Kosmos-2: Multimodal Large Language Model and OpenVINO#
This Jupyter notebook can be launched after a local installation only.
KOSMOS-2 is a multimodal large language model (MLLM) that has new capabilities of multimodal grounding and referring. KOSMOS-2 can understand multimodal input, follow instructions, perceive object descriptions (e.g., bounding boxes), and ground language to the visual world.
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have successfully played a role as a general-purpose interface across a wide range of tasks, such as language, vision, and vision-language tasks. MLLMs can perceive general modalities, including texts, images, and audio, and generate responses using free-form texts under zero-shot and few-shot settings.
In this work, authors unlock the grounding capability for multimodal large language models. Grounding capability can provide a more convenient and efficient human-AI interaction for vision-language tasks. It enables the user to point to the object or region in the image directly rather than input detailed text descriptions to refer to it, the model can understand that image region with its spatial locations. Grounding capability also enables the model to respond with visual answers (i.e., bounding boxes), which can support more vision-language tasks such as referring expression comprehension. Visual answers are more accurate and resolve the coreference ambiguity compared with text-only responses. In addition, grounding capability can link noun phrases and referring expressions in the generated free-form text response to the image regions, providing more accurate, informational, and comprehensive answers.

image#
Table of contents:
This is a self-contained example that relies solely on its own code.
We recommend running the notebook in a virtual environment. You only need a Jupyter server to start. For details, please refer to Installation Guide.
Install requirements#
%pip install --upgrade pip
%pip install -q "openvino>=2024.0.0" "nncf>=2.11.0" "datasets>=2.20.0"
%pip install -q "transformers>=4.35" Pillow "gradio>=4.19" opencv-python "matplotlib>=3.4"
%pip install -q --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu torch torchvision
Requirement already satisfied: pip in /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages (25.0)
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Original model inference#
Let’s take the original example
import requests
from pathlib import Path
from PIL import Image
from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModelForVision2Seq
if not Path("notebook_utils.py").exists():
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/notebook_utils.py",
)
open("notebook_utils.py", "w").write(r.text)
# Read more about telemetry collection at https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks?tab=readme-ov-file#-telemetry
from notebook_utils import collect_telemetry
collect_telemetry("kosmos2-multimodal-large-language-model.ipynb")
model = AutoModelForVision2Seq.from_pretrained("microsoft/kosmos-2-patch14-224")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/kosmos-2-patch14-224")
prompt = "<grounding>An image of" # <grounding> is used to prompt the model to generate locations tokens
input_image_path = Path("snowman.png")
if not input_image_path.exists():
url = "https://huggingface.co/microsoft/kosmos-2-patch14-224/resolve/main/snowman.png"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
image.save(input_image_path)
# The original Kosmos-2 demo saves the image first then reload it. For some images, this will give slightly different image input and change the generation outputs.
image = Image.open(input_image_path)
inputs = processor(text=prompt, images=image, return_tensors="pt")
generated_ids = model.generate(
pixel_values=inputs["pixel_values"],
input_ids=inputs["input_ids"],
attention_mask=inputs["attention_mask"],
image_embeds=None,
image_embeds_position_mask=inputs["image_embeds_position_mask"],
use_cache=True,
max_new_tokens=128,
)
generated_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
# Specify `cleanup_and_extract=False` in order to see the raw model generation.
processed_text = processor.post_process_generation(generated_text, cleanup_and_extract=False)
print(f"Raw model generation: {processed_text}")
# `<grounding> An image of<phrase> a snowman</phrase><object><patch_index_0044><patch_index_0863></object> warming himself by<phrase> a fire</phrase><object><patch_index_0005><patch_index_0911></object>.`
# By default, the generated text is cleanup and the entities are extracted.
processed_text, entities = processor.post_process_generation(generated_text)
print(f"Cleaned up generated text: {processed_text=}")
# `An image of a snowman warming himself by a fire.`
print(f"Extracted entities: {entities}")
