Single Image Super Resolution with OpenVINO™¶
This Jupyter notebook can be launched on-line, opening an interactive environment in a browser window. You can also make a local installation. Choose one of the following options:
Super Resolution is the process of enhancing the quality of an image by increasing the pixel count using deep learning. This notebook shows the Single Image Super Resolution (SISR) which takes just one low resolution image. A model called single-image-super-resolution-1032, which is available in Open Model Zoo, is used in this tutorial. It is based on the research paper cited below.
Y. Liu et al., “An Attention-Based Approach for Single Image Super Resolution,” 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2018, pp. 2777-2784, doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2018.8545760.
Table of contents:¶
Preparation¶
Install requirements¶
%pip install -q "openvino>=2023.1.0"
%pip install -q opencv-python
%pip install -q pillow matplotlib
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Imports¶
import os
import time
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from IPython.display import HTML, FileLink
from IPython.display import Image as DisplayImage
from IPython.display import Pretty, ProgressBar, clear_output, display
from PIL import Image
import openvino as ov
# Define a download file helper function
def download_file(url: str, path: Path) -> None:
"""Download file."""
import urllib.request
path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, path)
Settings¶
Select inference device¶
select device from dropdown list for running inference using OpenVINO
import ipywidgets as widgets
core = ov.Core()
device = widgets.Dropdown(
options=core.available_devices + ["AUTO"],
value='AUTO',
description='Device:',
disabled=False,
)
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
# 1032: 4x superresolution, 1033: 3x superresolution
model_name = 'single-image-super-resolution-1032'
base_model_dir = Path("./model").expanduser()
model_xml_name = f'{model_name}.xml'
model_bin_name = f'{model_name}.bin'
model_xml_path = base_model_dir / model_xml_name
model_bin_path = base_model_dir / model_bin_name
if not model_xml_path.exists():
base_url = f'https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/open_model_zoo/2023.0/models_bin/1/{model_name}/FP16/'
model_xml_url = base_url + model_xml_name
model_bin_url = base_url + model_bin_name
download_file(model_xml_url, model_xml_path)
download_file(model_bin_url, model_bin_path)
else:
print(f'{model_name} already downloaded to {base_model_dir}')
def write_text_on_image(image: np.ndarray, text: str) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Write the specified text in the top left corner of the image
as white text with a black border.
:param image: image as numpy arry with HWC shape, RGB or BGR
:param text: text to write
:return: image with written text, as numpy array
"""
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN
org = (20, 20)
font_scale = 4
font_color = (255, 255, 255)
line_type = 1
font_thickness = 2
text_color_bg = (0, 0, 0)
x, y = org
image = cv2.UMat(image)
(text_w, text_h), _ = cv2.getTextSize(text, font, font_scale, font_thickness)
result_im = cv2.rectangle(image, org, (x + text_w, y + text_h), text_color_bg, -1)
textim = cv2.putText(
result_im,
text,
(x, y + text_h + font_scale - 1),
font,
font_scale,
font_color,
font_thickness,
line_type,
)
return textim.get()
def convert_result_to_image(result) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Convert network result of floating point numbers to image with integer
values from 0-255. Values outside this range are clipped to 0 and 255.
:param result: a single superresolution network result in N,C,H,W shape
"""
result = result.squeeze(0).transpose(1, 2, 0)
result *= 255
result[result < 0] = 0
result[result > 255] = 255
result = result.astype(np.uint8)
return result
def to_rgb(image_data) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Convert image_data from BGR to RGB
"""
return cv2.cvtColor(image_data, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
Load the Superresolution Model¶
The Super Resolution model expects two inputs: the input image and a bicubic interpolation of the input image to the target size of 1920x1080. It returns the super resolution version of the image in 1920x1800 (for the default superresolution model (1032)).
Load the model in OpenVINO Runtime with core.read_model, compile it
for the specified device with core.compile_model, and get
information about the network inputs and outputs.
