Installation of OpenVINO™ Notebooks#
The notebooks can be run in various environments. This guide will show you how to run and manage them on your local system.
Contents:
Installation Guide#
The table below lists the supported operating systems and Python versions.
Supported Operating System (64-bit) |
|
|---|---|
Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, 64-bit |
3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, 64-bit |
3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 |
3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
CentOS 7, 64 bit |
3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
macOS 10.15.x versions or higher |
3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
Windows 10, 64-bit Pro, Enterprise or Education editions |
3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
Windows Server 2016 or higher |
3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
OpenVINO Notebooks also require Git. Follow the guide below for your operating system or environment.
Installing prerequisites#
Install Python
Download 64 bit version of Python software (3.9 - 3.12) from python.org
Run the installer by double clicking it. Follow the installation steps to set up the software.
While installing, make sure you check the box to add Python to system PATH. Also, it is recommended to use the installer option to disable the PATH length limit.
Note
Python software available in the Microsoft Store is not recommended. It may require additional packages.
Install GIT
Download 64 bit version of GIT from git-scm.org
Run the installer by double clicking it. Follow the installation steps to set up the software.
Install FFMPEG (Optional)
Download FFMPEG binary from here
Set FFMPEG’s path (e.g.,
C:\ffmpeg\bin) to the PATH environmental variable on Windows.
Install Python and GIT
Note
Linux Systems may require installation of additional libraries.
The following installation steps should work on a clean install of Ubuntu Desktop 20.04, and should also work on Ubuntu 22.04 and 20.10, and on Ubuntu Server.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get install python3-venv build-essential python3-dev git-all libgl1-mesa-dev ffmpeg
For an Intel Integrated Graphics Card, you can install the Intel Graphics Compute Runtime to enable inference on this device. The command for Ubuntu 20.04 is:
Note
Only execute this command if you do not yet have OpenCL drivers installed.
sudo apt-get install intel-opencl-icd
The following installation steps should work on a clean install of Red Hat, CentOS, Amazon Linux 2 or Fedora. If any issues occur, see the Troubleshooting section.
sudo yum update sudo yum upgrade sudo yum install python36-devel mesa-libGL
Alternatively, you may skip steps 1-3 if you prefer to manually install Python 3 and Git.
Install Xcode Command Line Tools
xcode-select --installInstall Homebrew
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
After you install it, follow the instructions from the Homebrew installation to set it up.
Install Python and dependencies
brew install python@3.9 brew install protobuf # optional but recommended brew install ffmpeg
Run each step below in a terminal.
Note
If OpenVINO is installed globally, do not run any of these commands in a terminal where
setupvars.shis sourced.
Note
An Azure account and access to Azure ML Studio are required.
Adding a Compute Instance
In Azure ML Studio, add a compute instance and pick any CPU-based instance. At least 4 CPU cores and 8GB of RAM are recommended.

Start the Terminal
Once the compute instance has started, open the terminal window and then follow the installation steps below.

To run the notebooks inside a Linux-based Docker container, use the Dockerfile:
:caption: Source: https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/blob/latest/Dockerfile
FROM quay.io/thoth-station/s2i-thoth-ubi8-py38:v0.29.0
LABEL name="OpenVINO(TM) Notebooks" \
maintainer="helena.kloosterman@intel.com" \
vendor="Intel Corporation" \
version="0.2.0" \
release="2021.4" \
summary="OpenVINO(TM) Developer Tools and Jupyter Notebooks" \
description="OpenVINO(TM) Notebooks Container"
ENV JUPYTER_ENABLE_LAB="true" \
ENABLE_MICROPIPENV="1" \
UPGRADE_PIP_TO_LATEST="1" \
WEB_CONCURRENCY="1" \
THOTH_ADVISE="0" \
THOTH_ERROR_FALLBACK="1" \
THOTH_DRY_RUN="1" \
THAMOS_DEBUG="0" \
THAMOS_VERBOSE="1" \
THOTH_PROVENANCE_CHECK="0"
USER root
# Upgrade NodeJS > 12.0
# Install dos2unix for line end conversion on Windows
RUN curl -sL https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | bash - && \
yum remove -y nodejs && \
yum install -y nodejs-14.18.1 mesa-libGL dos2unix libsndfile && \
yum -y update-minimal --security --sec-severity=Important --sec-severity=Critical --sec-severity=Moderate
# GPU drivers
RUN dnf install -y 'dnf-command(config-manager)' && \
dnf config-manager --add-repo https://repositories.intel.com/graphics/rhel/8.5/intel-graphics.repo
RUN rpm -ivh https://vault.centos.org/centos/8/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/mesa-filesystem-21.1.5-1.el8.x86_64.rpm && \
dnf install --refresh -y \
intel-opencl-22.28.23726.1-i419.el8.x86_64 intel-media intel-mediasdk libmfxgen1 libvpl2 \
level-zero intel-level-zero-gpu \
intel-metrics-library intel-igc-core intel-igc-cm \
libva libva-utils intel-gmmlib && \
rpm -ivh http://mirror.centos.org/centos/8-stream/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/ocl-icd-2.2.12-1.el8.x86_64.rpm && \
rpm -ivh https://download-ib01.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/8/Everything/x86_64/Packages/c/clinfo-3.0.21.02.21-4.el8.x86_64.rpm