# `[('a snowman', (12, 21), [(0.390625, 0.046875, 0.984375, 0.828125)]), ('a fire', (41, 47), [(0.171875, 0.015625, 0.484375, 0.890625)])]`
2025-02-04 02:47:22.531266: I tensorflow/core/util/port.cc:110] oneDNN custom operations are on. You may see slightly different numerical results due to floating-point round-off errors from different computation orders. To turn them off, set the environment variable TF_ENABLE_ONEDNN_OPTS=0. 2025-02-04 02:47:22.565281: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:182] This TensorFlow binary is optimized to use available CPU instructions in performance-critical operations. To enable the following instructions: AVX2 AVX512F AVX512_VNNI FMA, in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags. 2025-02-04 02:47:23.225923: W tensorflow/compiler/tf2tensorrt/utils/py_utils.cc:38] TF-TRT Warning: Could not find TensorRT
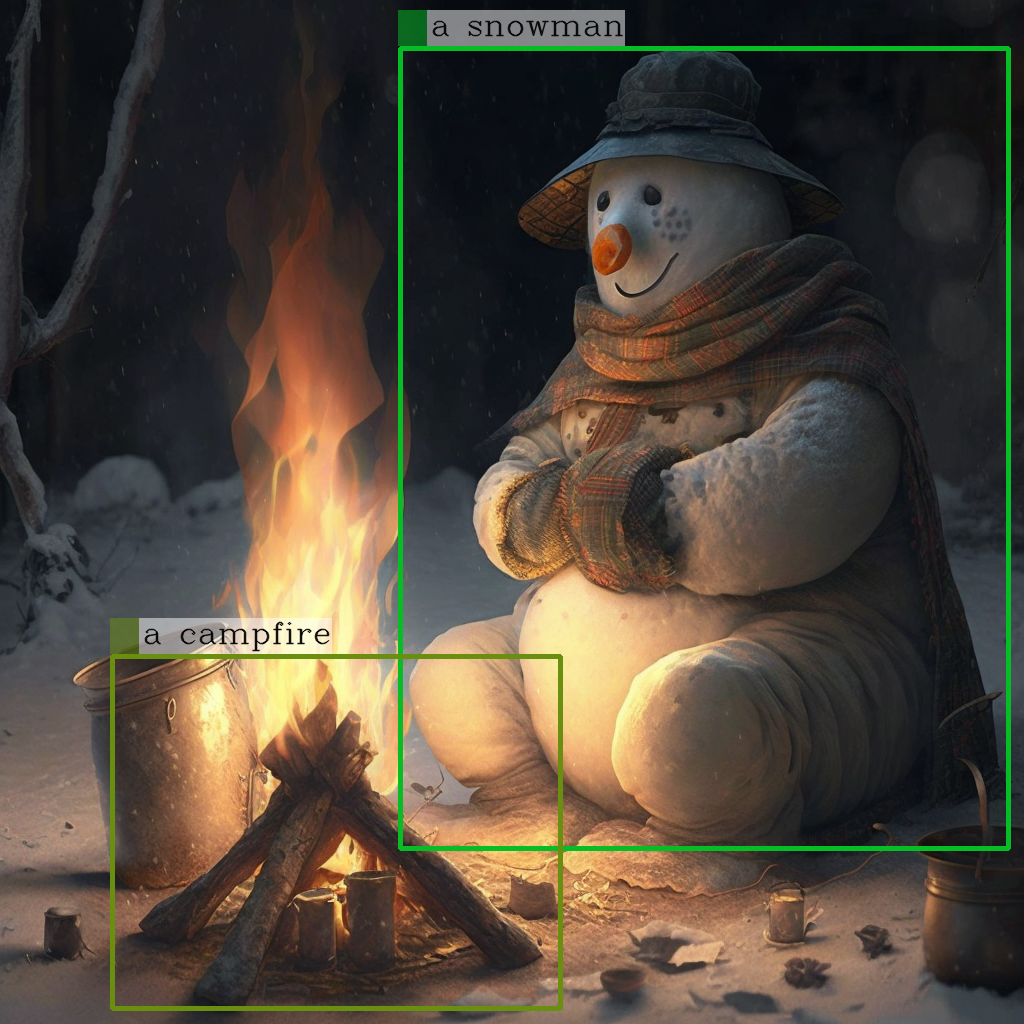
Raw model generation: <grounding> An image of<phrase> a snowman</phrase><object><patch_index_0044><patch_index_0863></object> warming himself by<phrase> a campfire</phrase><object><patch_index_0643><patch_index_1009></object>.
Cleaned up generated text: processed_text='An image of a snowman warming himself by a campfire.'
Extracted entities: [('a snowman', (12, 21), [(0.390625, 0.046875, 0.984375, 0.828125)]), ('a campfire', (41, 51), [(0.109375, 0.640625, 0.546875, 0.984375)])]
Once you have the entities, you can use the following helper function to draw their bounding bboxes on the image:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
def is_overlapping(rect1, rect2):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = rect1
x3, y3, x4, y4 = rect2
return not (x2 < x3 or x1 > x4 or y2 < y3 or y1 > y4)
def draw_entity_boxes_on_image(image, entities):
"""_summary_
Args:
image (_type_): image or image path
collect_entity_location (_type_): _description_
"""
if isinstance(image, Image.Image):
image_h = image.height
image_w = image.width
image = np.array(image)[:, :, [2, 1, 0]]
else:
raise ValueError(f"invaild image format, {type(image)} for {image}")
if len(entities) == 0:
return image
new_image = image.copy()
previous_bboxes = []
# size of text
text_size = 1
# thickness of text
text_line = 1 # int(max(1 * min(image_h, image_w) / 512, 1))
box_line = 3
(c_width, text_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize("F", cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, text_size, text_line)
base_height = int(text_height * 0.675)
text_offset_original = text_height - base_height
text_spaces = 3
for entity_name, (start, end), bboxes in entities:
for x1_norm, y1_norm, x2_norm, y2_norm in bboxes:
orig_x1, orig_y1, orig_x2, orig_y2 = (
int(x1_norm * image_w),
int(y1_norm * image_h),
int(x2_norm * image_w),
int(y2_norm * image_h),
)
# draw bbox
# random color
color = tuple(np.random.randint(0, 255, size=3).tolist())
new_image = cv2.rectangle(new_image, (orig_x1, orig_y1), (orig_x2, orig_y2), color, box_line)
l_o, r_o = box_line // 2 + box_line % 2, box_line // 2 + box_line % 2 + 1
x1 = orig_x1 - l_o
y1 = orig_y1 - l_o
if y1 < text_height + text_offset_original + 2 * text_spaces:
y1 = orig_y1 + r_o + text_height + text_offset_original + 2 * text_spaces
x1 = orig_x1 + r_o
# add text background
(text_width, text_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(f" {entity_name}", cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, text_size, text_line)
text_bg_x1, text_bg_y1, text_bg_x2, text_bg_y2 = (
x1,
y1 - (text_height + text_offset_original + 2 * text_spaces),
x1 + text_width,
y1,
)
for prev_bbox in previous_bboxes:
while is_overlapping((text_bg_x1, text_bg_y1, text_bg_x2, text_bg_y2), prev_bbox):
text_bg_y1 += text_height + text_offset_original + 2 * text_spaces
text_bg_y2 += text_height + text_offset_original + 2 * text_spaces
y1 += text_height + text_offset_original + 2 * text_spaces
if text_bg_y2 >= image_h:
text_bg_y1 = max(
0,
image_h - (text_height + text_offset_original + 2 * text_spaces),
)
text_bg_y2 = image_h
y1 = image_h
break
alpha = 0.5
for i in range(text_bg_y1, text_bg_y2):
for j in range(text_bg_x1, text_bg_x2):
if i < image_h and j < image_w:
if j < text_bg_x1 + 1.35 * c_width:
# original color
bg_color = color
else:
# white
bg_color = [255, 255, 255]
new_image[i, j] = (alpha * new_image[i, j] + (1 - alpha) * np.array(bg_color)).astype(np.uint8)
cv2.putText(
new_image,
f" {entity_name}",
(x1, y1 - text_offset_original - 1 * text_spaces),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX,
text_size,
(0, 0, 0),
text_line,
cv2.LINE_AA,
)
# previous_locations.append((x1, y1))
previous_bboxes.append((text_bg_x1, text_bg_y1, text_bg_x2, text_bg_y2))
pil_image = Image.fromarray(new_image[:, :, [2, 1, 0]])
return pil_image
# Draw the bounding bboxes
new_image = draw_entity_boxes_on_image(image, entities)
display(new_image)
Convert models to OpenVINO Intermediate representation (IR) format#
The original model includes 3 models: vision model
Kosmos2VisionModel, Kosmos2ImageToTextProjection that is the
layer that transforms the image model’s output to part of the text
model’s input (namely, image features), and transformer based text model
Kosmos2TextForCausalLM. We will convert all of them and then replace
the original models.