core = ov.Core()
model = core.read_model(model=model_xml_path)
compiled_model = core.compile_model(model=model, device_name=device.value)
# Network inputs and outputs are dictionaries. Get the keys for the
# dictionaries.
original_image_key, bicubic_image_key = compiled_model.inputs
output_key = compiled_model.output(0)
# Get the expected input and target shape. The `.dims[2:]` returns the height
# and width. The `resize` function of OpenCV expects the shape as (width, height),
# so reverse the shape with `[::-1]` and convert it to a tuple.
input_height, input_width = list(original_image_key.shape)[2:]
target_height, target_width = list(bicubic_image_key.shape)[2:]
upsample_factor = int(target_height / input_height)
print(f"The network expects inputs with a width of {input_width}, " f"height of {input_height}")
print(f"The network returns images with a width of {target_width}, " f"height of {target_height}")
print(
f"The image sides are upsampled by a factor of {upsample_factor}. "
f"The new image is {upsample_factor**2} times as large as the "
"original image"
)
The network expects inputs with a width of 480, height of 270
The network returns images with a width of 1920, height of 1080
The image sides are upsampled by a factor of 4. The new image is 16 times as large as the original image
Load and Show the Input Image¶
NOTE: For the best results, use raw images (like
TIFF,BMPorPNG). Compressed images (likeJPEG) may appear distorted after processing with the super resolution model.
IMAGE_PATH = Path("./data/tower.jpg")
OUTPUT_PATH = Path("output/")
os.makedirs(str(OUTPUT_PATH), exist_ok=True)
download_file('https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/openvino_notebooks/data/data/image/tower.jpg', IMAGE_PATH)
full_image = cv2.imread(str(IMAGE_PATH))
# Uncomment these lines to load a raw image as BGR.
# import rawpy
# with rawpy.imread(IMAGE_PATH) as raw:
# full_image = raw.postprocess()[:,:,(2,1,0)]
plt.imshow(to_rgb(full_image))
print(f"Showing full image with width {full_image.shape[1]} " f"and height {full_image.shape[0]}")
Showing full image with width 5976 and height 3770

Superresolution on a Crop of the Image¶
Crop the Input Image once.¶
Crop the network input size. Give the X (width) and Y (height)
coordinates for the top left corner of the crop. Set the CROP_FACTOR
variable to 2 to make a crop that is larger than the network input size
(this only works with the single-image-super-resolution-1032 model).
The crop will be downsampled before propagating to the network. This is
useful for very high resolution images, where a crop of the network
input size is too small to show enough information. It can also improve
the result. Keep in mind that with a CROP_FACTOR or 2 the net
upsampling factor will be halved. If the superresolution network
increases the side lengths of the image by a factor of 4, it upsamples a
480x270 crop to 1920x1080. With a CROP_FACTOR of 2, a 960x540 crop
is upsampled to the same 1920x1080: the side lengths are twice as large
as the crop size.
# Set `CROP_FACTOR` to 2 to crop with twice the input width and height
# This only works with the 1032 (4x) superresolution model!
# Set it to 1 to crop the image with the exact input size.
CROP_FACTOR = 2
adjusted_upsample_factor = upsample_factor // CROP_FACTOR
image_id = "flag" # A tag to recognize the saved images.
starty = 3200
startx = 0
# Perform the crop.
image_crop = full_image[
starty : starty + input_height * CROP_FACTOR,
startx : startx + input_width * CROP_FACTOR,
]
# Show the cropped image.
print(f"Showing image crop with width {image_crop.shape[1]} and " f"height {image_crop.shape[0]}.")
plt.imshow(to_rgb(image_crop));
Showing image crop with width 960 and height 540.
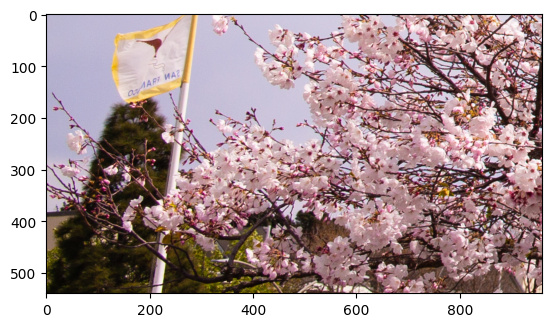
Reshape/Resize Crop for Model Input¶
The input image is resized to a network input size, and reshaped to (N,C,H,W) (N=number of images, C=number of channels, H=height, W=width). The image is also resized to the network output size, with bicubic interpolation. This bicubic image is the second input to the network.