# Copying in override assemble/run scripts
COPY .docker/.s2i/bin /tmp/scripts
# Copying in source code
COPY .docker /tmp/src
COPY .ci/patch_notebooks.py /tmp/scripts
COPY .ci/validate_notebooks.py /tmp/scripts
COPY .ci/ignore_treon_docker.txt /tmp/scripts
# Git on Windows may convert line endings. Run dos2unix to enable
# building the image when the scripts have CRLF line endings.
RUN dos2unix /tmp/scripts/*
RUN dos2unix /tmp/src/builder/*
# Change file ownership to the assemble user. Builder image must support chown command.
RUN chown -R 1001:0 /tmp/scripts /tmp/src
USER 1001
RUN mkdir /opt/app-root/notebooks
COPY notebooks/ /opt/app-root/notebooks
RUN /tmp/scripts/assemble
RUN pip check
USER root
RUN dos2unix /opt/app-root/bin/*sh
RUN yum remove -y dos2unix
RUN chown -R 1001:0 .
RUN chown -R 1001:0 /opt/app-root/notebooks
USER 1001
# RUN jupyter lab build
CMD /tmp/scripts/run
Note
An AWS account and access to Amazon SageMaker Studio are required.
Log into your Amazon SageMaker Studio Environment and
Add user.
Choose desired user profile name
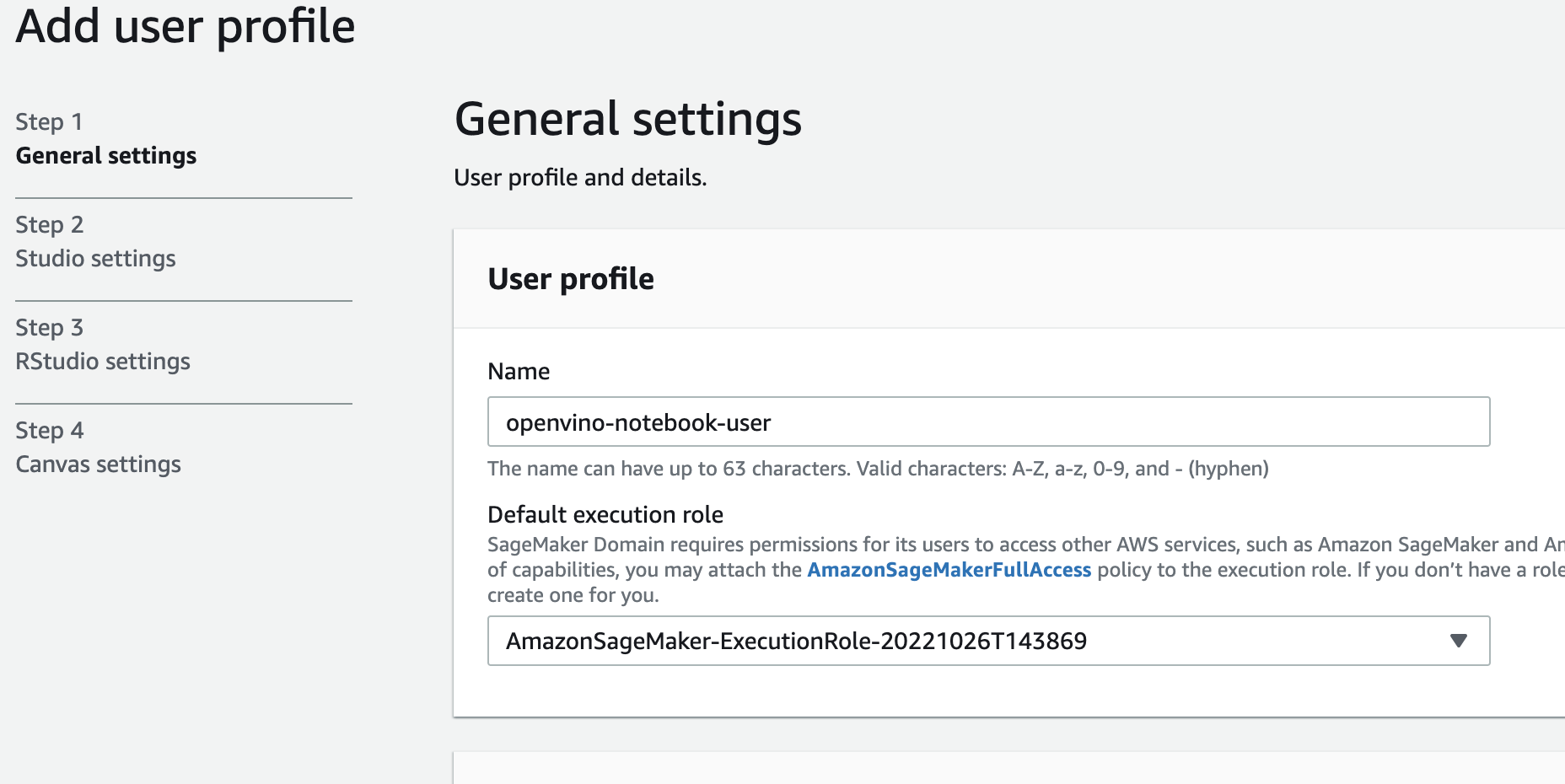
Choose Jupyter Lab version 3.0