Define paths for converted models:
from pathlib import Path
models_base_folder = Path("models")
VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH = models_base_folder / "vision_model.xml"
IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH = models_base_folder / "image_to_text_projection_model.xml"
FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH = models_base_folder / "kosmos_input_embed.xml"
SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH = models_base_folder / "kosmos_with_past.xml"
Define the conversion function for PyTorch modules. We use
ov.convert_model function to obtain OpenVINO Intermediate
Representation object and ov.save_model function to save it as XML
file.
import gc
import torch
import openvino as ov
def cleanup_torchscript_cache():
# cleanup memory
torch._C._jit_clear_class_registry()
torch.jit._recursive.concrete_type_store = torch.jit._recursive.ConcreteTypeStore()
torch.jit._state._clear_class_state()
gc.collect()
def convert(model: torch.nn.Module, xml_path: str, example_input):
xml_path = Path(xml_path)
if not xml_path.exists():
xml_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
with torch.no_grad():
converted_model = ov.convert_model(model, example_input=example_input)
ov.save_model(converted_model, xml_path, compress_to_fp16=False)
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
Convert the vision model#
Vision model accept pixel_values and returns image_embeds.
convert(model.vision_model, VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH, inputs["pixel_values"])
WARNING:tensorflow:Please fix your imports. Module tensorflow.python.training.tracking.base has been moved to tensorflow.python.trackable.base. The old module will be deleted in version 2.11.
[ WARNING ] Please fix your imports. Module %s has been moved to %s. The old module will be deleted in version %s. /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/modeling_utils.py:5006: FutureWarning: _is_quantized_training_enabled is going to be deprecated in transformers 4.39.0. Please use model.hf_quantizer.is_trainable instead warnings.warn( loss_type=None was set in the config but it is unrecognised.Using the default loss: ForCausalLMLoss. /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/kosmos2/modeling_kosmos2.py:452: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs! if not interpolate_pos_encoding and (height != self.image_size or width != self.image_size): /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/kosmos2/modeling_kosmos2.py:519: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs! if attn_weights.size() != (bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len): /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/kosmos2/modeling_kosmos2.py:559: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs! if attn_output.size() != (bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_dim):
Convert Image To Text Projection model#
from torch import nn
def get_image_embeds(pixel_values):
vision_model_output = model.vision_model(pixel_values)
image_embeds = model.vision_model.model.post_layernorm(vision_model_output[0])
image_embeds = nn.functional.normalize(image_embeds, dim=-1)
return image_embeds
image_embeds = get_image_embeds(inputs["pixel_values"])
convert(model.image_to_text_projection, IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH, image_embeds)
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/jit/_trace.py:168: UserWarning: The .grad attribute of a Tensor that is not a leaf Tensor is being accessed. Its .grad attribute won't be populated during autograd.backward(). If you indeed want the .grad field to be populated for a non-leaf Tensor, use .retain_grad() on the non-leaf Tensor. If you access the non-leaf Tensor by mistake, make sure you access the leaf Tensor instead. See github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/30531 for more informations. (Triggered internally at aten/src/ATen/core/TensorBody.h:489.)
if a.grad is not None:
Convert Text model#
The Text Model performs in generation pipeline and we can separate it
into two stage. In the first stage the model transforms image_embeds
into output for the second stage. In the second stage the model produces
tokens during several runs that can be transformed into raw model
generated text by AutoProcessor.