# Resize the image to the target shape with bicubic interpolation.
bicubic_image = cv2.resize(
src=image_crop, dsize=(target_width, target_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC
)
# If required, resize the image to the input image shape.
if CROP_FACTOR > 1:
image_crop = cv2.resize(src=image_crop, dsize=(input_width, input_height))
# Reshape the images from (H,W,C) to (N,C,H,W).
input_image_original = np.expand_dims(image_crop.transpose(2, 0, 1), axis=0)
input_image_bicubic = np.expand_dims(bicubic_image.transpose(2, 0, 1), axis=0)
Do Inference¶
Do inference and convert the inference result to an RGB image.
result = compiled_model(
{
original_image_key.any_name: input_image_original,
bicubic_image_key.any_name: input_image_bicubic,
}
)[output_key]
# Get inference result as numpy array and reshape to image shape and data type
result_image = convert_result_to_image(result)
Show and Save Results¶
Show the bicubic image and the enhanced superresolution image.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(30, 15))
ax[0].imshow(to_rgb(bicubic_image))
ax[1].imshow(to_rgb(result_image))
ax[0].set_title("Bicubic")
ax[1].set_title("Superresolution")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Superresolution')
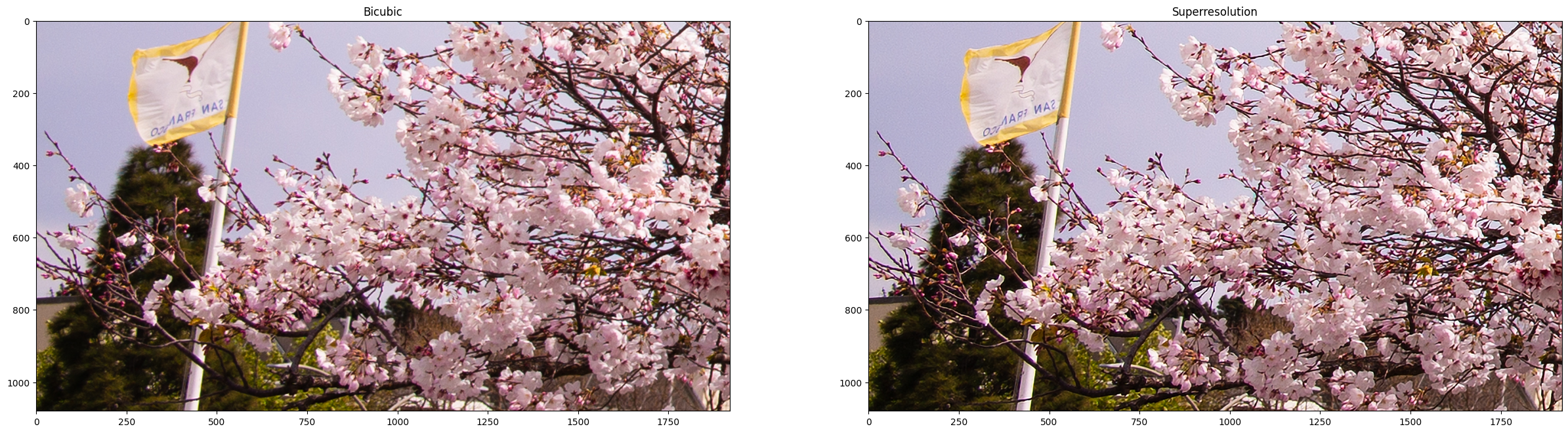
Save Superresolution and Bicubic Image Crop¶
# Add a text with "SUPER" or "BICUBIC" to the superresolution or bicubic image.
image_super = write_text_on_image(image=result_image, text="SUPER")
image_bicubic = write_text_on_image(image=bicubic_image, text="BICUBIC")
# Store the image and the results.
crop_image_path = Path(f"{OUTPUT_PATH.stem}/{image_id}_{adjusted_upsample_factor}x_crop.png")
superres_image_path = Path(
f"{OUTPUT_PATH.stem}/{image_id}_{adjusted_upsample_factor}x_crop_superres.png"
)
bicubic_image_path = Path(
f"{OUTPUT_PATH.stem}/{image_id}_{adjusted_upsample_factor}x_crop_bicubic.png"
)
cv2.imwrite(filename=str(crop_image_path), img=image_crop, params=[cv2.IMWRITE_PNG_COMPRESSION, 0])
cv2.imwrite(
filename=str(superres_image_path), img=image_super, params=[cv2.IMWRITE_PNG_COMPRESSION, 0]
)
cv2.imwrite(
filename=str(bicubic_image_path), img=image_bicubic, params=[cv2.IMWRITE_PNG_COMPRESSION, 0]
)
print(f"Images written to directory: {OUTPUT_PATH}")
Images written to directory: output
Write Animated GIF with Bicubic/Superresolution Comparison¶
print(image_bicubic.shape)
print(image_super.shape)
result_pil = Image.fromarray(to_rgb(image_super))
bicubic_pil = Image.fromarray(to_rgb(image_bicubic))
gif_image_path = Path(f"{OUTPUT_PATH.stem}/{image_id}_comparison_{adjusted_upsample_factor}x.gif")
result_pil.save(
fp=str(gif_image_path),
format="GIF",
append_images=[bicubic_pil],
save_all=True,
duration=1000,
loop=0,
)