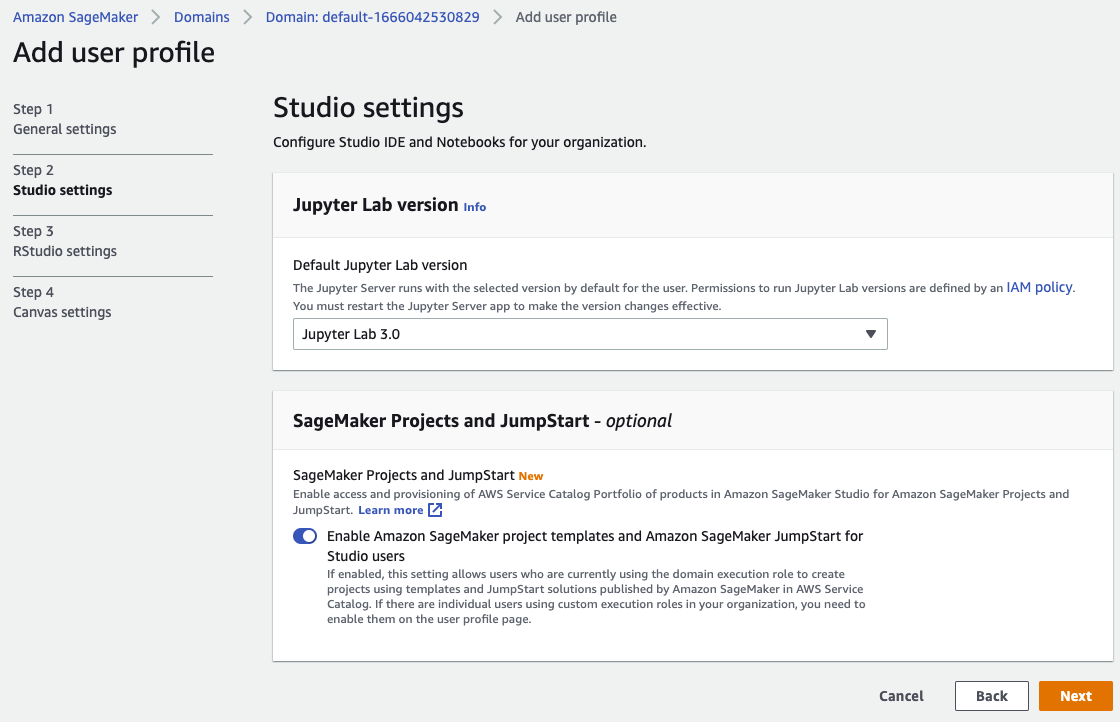
Choose the remaining default setting and click “Submit” to add a user.
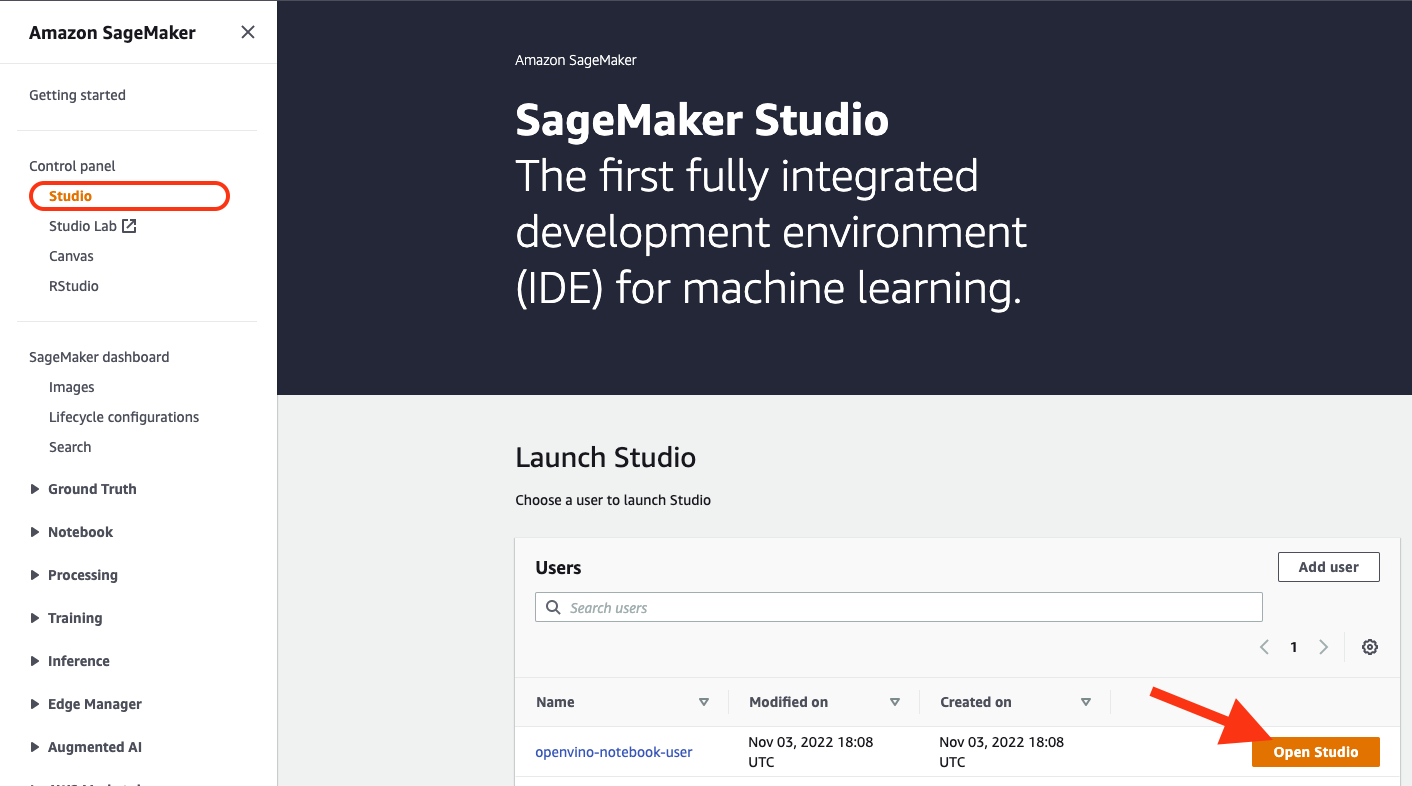
Launch the Amazon SageMaker Studio environment.
Click “Open Studio” to start the environment:
Note
You are using an
ml.t3.mediuminstance, which is for free for 250 hours per month for the first 2 months on Studio notebook.Wait for a couple of minutes for your environment to load.
You should be able to see the following screen:

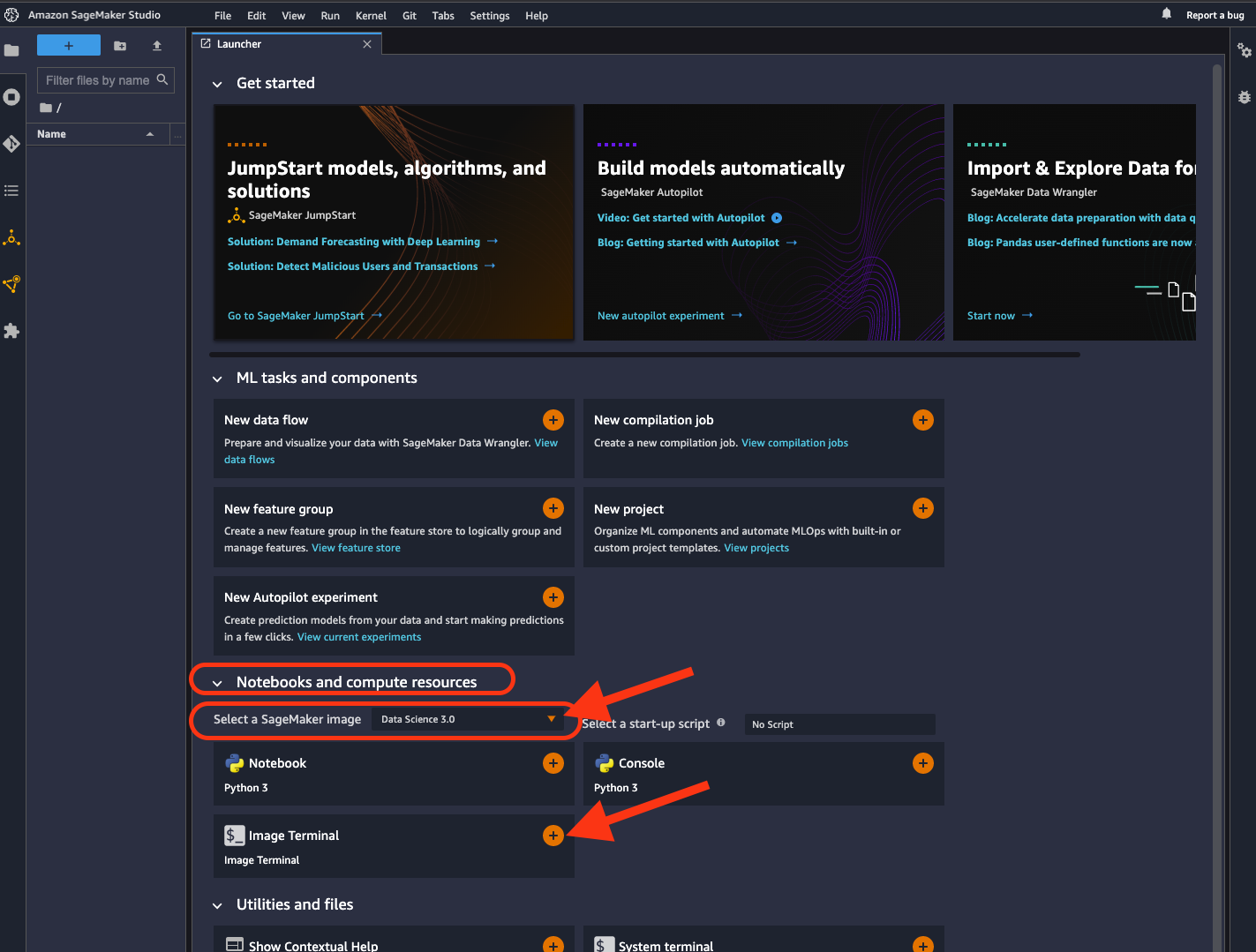
Select a SageMaker image.