from typing import Optional, List
from transformers.models.kosmos2.modeling_kosmos2 import (
create_position_ids_from_input_ids,
)
def get_projecton_image_embeds(pixel_values):
vision_model_output = model.vision_model(pixel_values)
image_embeds = model.vision_model.model.post_layernorm(vision_model_output[0])
image_embeds = nn.functional.normalize(image_embeds, dim=-1)
image_embeds, _ = model.image_to_text_projection(image_embeds)
return image_embeds
def flattenize_inputs(inputs):
"""
Helper function for making nested inputs flattens
"""
flatten_inputs = []
for input_data in inputs:
if input_data is None:
continue
if isinstance(input_data, (list, tuple)):
flatten_inputs.extend(flattenize_inputs(input_data))
else:
flatten_inputs.append(input_data)
return flatten_inputs
def postprocess_converted_model(
ov_model,
example_input=None,
input_names=None,
output_names=None,
dynamic_shapes=None,
):
"""
Helper function for appling postprocessing on converted model with updating input names, shapes and output names
acording to requested specification
"""
flatten_example_inputs = flattenize_inputs(example_input) if example_input else []
if input_names:
for inp_name, m_input, input_data in zip(input_names, ov_model.inputs, flatten_example_inputs):
m_input.get_tensor().set_names({inp_name})
if output_names:
for out, out_name in zip(ov_model.outputs, output_names):
out.get_tensor().set_names({out_name})
return ov_model
def convert_text_model():
model.text_model.model.config.torchscript = True
model.text_model.config.torchscript = True
image_embeds = get_projecton_image_embeds(inputs["pixel_values"])
conv_inputs = {
"input_ids": inputs["input_ids"],
"attention_mask": inputs["attention_mask"],
"image_embeds": image_embeds,
"image_embeds_position_mask": inputs["image_embeds_position_mask"],
}
outs = model.text_model.model(**conv_inputs)
inputs_ = ["input_ids", "attention_mask"]
outputs = ["logits"]
dynamic_shapes = {
"input_ids": {1: "seq_len"},
"attention_mask": {1: "seq_len"},
"position_ids": {0: "seq_len"},
}
for idx in range(len(outs[1])):
inputs_.extend([f"past_key_values.{idx}.key", f"past_key_values.{idx}.value"])
dynamic_shapes[inputs_[-1]] = {2: "past_sequence + sequence"}
dynamic_shapes[inputs_[-2]] = {2: "past_sequence + sequence"}
outputs.extend([f"present.{idx}.key", f"present.{idx}.value"])
if not FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH.exists():
ov_model = ov.convert_model(model.text_model.model, example_input=conv_inputs)
ov_model = postprocess_converted_model(ov_model, output_names=outputs)
ov.save_model(ov_model, FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
if not SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH.exists():
position_ids = create_position_ids_from_input_ids(
inputs["input_ids"],
padding_idx=model.text_model.config.pad_token_id,
past_key_values_length=0,
)[:, -1:]
example_input_second_stage = {
"input_ids": inputs["input_ids"][:, -1:],
"attention_mask": inputs["input_ids"].new_ones(1, inputs["input_ids"].shape[1] + 1),
"position_ids": position_ids,
"past_key_values": outs[1],
}
ov_model = ov.convert_model(model.text_model.model, example_input=example_input_second_stage)
ov_model = postprocess_converted_model(
ov_model,
example_input=example_input_second_stage.values(),
input_names=inputs_,
output_names=outputs,
dynamic_shapes=dynamic_shapes,
)
ov.save_model(ov_model, SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
convert_text_model()
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/kosmos2/modeling_kosmos2.py:859: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
if max_pos > self.weights.size(0):
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/kosmos2/modeling_kosmos2.py:1168: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
if input_shape[-1] > 1:
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/kosmos2/modeling_kosmos2.py:975: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
if attention_mask.size() != (batch_size, 1, seq_length, src_len):
/opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/jobs/ov-notebook/jobs/OVNotebookOps/builds/875/archive/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/kosmos2/modeling_kosmos2.py:1261: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs!
if past_key_values_length > 0:
Compiling models and prepare pipeline#
Select device that will be used to do models inference using OpenVINO from the dropdown list:
from notebook_utils import device_widget
core = ov.Core()
device = device_widget()
device
Dropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')
Let’s create callable wrapper classes for compiled models to allow
interaction with original pipeline. Note that all of wrapper classes
return torch.Tensors instead of np.arrays.
class WraperInternalVisionModel:
post_layernorm = model.vision_model.model.post_layernorm
class VisionModelWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_ir_path):
super().__init__()
self.model = WraperInternalVisionModel()
self.vision_model = core.compile_model(model_ir_path, device.value)
def forward(self, pixel_values, **kwargs):
vision_model_output = self.vision_model(pixel_values)[0]
return [torch.from_numpy(vision_model_output)]
class ImageToTextProjectionModelWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_ir_path):
super().__init__()
self.image_to_text_projection = core.compile_model(model_ir_path, device.value)
def forward(self, image_embeds):
output = self.image_to_text_projection(image_embeds)
image_embeds = output[0]
projection_attentions = output[1]
return image_embeds, projection_attentions
from transformers.generation import GenerationConfig, GenerationMixin
from transformers.models.kosmos2.modeling_kosmos2 import (
Kosmos2ForConditionalGenerationModelOutput,
)
class KosmosForCausalLMWrapper(GenerationMixin):
def __init__(self, first_stage_model_path, second_stage_model_path, device):
self.model_stage_1 = core.compile_model(first_stage_model_path, device.value)
self.model_stage_2 = core.read_model(second_stage_model_path)
self.input_names = {key.get_any_name(): idx for idx, key in enumerate(self.model_stage_2.inputs)}
self.output_names = {key.get_any_name(): idx for idx, key in enumerate(self.model_stage_2.outputs)}
self.key_value_input_names = [key for key in self.input_names if "key_values" in key]
self.key_value_output_names = [key for key in self.output_names if "present" in key]
self.model_stage_2 = core.compile_model(self.model_stage_2, device.value)
self.request = self.model_stage_2.create_infer_request()
self.config = model.config
self.generation_config = GenerationConfig.from_model_config(model.config)
self.main_input_name = "input_ids"
self.device = torch.device("cpu")
self.num_pkv = 2
self.lm_head = nn.Linear(
in_features=model.text_model.config.embed_dim,
out_features=model.text_model.config.vocab_size,
bias=False,
)
self._supports_cache_class = False
def get_input_embeddings(self) -> nn.Module:
return self.model.embed_tokens
def set_input_embeddings(self, value):
self.model.embed_tokens = value
def get_output_embeddings(self) -> nn.Module:
return self.lm_head
def set_output_embeddings(self, new_embeddings):
self.lm_head = new_embeddings
def can_generate(self):
"""Returns True to validate the check that the model using `GenerationMixin.generate()` can indeed generate."""
