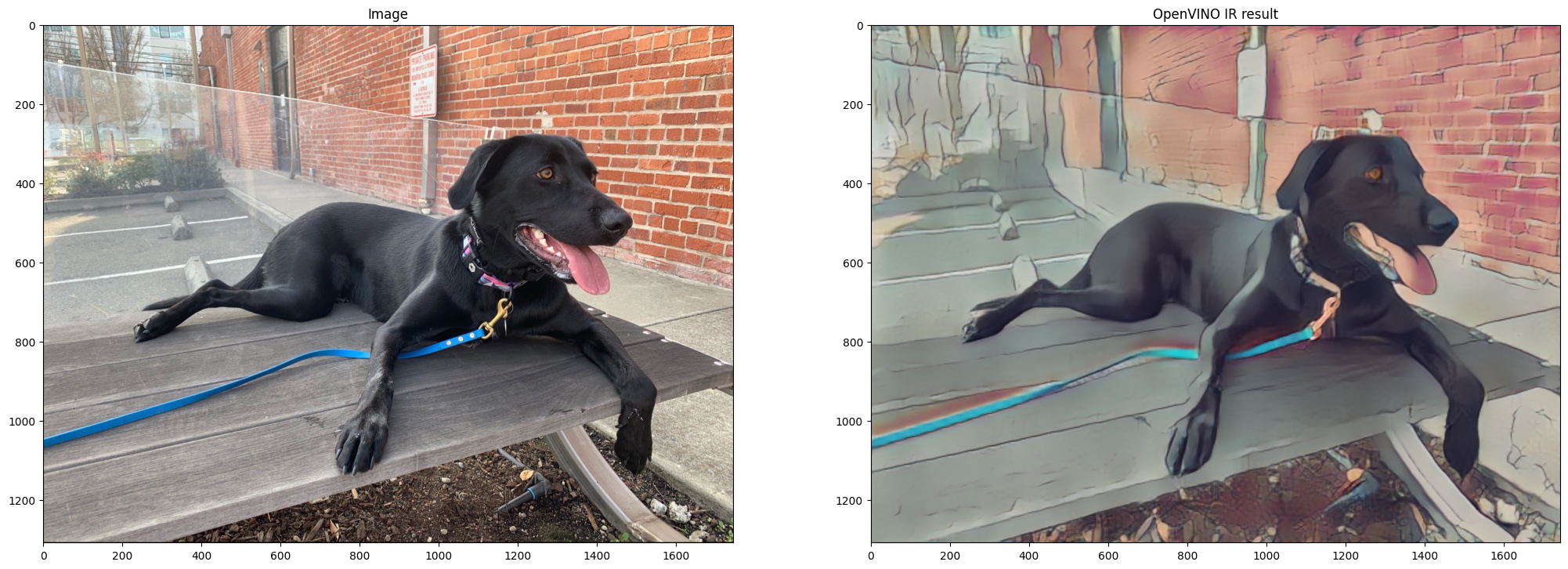
Performance Comparison¶
Measure the time it takes to do inference on an image. This gives an indication of performance. It is not a perfect measure. Since the PaddleGAN model requires quite a bit of memory for inference, only measure inference on one image. For more accurate benchmarking, use Benchmark Tool.
NUM_IMAGES = 1
start = time.perf_counter()
for _ in range(NUM_IMAGES):
compiled_model([input_image])
end = time.perf_counter()
time_ir = end - start
print(
f"OpenVINO IR model in OpenVINO Runtime/CPU: {time_ir/NUM_IMAGES:.3f} "
f"seconds per image, FPS: {NUM_IMAGES/time_ir:.2f}"
)
## `PADDLEGAN_INFERENCE` is defined in the "Inference on PaddleGAN model" section above.
## Uncomment the next line to enable a performance comparison with the PaddleGAN model
## if you disabled it earlier.
# PADDLEGAN_INFERENCE = True
if PADDLEGAN_INFERENCE:
with paddle.no_grad():
start = time.perf_counter()
for _ in range(NUM_IMAGES):
predictor.generator(input_tensor)
end = time.perf_counter()
time_paddle = end - start
print(
f"PaddleGAN model on CPU: {time_paddle/NUM_IMAGES:.3f} seconds per image, "
f"FPS: {NUM_IMAGES/time_paddle:.2f}"
)
OpenVINO IR model in OpenVINO Runtime/CPU: 0.427 seconds per image, FPS: 2.34
PaddleGAN model on CPU: 6.182 seconds per image, FPS: 0.16
References¶
The PaddleGAN code that is shown in this notebook is written by PaddlePaddle Authors and licensed under the Apache 2.0 license. The license for this code is displayed below.
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
#
#Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
#you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
#You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
#Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
#distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
#WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
#See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
#limitations under the License.