Choose
Data Science 3.0in “Select a SageMaker image” drop-down under “Notebooks and compute resources”.Then, click + on “Image Terminal” to start a terminal session:
Installing notebooks#
Create a Virtual Environment
python -m venv openvino_env
Activate the Environment
openvino_env\Scripts\activate
Clone the Repository
Using the –depth=1 option for git clone reduces download size.
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks.git cd openvino_notebooks
Upgrade PIP
python -m pip install --upgrade pip wheel setuptools
Install required packages
pip install -r requirements.txt .. important:: In case of problems with accessing HuggingFace in PRC, set-up the networking environment before you launch the notebooks: .. code-block:: pip install -U huggingface_hub set HF_ENDPOINT = https://hf-mirror.com For more information, visit `HF-Mirror HuggingFace <https://hf-mirror.com>`__.
Create a Virtual Environment
python3 -m venv openvino_env
Activate the Environment
source openvino_env/bin/activate
Clone the Repository
Using the –depth=1 option for git clone reduces download size.
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks.git cd openvino_notebooks
Upgrade PIP
python -m pip install --upgrade pip pip install wheel setuptools
Install required packages
pip install -r requirements.txt .. important:: In case of problems with accessing HuggingFace in PRC, set-up the networking environment before you launch the notebooks: .. code-block:: pip install -U huggingface_hub set HF_ENDPOINT = https://hf-mirror.com For more information, visit `HF-Mirror HuggingFace <https://hf-mirror.com>`__.
Create a Virtual Environment
python3 -m venv openvino_env
Activate the Environment
source openvino_env/bin/activate
Clone the Repository
Using the –depth=1 option for git clone reduces download size.
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks.git cd openvino_notebooks
Upgrade PIP
python -m pip install --upgrade pip wheel setuptools
Install required packages
pip install -r requirements.txt
Create a Conda environment
conda create --name openvino_env python=3.9 -y
Activate the environment
conda activate openvino_env
Clone OpenVINO notebooks
git clone https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks.git
Change directory to
openvino_notebookscd openvino_notebooks
Upgrade
pipand install required dependencies.python -m pip install --upgrade pip pip install -r requirements.txt
Add
openvino_envto PATHset PATH="/anaconda/envs/openvino_env/bin;%PATH%"
Run the notebooks.
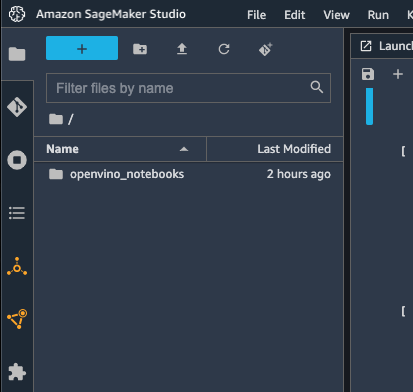
To run the notebooks, click on Notebooks and refresh your Files:



Note
Make sure you are using the
openvino_envenvironment (not Python 3).
Clone the Repository
git clone https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks.git cd openvino_notebooks
Build the Docker Image
docker build -t openvino_notebooks .
Run the Docker Image
docker run -it -p 8888:8888 openvino_notebooks
Note
For using model training notebooks, allocate additional memory:
docker run -it -p 8888:8888 --shm-size 8G openvino_notebooks
Start the browser
Copy the URL printed in the terminal window and open in a browser.If it is a remote machine, replace 127.0.0.1 with the correct IP address.
The Dockerfile can be used to run a local image on Windows, Linux or macOS. It is also compatible with Open Data Hub and Red Hat OpenShift Data Science. The base layer is a UBI 8-based image provided by Project Thoth.
Note
While running the container on Windows and macOS, only CPU devices can be used. To access the iGPU, install the notebooks locally, following the instructions above.
Use the terminal and follow the steps below.