return True
def __call__(
self,
input_ids,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
image_embeds: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
image_embeds_position_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids=None,
past_key_values: Optional[List[torch.FloatTensor]] = None,
**kwargs,
):
return self.forward(
input_ids,
attention_mask,
image_embeds,
image_embeds_position_mask,
position_ids,
past_key_values,
)
def forward(
self,
input_ids,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
image_embeds: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
image_embeds_position_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids=None,
past_key_values: Optional[List[torch.FloatTensor]] = None,
**kwargs,
):
if past_key_values is None:
outs = self.model_stage_1(
{
"input_ids": input_ids,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"image_embeds": image_embeds,
"image_embeds_position_mask": image_embeds_position_mask,
}
)
lm_logits = model.text_model.lm_head(torch.from_numpy(outs[0]))
pkv = list(outs.values())[1:]
pkv = tuple(pkv[i : i + 2] for i in range(0, len(pkv), 2))
return Kosmos2ForConditionalGenerationModelOutput(logits=lm_logits, past_key_values=pkv)
if past_key_values is not None:
past_key_values = tuple(past_key_value for pkv_per_layer in past_key_values for past_key_value in pkv_per_layer)
inputs_ = {
"input_ids": input_ids[:, -1].unsqueeze(-1),
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"position_ids": position_ids,
}
inputs_.update(dict(zip(self.key_value_input_names, past_key_values)))
# Run inference
self.request.start_async(inputs_, share_inputs=True)
self.request.wait()
logits = torch.from_numpy(self.request.get_tensor("logits").data)
logits = model.text_model.lm_head(logits)
# Tuple of length equal to : number of layer * number of past_key_value per decoder layer (2 corresponds to the self-attention layer)
past_key_values = tuple(self.request.get_tensor(key).data for key in self.key_value_output_names)
# Tuple of tuple of length `n_layers`, with each tuple of length equal to 2 (k/v of self-attention)
past_key_values = tuple(past_key_values[i : i + self.num_pkv] for i in range(0, len(past_key_values), self.num_pkv))
return Kosmos2ForConditionalGenerationModelOutput(logits=logits, past_key_values=past_key_values)
def prepare_inputs_for_generation(
self,
input_ids,
image_embeds=None,
image_embeds_position_mask=None,
past_key_values=None,
attention_mask=None,
use_cache=None,
**kwargs,
):
input_shape = input_ids.shape
# if model is used as a decoder in encoder-decoder model, the decoder attention mask is created on the fly
if attention_mask is None:
attention_mask = input_ids.new_ones(input_shape)
position_ids = None
# cut input_ids if past_key_values is used
if past_key_values is not None:
position_ids = create_position_ids_from_input_ids(
input_ids,
padding_idx=model.text_model.config.pad_token_id,
past_key_values_length=0,
)[:, -1:]
input_ids = input_ids[:, -1:]
image_embeds = None
image_embeds_position_mask = None
elif image_embeds_position_mask is not None:
batch_size, seq_len = input_ids.size()
mask_len = image_embeds_position_mask.size()[-1]
image_embeds_position_mask = torch.cat(
(
image_embeds_position_mask,
torch.zeros(
size=(batch_size, seq_len - mask_len),
dtype=torch.bool,
device=input_ids.device,
),
),
dim=1,
)
return {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"image_embeds": image_embeds,
"image_embeds_position_mask": image_embeds_position_mask,
"position_ids": position_ids,
"past_key_values": past_key_values,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
}
@staticmethod
# Copied from transformers.models.umt5.modeling_umt5.UMT5ForConditionalGeneration._reorder_cache
def _reorder_cache(past_key_values, beam_idx):
reordered_past = ()
for layer_past in past_key_values:
reordered_past += (tuple(past_state.index_select(0, beam_idx.to(past_state.device)) for past_state in layer_past),)
return reordered_past
class Kosmos2ForConditionalGenerationWrapper:
def __init__(
self,
vision_model_path,
image_to_text_projection_model_path,
first_stage_model_path,
second_stage_model_path,
device,
):
self.vision_model = VisionModelWrapper(vision_model_path)
self.image_to_text_projection = ImageToTextProjectionModelWrapper(image_to_text_projection_model_path)
self.text_model = KosmosForCausalLMWrapper(first_stage_model_path, second_stage_model_path, device)
def generate(
self,
pixel_values=None,
image_embeds_position_mask=None,
input_ids=None,
attention_mask=None,
image_embeds=None,
**kwargs,
):
vision_model_output = self.vision_model(pixel_values)
image_embeds = model.vision_model.model.post_layernorm(vision_model_output[0])
# normalized features
image_embeds = nn.functional.normalize(image_embeds, dim=-1)
image_embeds, projection_attentions = self.image_to_text_projection(image_embeds.detach().numpy())
output = self.text_model.generate(
input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
image_embeds=image_embeds,
image_embeds_position_mask=image_embeds_position_mask,
**kwargs,
)
return output
ov_model = Kosmos2ForConditionalGenerationWrapper(
VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH,
IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH,
FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH,
SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH,
device,
)
Inference#
def generate_entities(model):
generated_ids = model.generate(
pixel_values=inputs["pixel_values"],
input_ids=inputs["input_ids"],
attention_mask=inputs["attention_mask"],
image_embeds=None,
image_embeds_position_mask=inputs["image_embeds_position_mask"],
max_new_tokens=128,
)
generated_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
# Specify `cleanup_and_extract=False` in order to see the raw model generation.
processed_text = processor.post_process_generation(generated_text, cleanup_and_extract=False)
print(f"Raw model generation: {processed_text}")
# `<grounding> An image of<phrase> a snowman</phrase><object><patch_index_0044><patch_index_0863></object> warming himself by<phrase> a fire</phrase><object><patch_index_0005><patch_index_0911></object>.`