# The `DisplayImage(str(gif_image_path))` function does not work in Colab.
DisplayImage(data=open(gif_image_path, "rb").read(), width=1920 // 2)
(1080, 1920, 3)
(1080, 1920, 3)

Create a Video with Sliding Bicubic/Superresolution Comparison¶
This may take a while. For the video, the superresolution and bicubic
image are resized by a factor of 2 to improve processing speed. This
gives an indication of the superresolution effect. The video is saved as
an .avi file. You can click on the link to download the video, or
open it directly from the output/ directory, and play it locally. >
Note: If you run the example in Google Colab, download video files using
the Files tool.
FOURCC = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG")
result_video_path = Path(
f"{OUTPUT_PATH.stem}/{image_id}_crop_comparison_{adjusted_upsample_factor}x.avi"
)
video_target_height, video_target_width = (
result_image.shape[0] // 2,
result_image.shape[1] // 2,
)
out_video = cv2.VideoWriter(
filename=str(result_video_path),
fourcc=FOURCC,
fps=90,
frameSize=(video_target_width, video_target_height),
)
resized_result_image = cv2.resize(src=result_image, dsize=(video_target_width, video_target_height))
resized_bicubic_image = cv2.resize(
src=bicubic_image, dsize=(video_target_width, video_target_height)
)
progress_bar = ProgressBar(total=video_target_width)
progress_bar.display()
for i in range(video_target_width):
# Create a frame where the left part (until i pixels width) contains the
# superresolution image, and the right part (from i pixels width) contains
# the bicubic image.
comparison_frame = np.hstack(
(
resized_result_image[:, :i, :],
resized_bicubic_image[:, i:, :],
)
)
# Create a small black border line between the superresolution
# and bicubic part of the image.
comparison_frame[:, i - 1 : i + 1, :] = 0
out_video.write(image=comparison_frame)
progress_bar.progress = i
progress_bar.update()
out_video.release()
clear_output()
video_link = FileLink(result_video_path)
video_link.html_link_str = "<a href='%s' download>%s</a>"
display(HTML(f"The video has been saved to {video_link._repr_html_()}"))
Superresolution on full input image¶
Superresolution on the full image is done by dividing the image into patches of equal size, doing superresolution on each path, and then stitching the resulting patches together again. For this demo, patches near the border of the image are ignored.
Adjust the CROPLINES setting in the next cell if you see boundary
effects.
Compute patches¶
# Set the number of lines to crop from the network result to prevent
# boundary effects. The value of `CROPLINES` should be an integer >= 1.
CROPLINES = 10
# See Superresolution on one crop of the image for description of `CROP_FACTOR`.
CROP_FACTOR = 2
full_image_height, full_image_width = full_image.shape[:2]
# Compute x and y coordinates of left top of image tiles.
x_coords = list(range(0, full_image_width, input_width * CROP_FACTOR - CROPLINES * 2))
while full_image_width - x_coords[-1] < input_width * CROP_FACTOR:
x_coords.pop(-1)
y_coords = list(range(0, full_image_height, input_height * CROP_FACTOR - CROPLINES * 2))
while full_image_height - y_coords[-1] < input_height * CROP_FACTOR:
y_coords.pop(-1)
# Compute the width and height to crop the full image. The full image is
# cropped at the border to tiles of the input size.
crop_width = x_coords[-1] + input_width * CROP_FACTOR
crop_height = y_coords[-1] + input_height * CROP_FACTOR
# Compute the width and height of the target superresolution image.
new_width = (
x_coords[-1] * (upsample_factor // CROP_FACTOR)
+ target_width
- CROPLINES * 2 * (upsample_factor // CROP_FACTOR)
)
new_height = (
y_coords[-1] * (upsample_factor // CROP_FACTOR)
+ target_height
- CROPLINES * 2 * (upsample_factor // CROP_FACTOR)
)
print(f"The output image will have a width of {new_width} " f"and a height of {new_height}")
The output image will have a width of 11280 and a height of 7280
Do Inference¶
The code below reads one patch of the image at a time. Each patch is
reshaped to the network input shape and upsampled with bicubic
interpolation to the target shape. Both the original and the bicubic
images are propagated through the network. The network result is a numpy
array with floating point values, with a shape of (1,3,1920,1080).