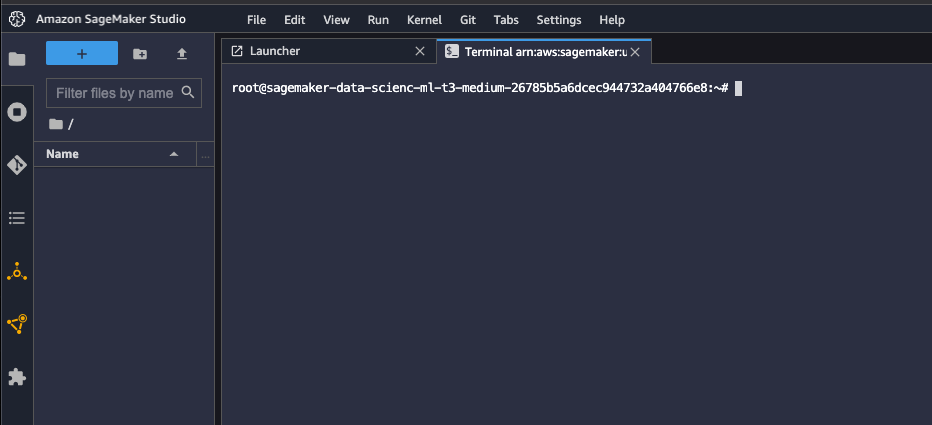
Install few system dependencies.
apt update apt install build-essential -y apt install libpython3.9-dev -y apt install libgl1-mesa-glx -y
Setup OpenVINO conda environment.
conda create --name openvino_env python=3.9 conda activate openvino_env conda install ipykernel set PATH="/anaconda/envs/openvino_env/bin;%PATH%"
Setup OpenVINO Notebooks.
git clone https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks.git cd openvino_notebooks # Install OpenVINO and OpenVINO notebook Requirements python -m pip install --upgrade pip pip install -r requirements.txt
Run the Notebooks
To run the notebooks, click the top level “openvino_notebooks” folder and navigate to your example:
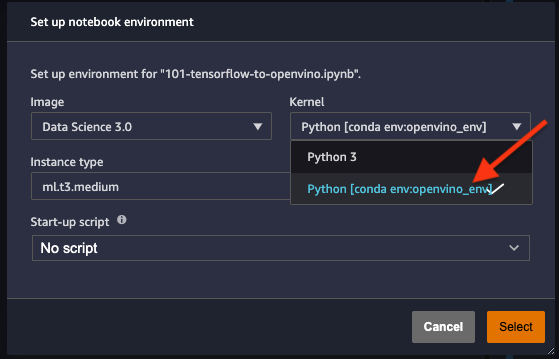
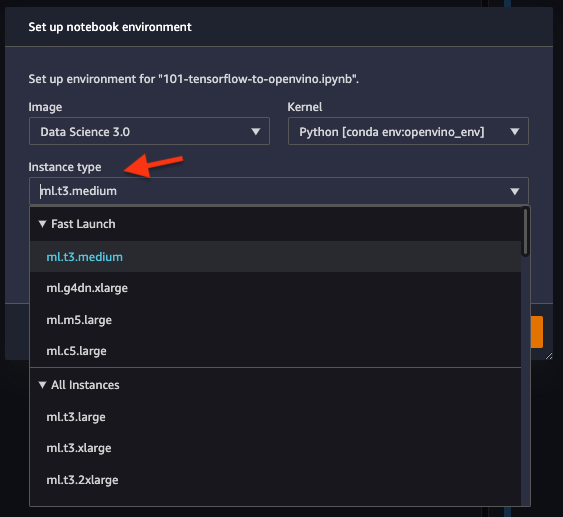
Choose “Image” -
Data Science 3.0, “Kernel” -Python [conda env:openvino_env],“Instance type”- your desired compute instance.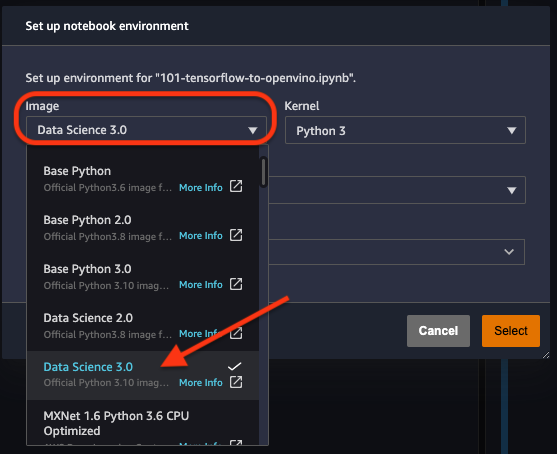
Note
Make sure you use the
Python [conda env:openvino_env]environment (notPython 3).Next, run the cells of the notebook. You may try other notebooks to explore OpenVINO features and examples.
Run the Notebooks#
Launch a Single Notebook#
If you want to launch only one notebook, such as the Monodepth notebook, run the command below.
jupyter lab notebooks/vision-monodepth/vision-monodepth.ipynb
Launch All Notebooks#
jupyter lab notebooks
In your browser, select a notebook from the file browser in Jupyter Lab, using the left sidebar. Each tutorial is located in a subdirectory within the notebooks directory.