# By default, the generated text is cleanup and the entities are extracted.
processed_text, entities = processor.post_process_generation(generated_text)
print(f"Cleaned up generated text: {processed_text=}")
# `An image of a snowman warming himself by a fire.`
print(f"Extracted entities: {entities}")
# `[('a snowman', (12, 21), [(0.390625, 0.046875, 0.984375, 0.828125)]), ('a fire', (41, 47), [(0.171875, 0.015625, 0.484375, 0.890625)])]`
return entities
entities = generate_entities(ov_model)
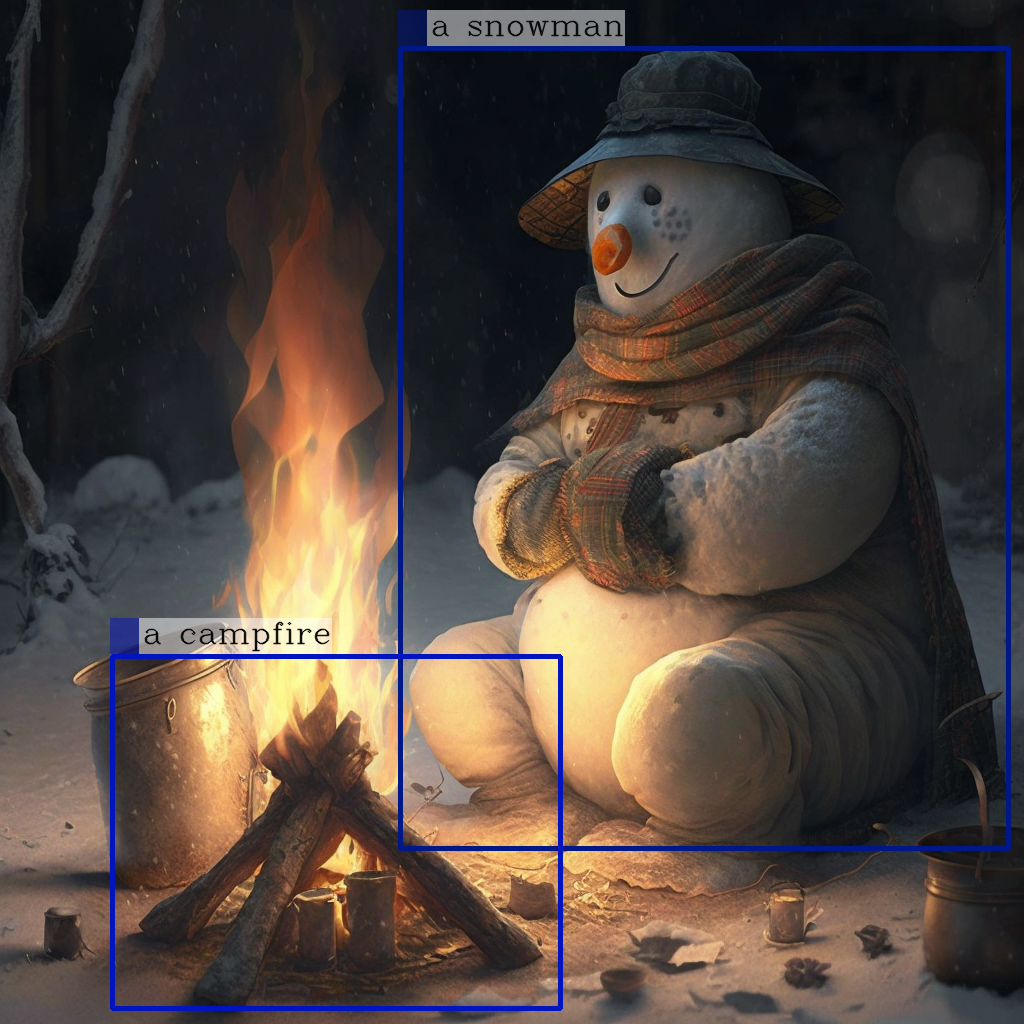
new_image = draw_entity_boxes_on_image(image, entities)
display(new_image)
Raw model generation: <grounding> An image of<phrase> a snowman</phrase><object><patch_index_0044><patch_index_0863></object> warming himself by<phrase> a campfire</phrase><object><patch_index_0643><patch_index_1009></object>.
Cleaned up generated text: processed_text='An image of a snowman warming himself by a campfire.'
Extracted entities: [('a snowman', (12, 21), [(0.390625, 0.046875, 0.984375, 0.828125)]), ('a campfire', (41, 51), [(0.109375, 0.640625, 0.546875, 0.984375)])]
Quantization#
NNCF enables
post-training quantization by adding quantization layers into model
graph and then using a subset of the training dataset to initialize the
parameters of these additional quantization layers. Quantized operations
are executed in INT8 instead of FP32/FP16 making model
inference faster.
Please select below whether you would like to run quantization to improve model inference speed.
NOTE: Quantization is time and memory consuming operation. Running quantization code below may take some time.
from notebook_utils import quantization_widget
to_quantize = quantization_widget()
to_quantize
Checkbox(value=True, description='Quantization')
Let’s load skip magic extension to skip quantization if
to_quantize is not selected
# Fetch `skip_kernel_extension` module
import requests
if not Path("skip_kernel_extension.py").exists():
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/skip_kernel_extension.py",
)
open("skip_kernel_extension.py", "w").write(r.text)
ov_optimized_model = None
%load_ext skip_kernel_extension
Prepare calibration datasets#
We use a portion of KoalaAI/StockImages-CC0 dataset from Hugging Face as calibration data.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
INT8_VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH = models_base_folder / "vision_model_int8.xml"
INT8_IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH = models_base_folder / "image_to_text_projection_model_int8.xml"
INT4_FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH = models_base_folder / "kosmos_input_embed_int4.xml"
INT4_SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH = models_base_folder / "kosmos_with_past_int4.xml"
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import datasets
prompt = "<grounding>An image of"
subset_size = 200
dataset = datasets.load_dataset("KoalaAI/StockImages-CC0", split="train", streaming=True, trust_remote_code=True)
dataset = dataset.shuffle(seed=42).take(subset_size).select_columns(["image"])
To collect intermediate model inputs for calibration we should customize
CompiledModel and InferRequest.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
from transformers import set_seed
set_seed(42)
def collect_calibration_data(pipeline, dataset, subset_size):
calibration_dataset = {
"vision_model": [],
"image_to_text_proj": [],
}
for data in tqdm(dataset, total=subset_size, desc="Collecting calibration dataset"):
img = data["image"]
pixel_values = processor(text=prompt, images=img, return_tensors="pt")["pixel_values"]
vision_model_output = pipeline.vision_model(pixel_values)
image_embeds = model.vision_model.model.post_layernorm(vision_model_output[0])
image_embeds = nn.functional.normalize(image_embeds, dim=-1)
calibration_dataset["vision_model"].append(pixel_values)
calibration_dataset["image_to_text_proj"].append(image_embeds.detach().numpy())
return calibration_dataset
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not (INT8_VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH.exists() and INT8_IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH.exists()):
calibration_dataset = collect_calibration_data(ov_model, dataset, subset_size)
Collecting calibration dataset: 0%| | 0/200 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Run Quantization#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import nncf
if not INT8_VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH.exists():
vision_model = core.read_model(VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH)
quantized_model = nncf.quantize(
model=vision_model,
calibration_dataset=nncf.Dataset(calibration_dataset["vision_model"]),
subset_size=subset_size,
