Inference Engine with low-precision 8-bit integer inference requires the following prerequisites to be satisfied:
The 8-bit inference feature was validated on the following topologies:
A lot of investigation was made in the field of deep learning with the idea of using low precision computations during inference in order to boost deep learning pipelines and gather higher performance. For example, one of the popular approaches is to shrink the precision of activations and weights values from fp32 precision to smaller ones, for example, to fp11 or int8. For more information about this approach, refer to Brief History of Lower Precision in Deep Learning section in this whitepaper.
8-bit computations (referred to as int8) offer better performance compared to the results of inference in higher precision (for example, fp32), because they allow loading more data into a single processor instruction. Usually the cost for significant boost is a reduced accuracy. However, it is proved that an accuracy drop can be negligible and depends on task requirements, so that the application engineer can set up the maximum accuracy drop that is acceptable.
Current Inference Engine solution for low-precision inference uses Intel MKL-DNN and supports inference of the following layers in 8-bit integer computation mode:
This means that 8-bit inference can only be performed with the CPU plugin on the layers listed above. All other layers are executed in the format supported by the CPU plugin: 32-bit floating point format (fp32).
For 8-bit integer computations, a model must be quantized. If the model is not quantized then you can use the Post-Training Optimization Tool to quantize the model. The quantization process adds FakeQuantize layers on activations and weights for most layers. Read more about mathematical computations under the hood in the white paper.
8-bit inference pipeline includes two stages (also refer to the figure below):
FakeQuantize layers are added before most layers to have quantized tensors before layers in a way that low-precision accuracy drop for 8-bit integer inference satisfies the specified threshold. The output of this stage is a quantized model. Quantized model precision is not changed, quantized tensors are in original precision range (fp32). FakeQuantize layer has Quantization Levels attribute which defines quants count. Quants count defines precision which is used during inference. For int8 range Quantization Levels attribute value has to be 255 or 256.FakeQuantize layer on activations and weights to have FakeQuantize output tensor values in low precision range. 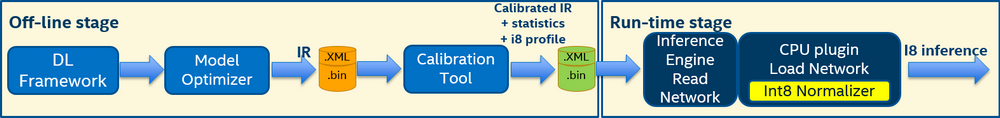
To infer a layer in low precision and get maximum performance, the input tensor for the layer has to be quantized and each value has to be in the target low precision range. For this purpose, FakeQuantize layer is used in the OpenVINO™ intermediate representation file (IR). To quantize the model, you can use the Post-Training Optimization Tool delivered with the Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit release package.
When you pass the calibrated IR to the CPU plugin, the plugin automatically recognizes it as a quantized model and performs 8-bit inference. Note, if you pass a quantized model to another plugin that does not support 8-bit inference, the model is inferred in precision that this plugin supports.
This is the second stage of the 8-bit integer inference. After you load the quantized model IR to a plugin, the pluing uses the Low Precision Transformation component to update the model to infer it in low precision:
FakeQuantize layers to have quantized output tensors in low precision range and add dequantization layers to compensate the update. Dequantization layers are pushed through as many layers as possible to have more layers in low precision. After that, most layers have quantized input tensors in low precision range and can be inferred in low precision. Ideally, dequantization layers should be fused in next FakeQuantize or ScaleShift layers.Const layers.Information about layer precision is stored in the performance counters that are available from the Inference Engine API. The layers have the following marks:
I8 for layers that had 8-bit data type input and were computed in 8-bit precisionFP32 for layers computed in 32-bit precisionFor example, the performance counters table for the Inception model can look as follows:
The execType column of the table includes inference primitives with specific suffixes.