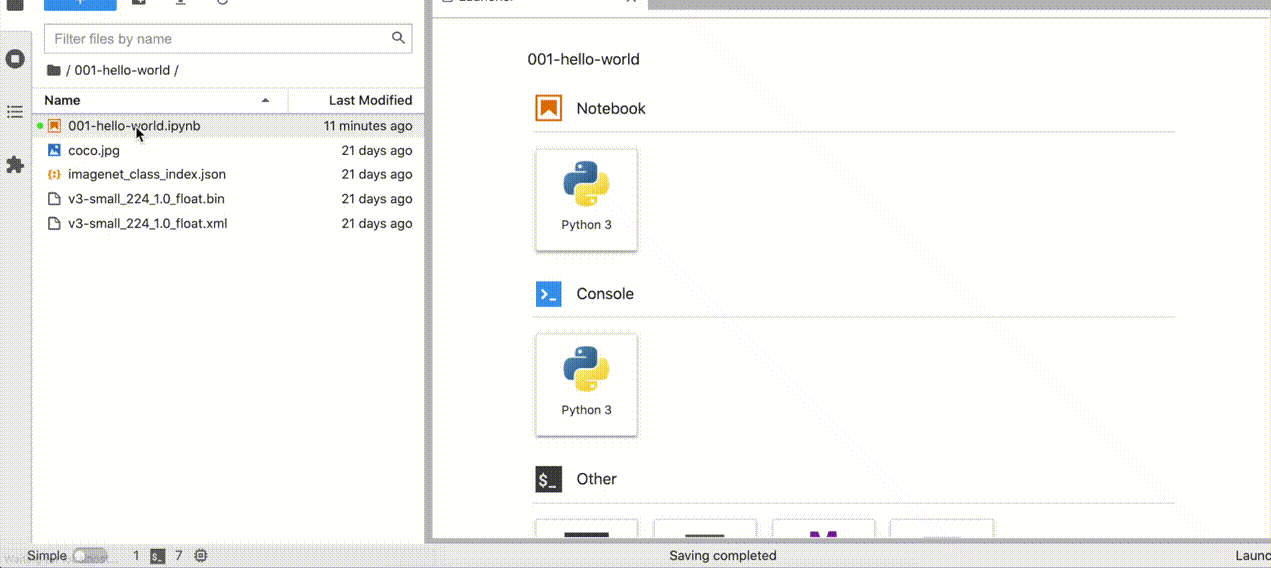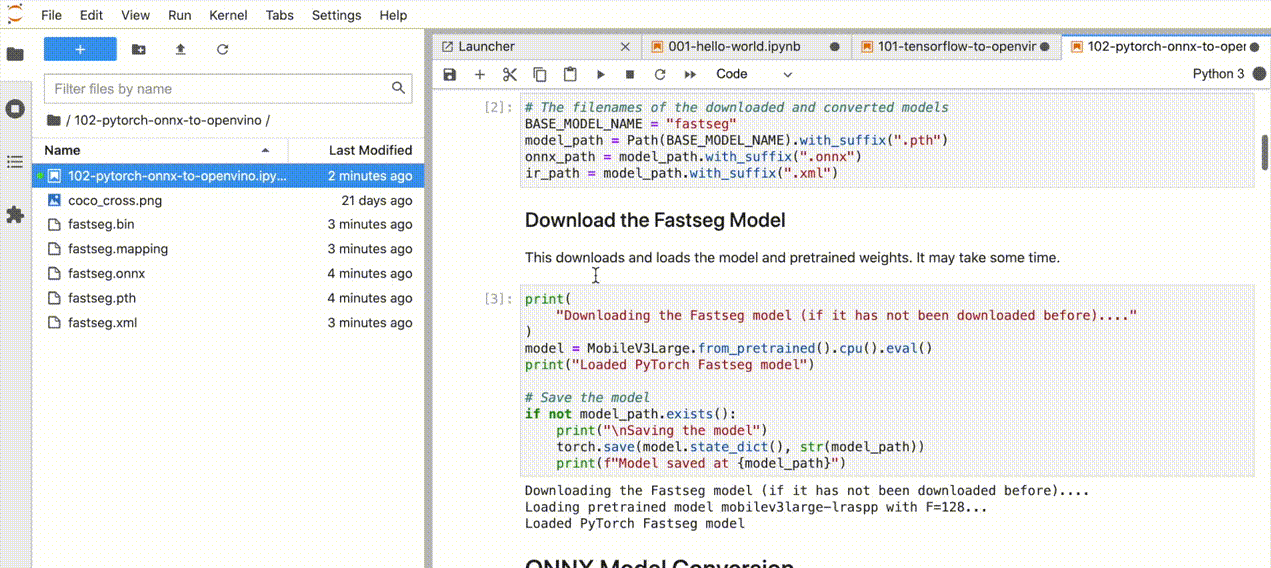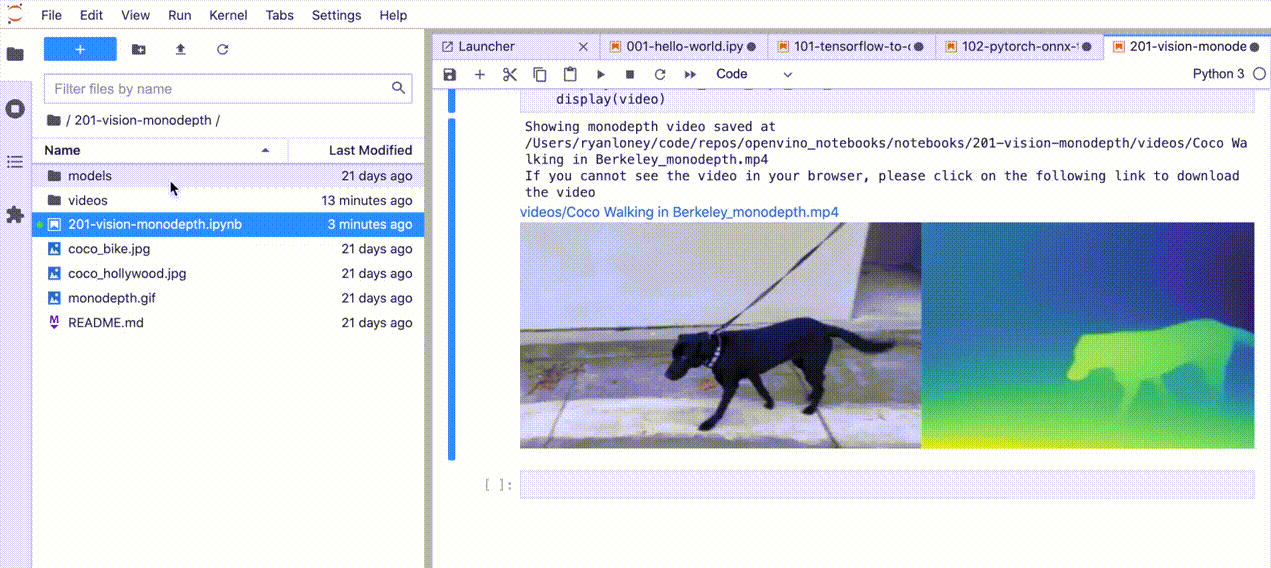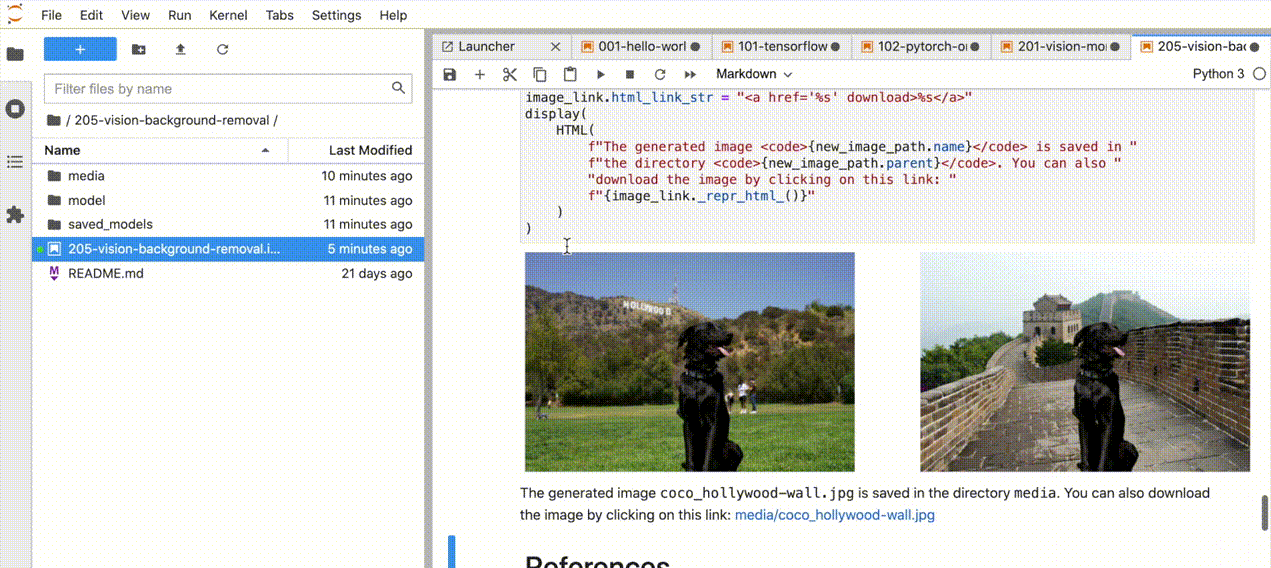
Manage the Notebooks#
Shut Down Jupyter Kernel#
To end your Jupyter session, press Ctrl-c. This will prompt you to
Shutdown this Jupyter server (y/[n])? enter y and hit Enter.
Deactivate Virtual Environment#
First, make sure you use the terminal window where you activated openvino_env. To deactivate your virtualenv, simply run:
deactivate
This will deactivate your virtual environment.
Reactivate Virtual Environment#
To reactivate your environment, run:
source openvino_env\Scripts\activate
source openvino_env/bin/activate
source openvino_env/bin/activate
Then type jupyter lab or jupyter notebook to launch the notebooks again.
Delete Virtual Environment#
This operation is optional. However, if you want to remove your virtual environment, simply delete the openvino_env directory:
rmdir /s openvino_env
rm -rf openvino_env
rm -rf openvino_env
Remove openvino_env Kernel from Jupyter#
jupyter kernelspec remove openvino_env
If you run into issues, check the Troubleshooting, and FAQs sections or start a GitHub discussion.
Troubleshooting#
For solutions to common issues during installation, refer to the Troubleshooting and FAQ sections in openvino_notebooks repository.
If the above tips do not solve your problem, feel free to open a discussion topic or create an issue on Github.