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
)
ov.save_model(quantized_model, INT8_VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH)
INFO:nncf:NNCF initialized successfully. Supported frameworks detected: torch, tensorflow, onnx, openvino
Output()
Output()
Output()
Output()
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not INT8_IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH.exists():
image_to_text_proj_model = core.read_model(IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH)
quantized_model = nncf.quantize(
model=image_to_text_proj_model,
calibration_dataset=nncf.Dataset(calibration_dataset["image_to_text_proj"]),
subset_size=subset_size,
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
)
ov.save_model(quantized_model, INT8_IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH)
Output()
Output()
Output()
Output()
Run Weights Compression#
Quantizing of the Text Model does not significantly improve inference performance but can lead to a substantial degradation of accuracy. The weight compression will be applied to footprint reduction.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import nncf
if not INT4_FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH.exists():
model_stage_1 = core.read_model(FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH)
quantized_model = nncf.compress_weights(model_stage_1, nncf.CompressWeightsMode.INT4_ASYM)
ov.save_model(quantized_model, INT4_FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH)
if not INT4_SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH.exists():
model_stage_2 = core.read_model(SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH)
quantized_model = nncf.compress_weights(model_stage_2, nncf.CompressWeightsMode.INT4_ASYM)
ov.save_model(quantized_model, INT4_SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH)
INFO:nncf:Statistics of the bitwidth distribution:
┍━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┑
│ Num bits (N) │ % all parameters (layers) │ % ratio-defining parameters (layers) │
┝━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┥
│ 8 │ 11% (3 / 146) │ 0% (0 / 143) │
├────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 4 │ 89% (143 / 146) │ 100% (143 / 143) │
┕━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┙
Output()
INFO:nncf:Statistics of the bitwidth distribution:
┍━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┯━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┑
│ Num bits (N) │ % all parameters (layers) │ % ratio-defining parameters (layers) │
┝━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┿━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┥
│ 8 │ 11% (3 / 146) │ 0% (0 / 143) │
├────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 4 │ 89% (143 / 146) │ 100% (143 / 143) │
┕━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┷━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┙
Output()
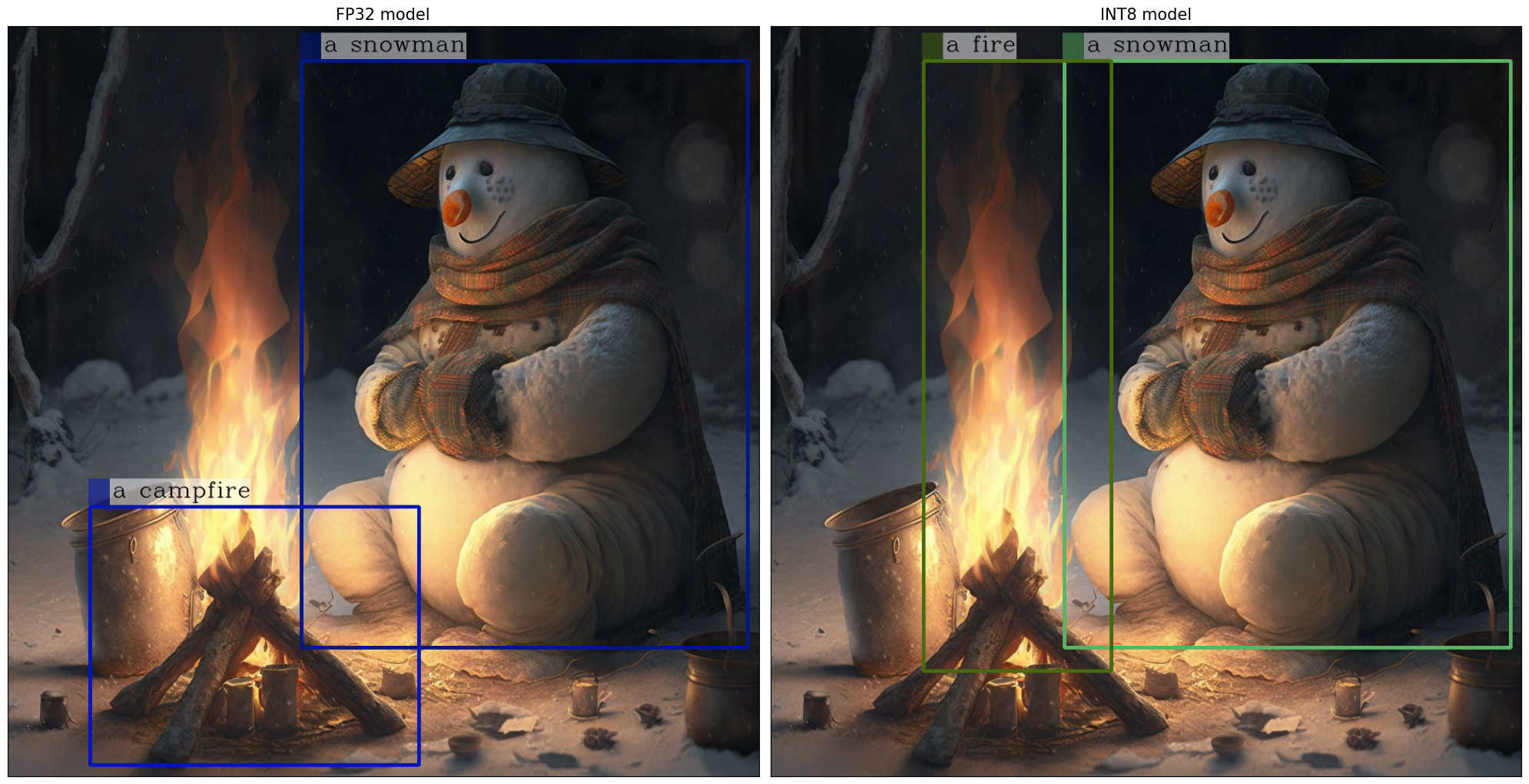
Let’s compare the images generated by the original and optimized pipelines.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
ov_optimized_model = Kosmos2ForConditionalGenerationWrapper(
INT8_VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH,
INT8_IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH,
INT4_FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH,
INT4_SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH,
device,
)
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def visualize_results(orig_img: Image, optimized_img: Image):
"""
Helper function for results visualization
Parameters:
orig_img (Image.Image): generated image using FP16 models
optimized_img (Image.Image): generated image using quantized models
Returns:
fig (matplotlib.pyplot.Figure): matplotlib generated figure contains drawing result
"""
orig_title = "FP32 model"
control_title = "INT8 model"
figsize = (20, 20)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=figsize, sharex="all", sharey="all")
list_axes = list(axs.flat)
for a in list_axes:
a.set_xticklabels([])
a.set_yticklabels([])
a.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
a.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
a.grid(False)
list_axes[0].imshow(np.array(orig_img))
list_axes[1].imshow(np.array(optimized_img))
list_axes[0].set_title(orig_title, fontsize=15)
list_axes[1].set_title(control_title, fontsize=15)
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.01, hspace=0.01)
fig.tight_layout()
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
int_entities = generate_entities(ov_optimized_model)
int_image = draw_entity_boxes_on_image(image, int_entities)
visualize_results(new_image, int_image)