This array is converted to an 8-bit image with the (1080,1920,3)
shape and written to a full_superresolution_image. The bicubic image
is written to a full_bicubic_image for comparison. A progress bar
shows the progress of the process. Inference time is measured, as well
as total time to process each patch.
start_time = time.perf_counter()
patch_nr = 0
num_patches = len(x_coords) * len(y_coords)
progress_bar = ProgressBar(total=num_patches)
progress_bar.display()
# Crop image to fit tiles of the input size.
full_image_crop = full_image.copy()[:crop_height, :crop_width, :]
# Create an empty array of the target size.
full_superresolution_image = np.empty((new_height, new_width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# Create a bicubic upsampled image of the target size for comparison.
full_bicubic_image = cv2.resize(
src=full_image_crop[CROPLINES:-CROPLINES, CROPLINES:-CROPLINES, :],
dsize=(new_width, new_height),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC,
)
total_inference_duration = 0
for y in y_coords:
for x in x_coords:
patch_nr += 1
# Crop the input image.
image_crop = full_image_crop[
y : y + input_height * CROP_FACTOR,
x : x + input_width * CROP_FACTOR,
]
# Resize the images to the target shape with bicubic interpolation
bicubic_image = cv2.resize(
src=image_crop,
dsize=(target_width, target_height),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC,
)
if CROP_FACTOR > 1:
image_crop = cv2.resize(src=image_crop, dsize=(input_width, input_height))
input_image_original = np.expand_dims(image_crop.transpose(2, 0, 1), axis=0)
input_image_bicubic = np.expand_dims(bicubic_image.transpose(2, 0, 1), axis=0)
# Do inference.
inference_start_time = time.perf_counter()
result = compiled_model(
{
original_image_key.any_name: input_image_original,
bicubic_image_key.any_name: input_image_bicubic,
}
)[output_key]
inference_stop_time = time.perf_counter()
inference_duration = inference_stop_time - inference_start_time
total_inference_duration += inference_duration
# Reshape an inference result to the image shape and the data type.
result_image = convert_result_to_image(result)
# Add the inference result of this patch to the full superresolution
# image.
adjusted_upsample_factor = upsample_factor // CROP_FACTOR
new_y = y * adjusted_upsample_factor
new_x = x * adjusted_upsample_factor
full_superresolution_image[
new_y : new_y + target_height - CROPLINES * adjusted_upsample_factor * 2,
new_x : new_x + target_width - CROPLINES * adjusted_upsample_factor * 2,
] = result_image[
CROPLINES * adjusted_upsample_factor : -CROPLINES * adjusted_upsample_factor,
CROPLINES * adjusted_upsample_factor : -CROPLINES * adjusted_upsample_factor,
:,
]
progress_bar.progress = patch_nr
progress_bar.update()
if patch_nr % 10 == 0:
clear_output(wait=True)
progress_bar.display()
display(
Pretty(
f"Processed patch {patch_nr}/{num_patches}. "
f"Inference time: {inference_duration:.2f} seconds "
f"({1/inference_duration:.2f} FPS)"
)
)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
duration = end_time - start_time
clear_output(wait=True)
print(
f"Processed {num_patches} patches in {duration:.2f} seconds. "
f"Total patches per second (including processing): "
f"{num_patches/duration:.2f}.\nInference patches per second: "
f"{num_patches/total_inference_duration:.2f} "
)
Processed 42 patches in 4.64 seconds. Total patches per second (including processing): 9.05.
Inference patches per second: 17.92
Save superresolution image and the bicubic image¶
full_superresolution_image_path = Path(
f"{OUTPUT_PATH.stem}/full_superres_{adjusted_upsample_factor}x.jpg"
)
full_bicubic_image_path = Path(f"{OUTPUT_PATH.stem}/full_bicubic_{adjusted_upsample_factor}x.jpg")
cv2.imwrite(str(full_superresolution_image_path), full_superresolution_image)
cv2.imwrite(str(full_bicubic_image_path), full_bicubic_image);
bicubic_link = FileLink(full_bicubic_image_path)
image_link = FileLink(full_superresolution_image_path)
bicubic_link.html_link_str = "<a href='%s' download>%s</a>"
image_link.html_link_str = "<a href='%s' download>%s</a>"
display(
HTML(
"The images are saved in the images directory. You can also download "
"them by clicking on these links:"
f"<ul><li>{image_link._repr_html_()}<li>{bicubic_link._repr_html_()}"
)
)
- output/full_bicubic_2x.jpg