Raw model generation: <grounding> An image of<phrase> a snowman</phrase><object><patch_index_0044><patch_index_0863></object> warming himself by<phrase> a fire</phrase><object><patch_index_0038><patch_index_0878></object> in the winter
Cleaned up generated text: processed_text='An image of a snowman warming himself by a fire in the winter'
Extracted entities: [('a snowman', (12, 21), [(0.390625, 0.046875, 0.984375, 0.828125)]), ('a fire', (41, 47), [(0.203125, 0.046875, 0.453125, 0.859375)])]
Compare model file sizes#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
fp32_model_paths = [VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH, IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH, FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH, SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH]
int8_model_paths = [INT8_VISION_MODEL_IR_PATH, INT8_IMAGE_TO_TEXT_PROJECTION_MODEL_IR_PATH, INT4_FIRST_STAGE_MODEL_PATH, INT4_SECOND_STAGE_MODEL_PATH]
for fp32_path, int8_path in zip(fp32_model_paths, int8_model_paths):
fp32_ir_model_size = fp32_path.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size
int8_model_size = int8_path.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size
print(f"{fp32_path.stem} compression rate: {fp32_ir_model_size / int8_model_size:.3f}")
vision_model compression rate: 3.956
image_to_text_projection_model compression rate: 3.899
kosmos_input_embed compression rate: 3.475
kosmos_with_past compression rate: 3.475
Compare inference time of the FP32 and optimized pipelines#
To measure the inference performance of the FP32 and optimized
pipelines, we use mean inference time on 7 samples.
NOTE: For the most accurate performance estimation, it is recommended to run
benchmark_appin a terminal/command prompt after closing other applications.
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import time
def calculate_inference_time(pipeline, dataset):
inference_time = []
for data in dataset.take(7):
img = data["image"]
inputs = processor(text=prompt, images=img, return_tensors="pt")
start = time.perf_counter()
_ = pipeline.generate(
pixel_values=inputs["pixel_values"],
input_ids=inputs["input_ids"],
attention_mask=inputs["attention_mask"],
image_embeds=None,
image_embeds_position_mask=inputs["image_embeds_position_mask"],
max_new_tokens=128,
)
end = time.perf_counter()
delta = end - start
inference_time.append(delta)
return np.mean(inference_time)
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
fp_latency = calculate_inference_time(ov_model, dataset)
print(f"FP32 pipeline: {fp_latency:.3f} seconds")
int_latency = calculate_inference_time(ov_optimized_model, dataset)
print(f"Optimized pipeline: {int_latency:.3f} seconds")
print(f"Performance speed-up: {fp_latency / int_latency:.3f}")
FP32 pipeline: 2.716 seconds
Optimized pipeline: 1.177 seconds
Performance speed-up: 2.308
Interactive inference#
Please select below whether you would like to use the quantized models to launch the interactive demo.
import ipywidgets as widgets
quantized_models_present = ov_optimized_model is not None
use_quantized_models = widgets.Checkbox(
value=quantized_models_present,
description="Use quantized models",
disabled=not quantized_models_present,
)
use_quantized_models
Checkbox(value=True, description='Use quantized models')
import gradio as gr
pipeline = ov_optimized_model if use_quantized_models.value else ov_model
def generate(image, prompt, use_bbox, _=gr.Progress(track_tqdm=True)):
if use_bbox:
prompt = "<grounding> " + prompt
inputs = processor(text=prompt, images=image, return_tensors="pt")
generated_ids_ = pipeline.generate(
pixel_values=inputs["pixel_values"],
input_ids=inputs["input_ids"],
attention_mask=inputs["attention_mask"],
image_embeds=None,
image_embeds_position_mask=inputs["image_embeds_position_mask"],
max_new_tokens=128,
)
generated_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids_, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
processed_text, entities = processor.post_process_generation(generated_text)
new_image = draw_entity_boxes_on_image(Image.fromarray(image), entities)
return new_image, processed_text
if not Path("gradio_helper.py").exists():
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/notebooks/kosmos2-multimodal-large-language-model/gradio_helper.py"
)
open("gradio_helper.py", "w").write(r.text)
from gradio_helper import make_demo
demo = make_demo(fn=generate)
try:
demo.queue().launch(debug=False)
except Exception:
demo.queue().launch(debug=False, share=True)
# if you are launching remotely, specify server_name and server_port
# demo.launch(server_name='your server name', server_port='server port in int')
# Read more in the docs: https://gradio.app/docs/
Running on local URL: http://127.0.0.1:7860 To create a public link, set share=True in launch().